Sakshum Kulshrestha
CodedEvents: Optimal Point-Spread-Function Engineering for 3D-Tracking with Event Cameras
Jun 13, 2024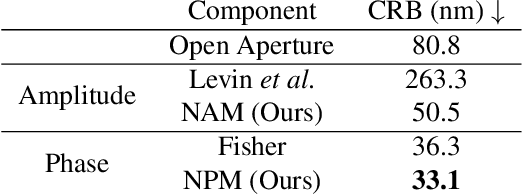
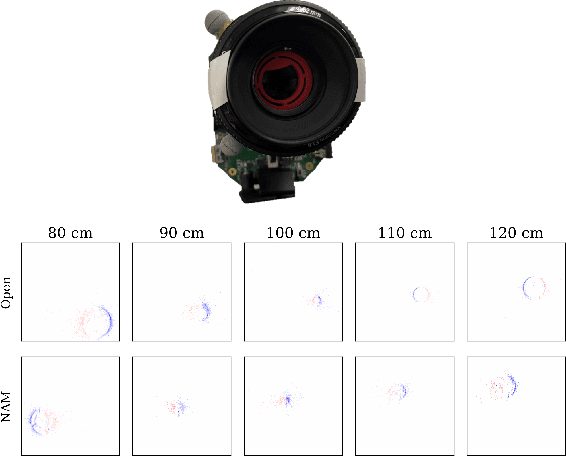
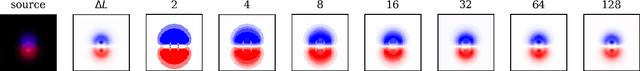
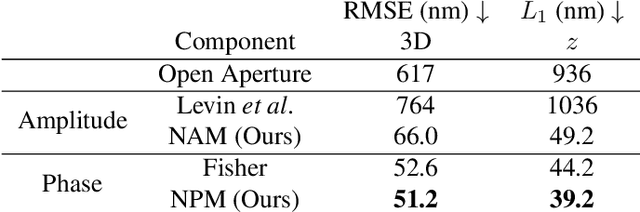
Abstract:Point-spread-function (PSF) engineering is a well-established computational imaging technique that uses phase masks and other optical elements to embed extra information (e.g., depth) into the images captured by conventional CMOS image sensors. To date, however, PSF-engineering has not been applied to neuromorphic event cameras; a powerful new image sensing technology that responds to changes in the log-intensity of light. This paper establishes theoretical limits (Cram\'er Rao bounds) on 3D point localization and tracking with PSF-engineered event cameras. Using these bounds, we first demonstrate that existing Fisher phase masks are already near-optimal for localizing static flashing point sources (e.g., blinking fluorescent molecules). We then demonstrate that existing designs are sub-optimal for tracking moving point sources and proceed to use our theory to design optimal phase masks and binary amplitude masks for this task. To overcome the non-convexity of the design problem, we leverage novel implicit neural representation based parameterizations of the phase and amplitude masks. We demonstrate the efficacy of our designs through extensive simulations. We also validate our method with a simple prototype.
A Scalable Training Strategy for Blind Multi-Distribution Noise Removal
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:Despite recent advances, developing general-purpose universal denoising and artifact-removal networks remains largely an open problem: Given fixed network weights, one inherently trades-off specialization at one task (e.g.,~removing Poisson noise) for performance at another (e.g.,~removing speckle noise). In addition, training such a network is challenging due to the curse of dimensionality: As one increases the dimensions of the specification-space (i.e.,~the number of parameters needed to describe the noise distribution) the number of unique specifications one needs to train for grows exponentially. Uniformly sampling this space will result in a network that does well at very challenging problem specifications but poorly at easy problem specifications, where even large errors will have a small effect on the overall mean squared error. In this work we propose training denoising networks using an adaptive-sampling/active-learning strategy. Our work improves upon a recently proposed universal denoiser training strategy by extending these results to higher dimensions and by incorporating a polynomial approximation of the true specification-loss landscape. This approximation allows us to reduce training times by almost two orders of magnitude. We test our method on simulated joint Poisson-Gaussian-Speckle noise and demonstrate that with our proposed training strategy, a single blind, generalist denoiser network can achieve peak signal-to-noise ratios within a uniform bound of specialized denoiser networks across a large range of operating conditions. We also capture a small dataset of images with varying amounts of joint Poisson-Gaussian-Speckle noise and demonstrate that a universal denoiser trained using our adaptive-sampling strategy outperforms uniformly trained baselines.
TiDy-PSFs: Computational Imaging with Time-Averaged Dynamic Point-Spread-Functions
Mar 30, 2023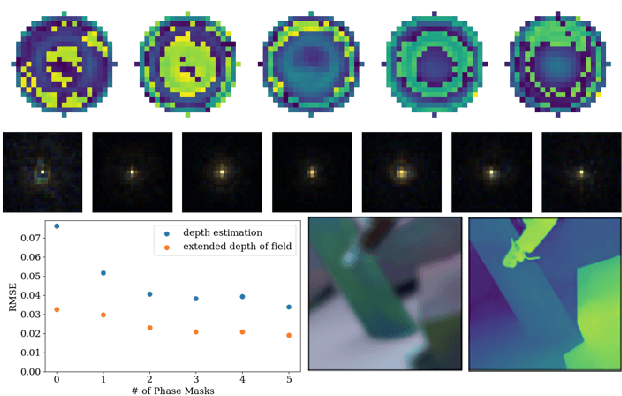
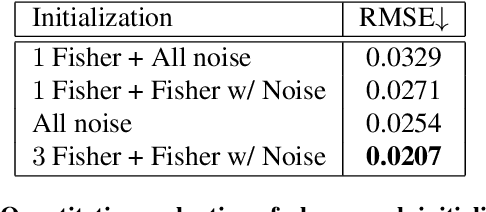
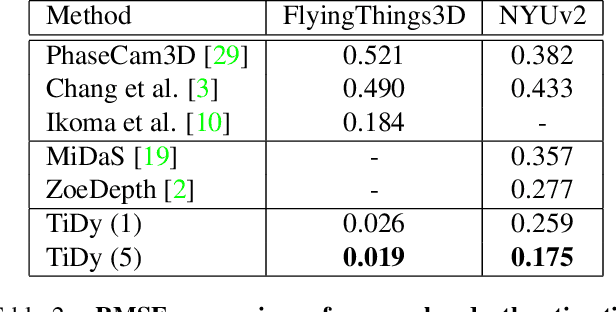
Abstract:Point-spread-function (PSF) engineering is a powerful computational imaging techniques wherein a custom phase mask is integrated into an optical system to encode additional information into captured images. Used in combination with deep learning, such systems now offer state-of-the-art performance at monocular depth estimation, extended depth-of-field imaging, lensless imaging, and other tasks. Inspired by recent advances in spatial light modulator (SLM) technology, this paper answers a natural question: Can one encode additional information and achieve superior performance by changing a phase mask dynamically over time? We first prove that the set of PSFs described by static phase masks is non-convex and that, as a result, time-averaged PSFs generated by dynamic phase masks are fundamentally more expressive. We then demonstrate, in simulation, that time-averaged dynamic (TiDy) phase masks can offer substantially improved monocular depth estimation and extended depth-of-field imaging performance.
Secret-Keeping in Question Answering
Mar 16, 2023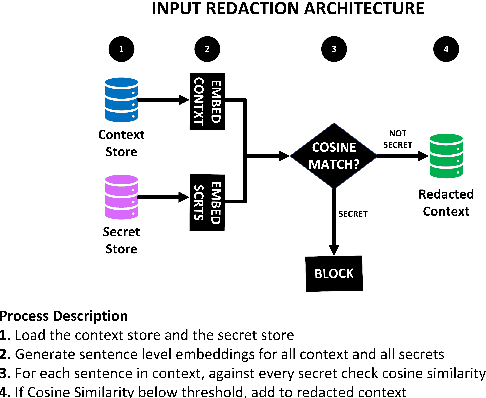
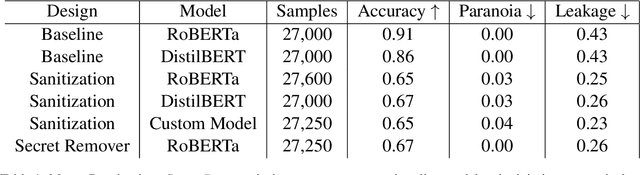
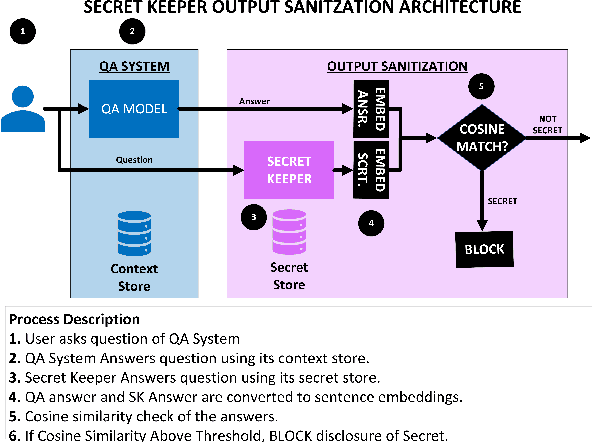
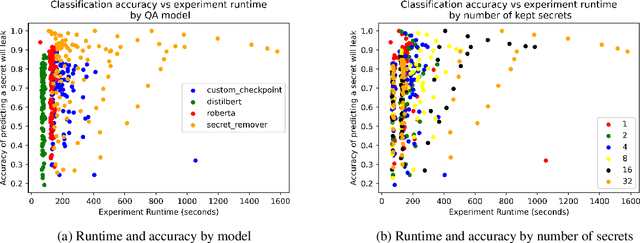
Abstract:Existing question-answering research focuses on unanswerable questions in the context of always providing an answer when a system can\dots but what about cases where a system {\bf should not} answer a question. This can either be to protect sensitive users or sensitive information. Many models expose sensitive information under interrogation by an adversarial user. We seek to determine if it is possible to teach a question-answering system to keep a specific fact secret. We design and implement a proof-of-concept architecture and through our evaluation determine that while possible, there are numerous directions for future research to reduce system paranoia (false positives), information leakage (false negatives) and extend the implementation of the work to more complex problems with preserving secrecy in the presence of information aggregation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge