Ryoma Sato
Even GPT-5.2 Can't Count to Five: The Case for Zero-Error Horizons in Trustworthy LLMs
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:We propose Zero-Error Horizon (ZEH) for trustworthy LLMs, which represents the maximum range that a model can solve without any errors. While ZEH itself is simple, we demonstrate that evaluating the ZEH of state-of-the-art LLMs yields abundant insights. For example, by evaluating the ZEH of GPT-5.2, we found that GPT-5.2 cannot even compute the parity of a short string like 11000, and GPT-5.2 cannot determine whether the parentheses in ((((()))))) are balanced. This is surprising given the excellent capabilities of GPT-5.2. The fact that LLMs make mistakes on such simple problems serves as an important lesson when applying LLMs to safety-critical domains. By applying ZEH to Qwen2.5 and conducting detailed analysis, we found that while ZEH correlates with accuracy, the detailed behaviors differ, and ZEH provides clues about the emergence of algorithmic capabilities. Finally, while computing ZEH incurs significant computational cost, we discuss how to mitigate this cost by achieving up to one order of magnitude speedup using tree structures and online softmax.
Fast EXP3 Algorithms
Dec 12, 2025
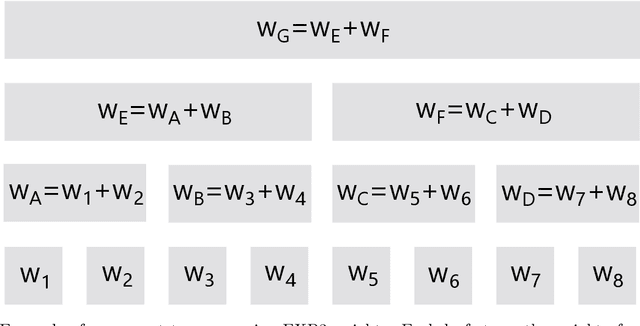
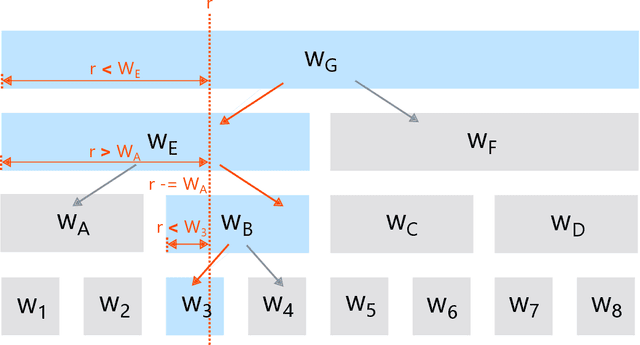
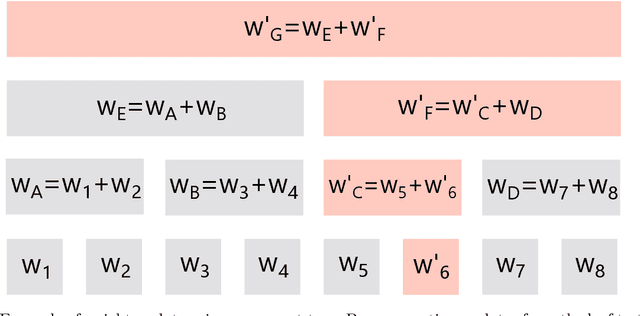
Abstract:We point out that EXP3 can be implemented in constant time per round, propose more practical algorithms, and analyze the trade-offs between the regret bounds and time complexities of these algorithms.
Interestingness First Classifiers
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Most machine learning models are designed to maximize predictive accuracy. In this work, we explore a different goal: building classifiers that are interesting. An ``interesting classifier'' is one that uses unusual or unexpected features, even if its accuracy is lower than the best possible model. For example, predicting room congestion from CO2 levels achieves near-perfect accuracy but is unsurprising. In contrast, predicting room congestion from humidity is less accurate yet more nuanced and intriguing. We introduce EUREKA, a simple framework that selects features according to their perceived interestingness. Our method leverages large language models to rank features by their interestingness and then builds interpretable classifiers using only the selected interesting features. Across several benchmark datasets, EUREKA consistently identifies features that are non-obvious yet still predictive. For example, in the Occupancy Detection dataset, our method favors humidity over CO2 levels and light intensity, producing classifiers that achieve meaningful accuracy while offering insights. In the Twin Papers dataset, our method discovers the rule that papers with a colon in the title are more likely to be cited in the future. We argue that such models can support new ways of knowledge discovery and communication, especially in settings where moderate accuracy is sufficient but novelty and interpretability are valued.
Influential Bandits: Pulling an Arm May Change the Environment
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:While classical formulations of multi-armed bandit problems assume that each arm's reward is independent and stationary, real-world applications often involve non-stationary environments and interdependencies between arms. In particular, selecting one arm may influence the future rewards of other arms, a scenario not adequately captured by existing models such as rotting bandits or restless bandits. To address this limitation, we propose the influential bandit problem, which models inter-arm interactions through an unknown, symmetric, positive semi-definite interaction matrix that governs the dynamics of arm losses. We formally define this problem and establish two regret lower bounds, including a superlinear $\Omega(T^2 / \log^2 T)$ bound for the standard UCB algorithm and an algorithm-independent $\Omega(T)$ bound, which highlight the inherent difficulty of the setting. We then introduce a new algorithm based on a lower confidence bound (LCB) estimator tailored to the structure of the loss dynamics. Under mild assumptions, our algorithm achieves a regret of $O(KT \log T)$, which is nearly optimal in terms of its dependence on the time horizon. The algorithm is simple to implement and computationally efficient. Empirical evaluations on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the presence of inter-arm influence and confirm the superior performance of our method compared to conventional bandit algorithms.
Solving the Cold Start Problem on One's Own as an End User via Preference Transfer
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:We propose a new approach that enables end users to directly solve the cold start problem by themselves. The cold start problem is a common issue in recommender systems, and many methods have been proposed to address the problem on the service provider's side. However, when the service provider does not take action, users are left with poor recommendations and no means to improve their experience. We propose an algorithm, Pretender, that allows end users to proactively solve the cold start problem on their own. Pretender does not require any special support from the service provider and can be deployed independently by users. We formulate the problem as minimizing the distance between the source and target distributions and optimize item selection from the target service accordingly. Furthermore, we establish theoretical guarantees for Pretender based on a discrete quadrature problem. We conduct experiments on real-world datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness of Pretender.
Overhead-free User-side Recommender Systems
Nov 12, 2024Abstract:Traditionally, recommendation algorithms have been designed for service developers. But recently, a new paradigm called user-side recommender systems has been proposed. User-side recommender systems are built and used by end users, in sharp contrast to traditional provider-side recommender systems. Even if the official recommender system offered by the provider is not fair, end users can create and enjoy their own user-side recommender systems by themselves. Although the concept of user-side recommender systems is attractive, the problem is they require tremendous communication costs between the user and the official system. Even the most efficient user-side recommender systems require about 5 times more costs than provider-side recommender systems. Such high costs hinder the adoption of user-side recommender systems. In this paper, we propose overhead-free user-side recommender systems, RecCycle, which realizes user-side recommender systems without any communication overhead. The main idea of RecCycle is to recycle past recommendation results offered by the provider's recommender systems. The ingredients of RecCycle can be retrieved ``for free,'' and it greatly reduces the cost of user-side recommendations. In the experiments, we confirm that RecCycle performs as well as state-of-the-art user-side recommendation algorithms while RecCycle reduces costs significantly.
Polyak Meets Parameter-free Clipped Gradient Descent
May 23, 2024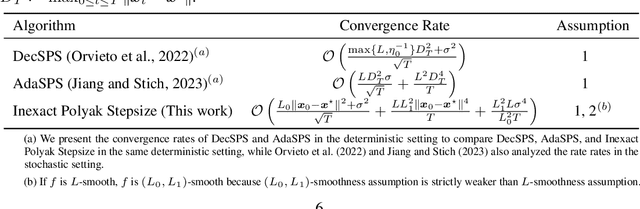
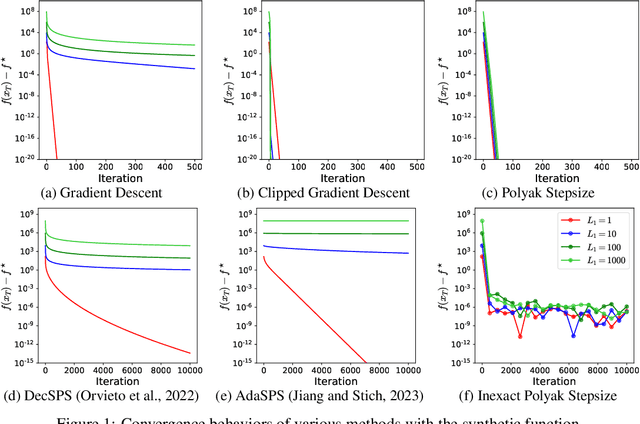
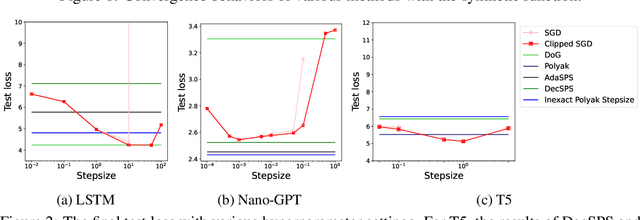
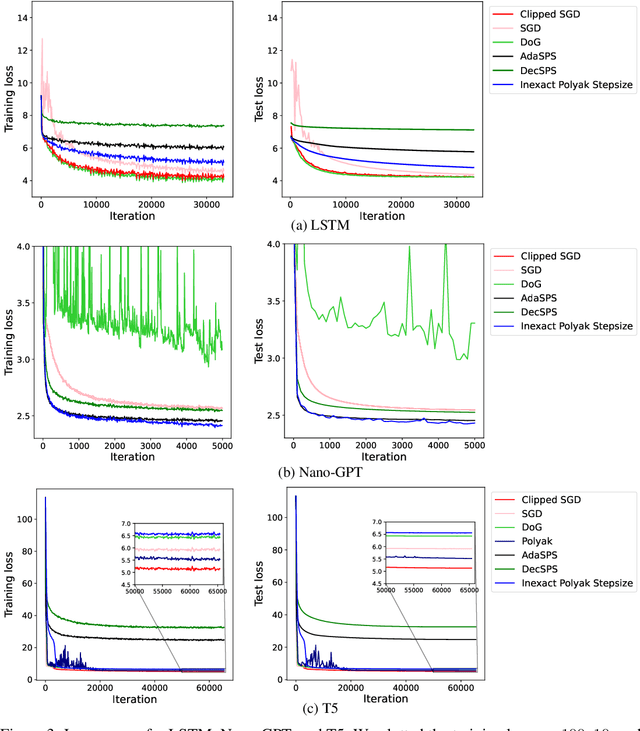
Abstract:Gradient descent and its variants are de facto standard algorithms for training machine learning models. As gradient descent is sensitive to its hyperparameters, we need to tune the hyperparameters carefully using a grid search, but it is time-consuming, especially when multiple hyperparameters exist. Recently, parameter-free methods that adjust the hyperparameters on the fly have been studied. However, the existing work only studied parameter-free methods for the stepsize, and parameter-free methods for other hyperparameters have not been explored. For instance, the gradient clipping threshold is also a crucial hyperparameter in addition to the stepsize to prevent gradient explosion issues, but none of the existing studies investigated the parameter-free methods for clipped gradient descent. In this work, we study the parameter-free methods for clipped gradient descent. Specifically, we propose Inexact Polyak Stepsize, which converges to the optimal solution without any hyperparameters tuning, and its convergence rate is asymptotically independent of L under L-smooth and $(L_0, L_1)$-smooth assumptions of the loss function as that of clipped gradient descent with well-tuned hyperparameters. We numerically validated our convergence results using a synthetic function and demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed methods using LSTM, Nano-GPT, and T5.
Training-free Graph Neural Networks and the Power of Labels as Features
Apr 30, 2024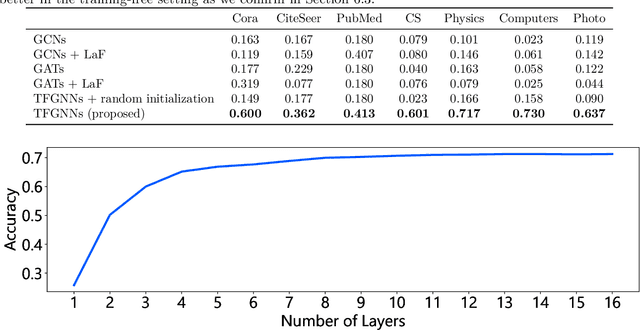
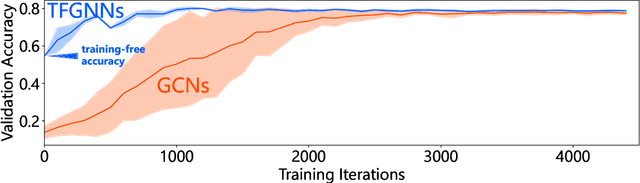
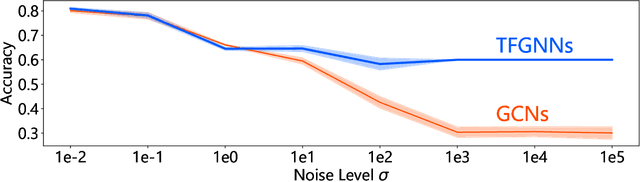
Abstract:We propose training-free graph neural networks (TFGNNs), which can be used without training and can also be improved with optional training, for transductive node classification. We first advocate labels as features (LaF), which is an admissible but not explored technique. We show that LaF provably enhances the expressive power of graph neural networks. We design TFGNNs based on this analysis. In the experiments, we confirm that TFGNNs outperform existing GNNs in the training-free setting and converge with much fewer training iterations than traditional GNNs.
User-Side Realization
Mar 23, 2024



Abstract:Users are dissatisfied with services. Since the service is not tailor-made for a user, it is natural for dissatisfaction to arise. The problem is, that even if users are dissatisfied, they often do not have the means to resolve their dissatisfaction. The user cannot alter the source code of the service, nor can they force the service provider to change. The user has no choice but to remain dissatisfied or quit the service. User-side realization offers proactive solutions to this problem by providing general algorithms to deal with common problems on the user's side. These algorithms run on the user's side and solve the problems without having the service provider change the service itself.
Making Translators Privacy-aware on the User's Side
Dec 07, 2023



Abstract:We propose PRISM to enable users of machine translation systems to preserve the privacy of data on their own initiative. There is a growing demand to apply machine translation systems to data that require privacy protection. While several machine translation engines claim to prioritize privacy, the extent and specifics of such protection are largely ambiguous. First, there is often a lack of clarity on how and to what degree the data is protected. Even if service providers believe they have sufficient safeguards in place, sophisticated adversaries might still extract sensitive information. Second, vulnerabilities may exist outside of these protective measures, such as within communication channels, potentially leading to data leakage. As a result, users are hesitant to utilize machine translation engines for data demanding high levels of privacy protection, thereby missing out on their benefits. PRISM resolves this problem. Instead of relying on the translation service to keep data safe, PRISM provides the means to protect data on the user's side. This approach ensures that even machine translation engines with inadequate privacy measures can be used securely. For platforms already equipped with privacy safeguards, PRISM acts as an additional protection layer, reinforcing their security furthermore. PRISM adds these privacy features without significantly compromising translation accuracy. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of PRISM using real-world translators, T5 and ChatGPT (GPT-3.5-turbo), and the datasets with two languages. PRISM effectively balances privacy protection with translation accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge