Ryan Oldja
NVRadarNet: Real-Time Radar Obstacle and Free Space Detection for Autonomous Driving
Sep 29, 2022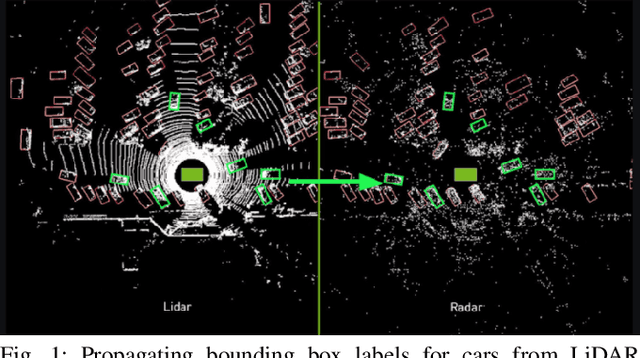

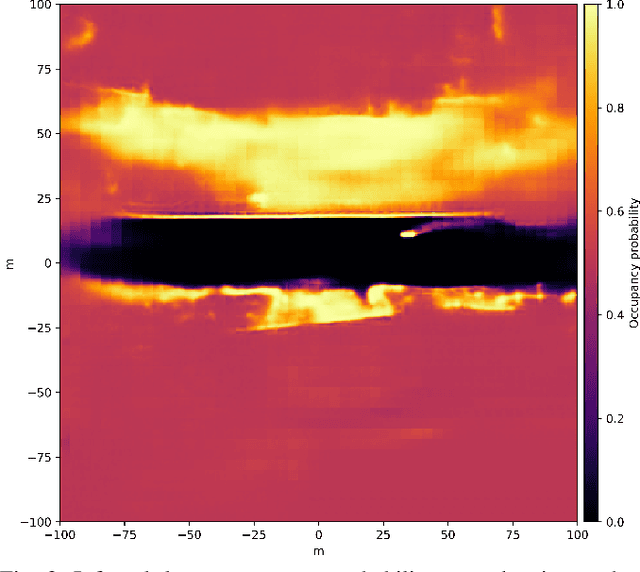
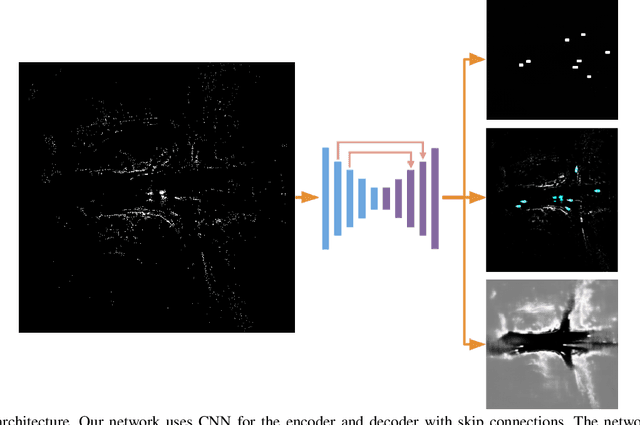
Abstract:Detecting obstacles is crucial for safe and efficient autonomous driving. To this end, we present NVRadarNet, a deep neural network (DNN) that detects dynamic obstacles and drivable free space using automotive RADAR sensors. The network utilizes temporally accumulated data from multiple RADAR sensors to detect dynamic obstacles and compute their orientation in a top-down bird's-eye view (BEV). The network also regresses drivable free space to detect unclassified obstacles. Our DNN is the first of its kind to utilize sparse RADAR signals in order to perform obstacle and free space detection in real time from RADAR data only. The network has been successfully used for perception on our autonomous vehicles in real self-driving scenarios. The network runs faster than real time on an embedded GPU and shows good generalization across geographic regions.
MVLidarNet: Real-Time Multi-Class Scene Understanding for Autonomous Driving Using Multiple Views
Jun 09, 2020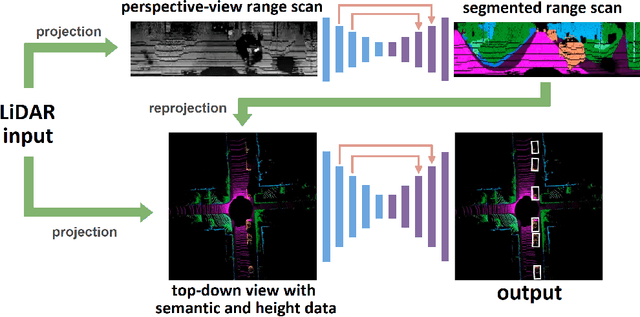
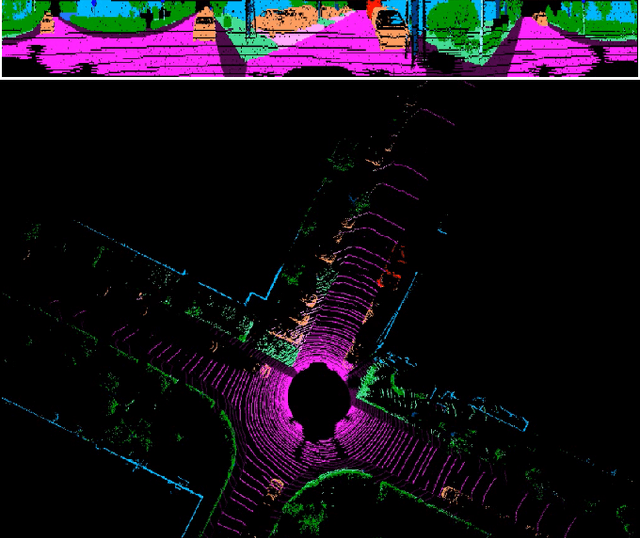
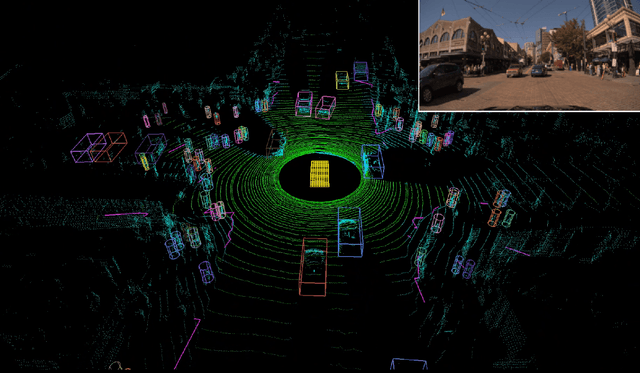
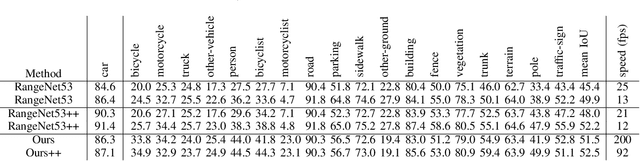
Abstract:Autonomous driving requires the inference of actionable information such as detecting and classifying objects, and determining the drivable space. To this end, we present a two-stage deep neural network (MVLidarNet) for multi-class object detection and drivable segmentation using multiple views of a single LiDAR point cloud. The first stage processes the point cloud projected onto a perspective view in order to semantically segment the scene. The second stage then processes the point cloud (along with semantic labels from the first stage) projected onto a bird's eye view, to detect and classify objects. Both stages are simple encoder-decoders. We show that our multi-view, multi-stage, multi-class approach is able to detect and classify objects while simultaneously determining the drivable space using a single LiDAR scan as input, in challenging scenes with more than one hundred vehicles and pedestrians at a time. The system operates efficiently at 150 fps on an embedded GPU designed for a self-driving car, including a postprocessing step to maintain identities over time. We show results on both KITTI and a much larger internal dataset, thus demonstrating the method's ability to scale by an order of magnitude.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge