Rupayan Chakraborty
Text-to-Audio Grounding Based Novel Metric for Evaluating Audio Caption Similarity
Oct 03, 2022
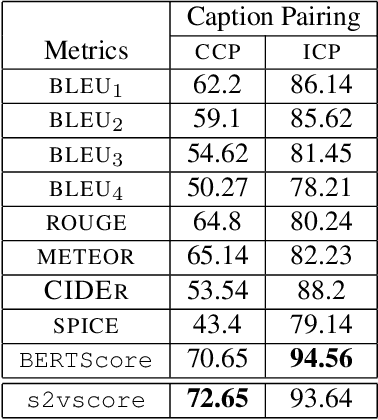
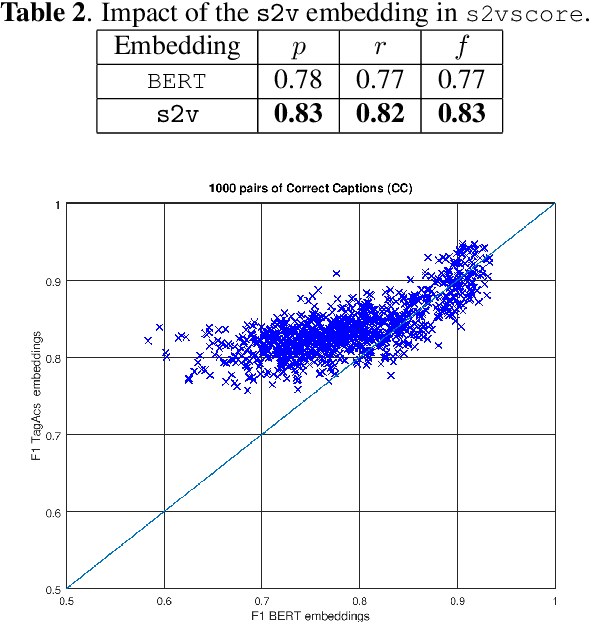
Abstract:Automatic Audio Captioning (AAC) refers to the task of translating an audio sample into a natural language (NL) text that describes the audio events, source of the events and their relationships. Unlike NL text generation tasks, which rely on metrics like BLEU, ROUGE, METEOR based on lexical semantics for evaluation, the AAC evaluation metric requires an ability to map NL text (phrases) that correspond to similar sounds in addition lexical semantics. Current metrics used for evaluation of AAC tasks lack an understanding of the perceived properties of sound represented by text. In this paper, wepropose a novel metric based on Text-to-Audio Grounding (TAG), which is, useful for evaluating cross modal tasks like AAC. Experiments on publicly available AAC data-set shows our evaluation metric to perform better compared to existing metrics used in NL text and image captioning literature.
Spectro Temporal EEG Biomarkers For Binary Emotion Classification
Feb 02, 2022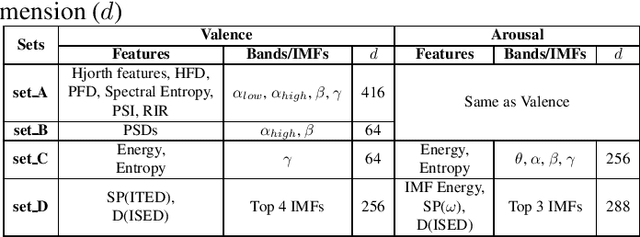
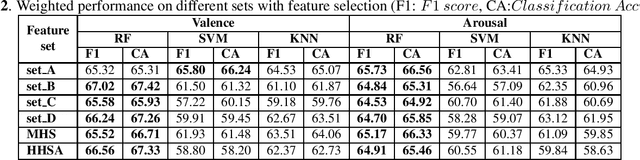
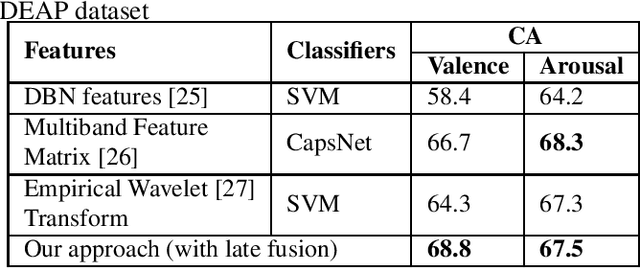
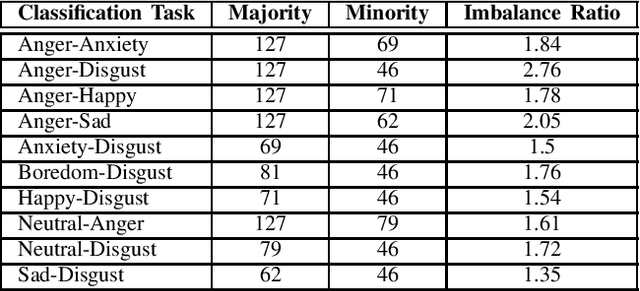
Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG) is one of the most reliable physiological signal for emotion detection. Being non-stationary in nature, EEGs are better analysed by spectro temporal representations. Standard features like Discrete Wavelet Transformation (DWT) can represent temporal changes in spectral dynamics of an EEG, but is insufficient to extract information other way around, i.e. spectral changes in temporal dynamics. On the other hand, Empirical mode decomposition (EMD) based features can be useful to bridge the above mentioned gap. Towards this direction, we extract two novel features on top of EMD, namely, (a) marginal hilbert spectrum (MHS) and (b) Holo-Hilbert spectral analysis (HHSA) based on EMD, to better represent emotions in 2D arousal-valence (A-V) space. The usefulness of these features for EEG emotion classification is investigated through extensive experiments using state-of-the-art classifiers. In addition, experiments conducted on DEAP dataset for binary emotion classification in both A-V space, reveal the efficacy of the proposed features over the standard set of temporal and spectral features.
Automatic Audio Captioning using Attention weighted Event based Embeddings
Jan 28, 2022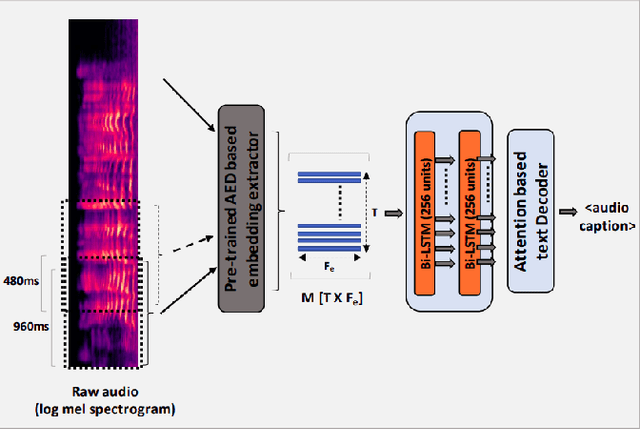
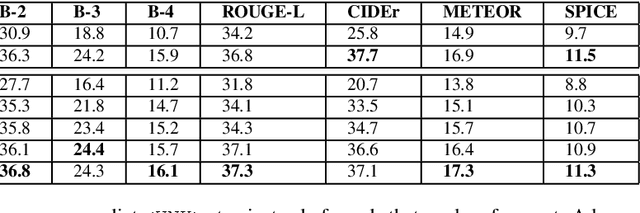
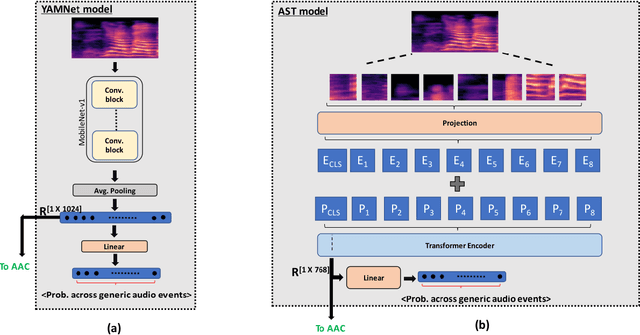
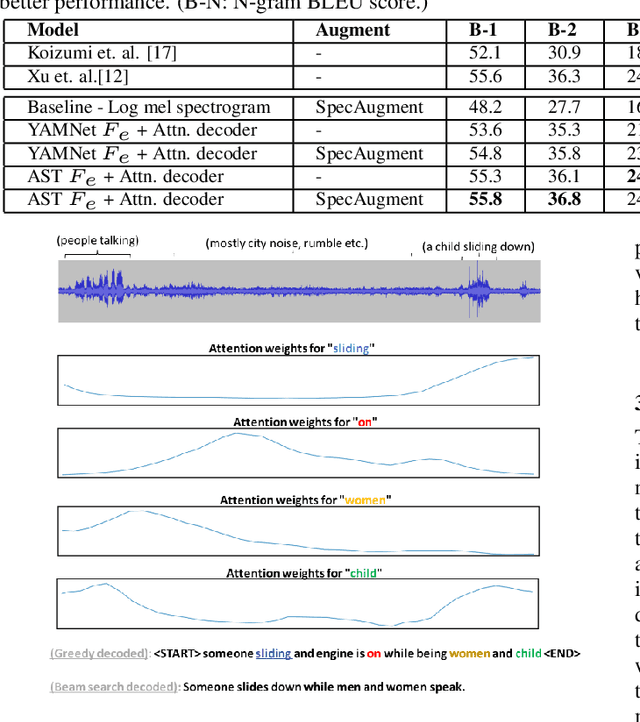
Abstract:Automatic Audio Captioning (AAC) refers to the task of translating audio into a natural language that describes the audio events, source of the events and their relationships. The limited samples in AAC datasets at present, has set up a trend to incorporate transfer learning with Audio Event Detection (AED) as a parent task. Towards this direction, in this paper, we propose an encoder-decoder architecture with light-weight (i.e. with lesser learnable parameters) Bi-LSTM recurrent layers for AAC and compare the performance of two state-of-the-art pre-trained AED models as embedding extractors. Our results show that an efficient AED based embedding extractor combined with temporal attention and augmentation techniques is able to surpass existing literature with computationally intensive architectures. Further, we provide evidence of the ability of the non-uniform attention weighted encoding generated as a part of our model to facilitate the decoder glance over specific sections of the audio while generating each token.
A Novel Adaptive Minority Oversampling Technique for Improved Classification in Data Imbalanced Scenarios
Mar 26, 2021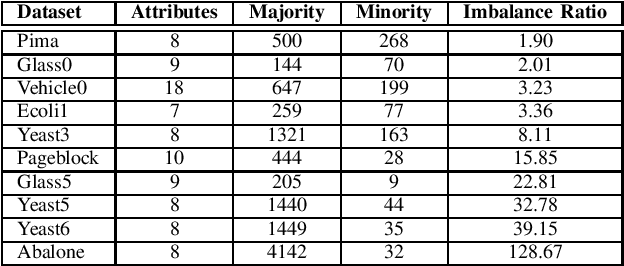
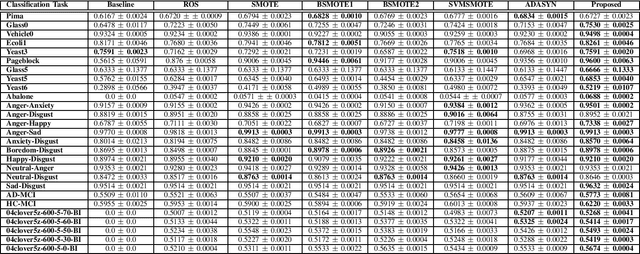
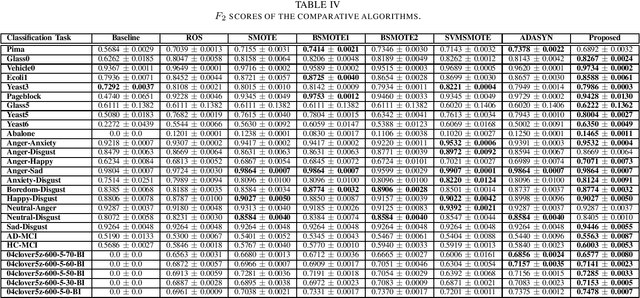
Abstract:Imbalance in the proportion of training samples belonging to different classes often poses performance degradation of conventional classifiers. This is primarily due to the tendency of the classifier to be biased towards the majority classes in the imbalanced dataset. In this paper, we propose a novel three step technique to address imbalanced data. As a first step we significantly oversample the minority class distribution by employing the traditional Synthetic Minority OverSampling Technique (SMOTE) algorithm using the neighborhood of the minority class samples and in the next step we partition the generated samples using a Gaussian-Mixture Model based clustering algorithm. In the final step synthetic data samples are chosen based on the weight associated with the cluster, the weight itself being determined by the distribution of the majority class samples. Extensive experiments on several standard datasets from diverse domains shows the usefulness of the proposed technique in comparison with the original SMOTE and its state-of-the-art variants algorithms.
* 8 pages
Semi Supervised Learning For Few-shot Audio Classification By Episodic Triplet Mining
Feb 16, 2021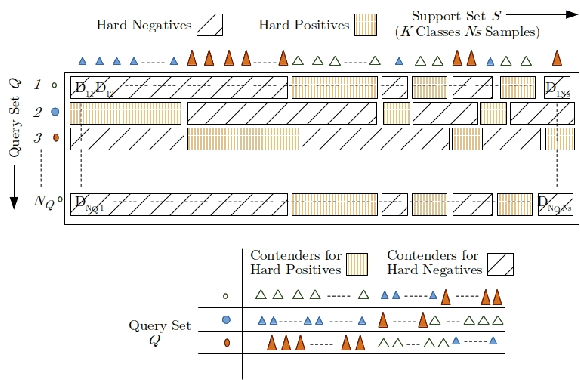
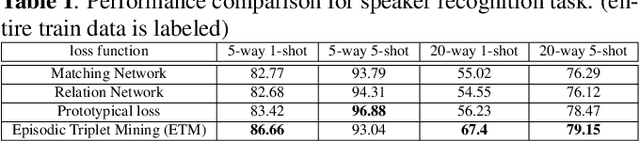
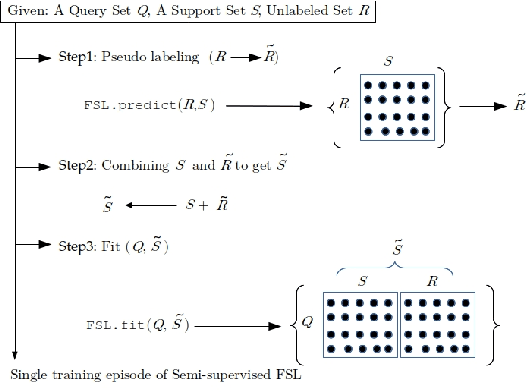
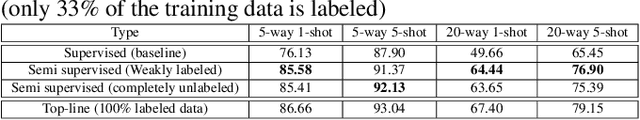
Abstract:Few-shot learning aims to generalize unseen classes that appear during testing but are unavailable during training. Prototypical networks incorporate few-shot metric learning, by constructing a class prototype in the form of a mean vector of the embedded support points within a class. The performance of prototypical networks in extreme few-shot scenarios (like one-shot) degrades drastically, mainly due to the desuetude of variations within the clusters while constructing prototypes. In this paper, we propose to replace the typical prototypical loss function with an Episodic Triplet Mining (ETM) technique. The conventional triplet selection leads to overfitting, because of all possible combinations being used during training. We incorporate episodic training for mining the semi hard positive and the semi hard negative triplets to overcome the overfitting. We also propose an adaptation to make use of unlabeled training samples for better modeling. Experimenting on two different audio processing tasks, namely speaker recognition and audio event detection; show improved performances and hence the efficacy of ETM over the prototypical loss function and other meta-learning frameworks. Further, we show improved performances when unlabeled training samples are used.
A Cycle-GAN Approach to Model Natural Perturbations in Speech for ASR Applications
Dec 18, 2019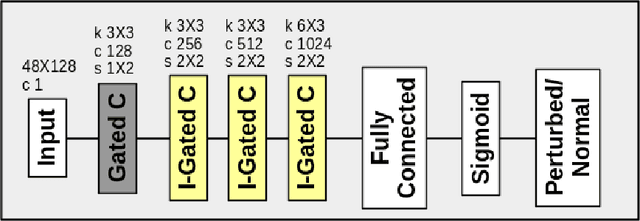
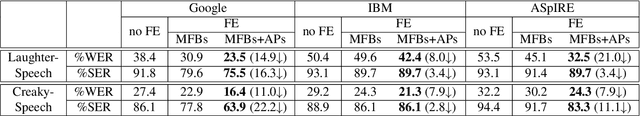
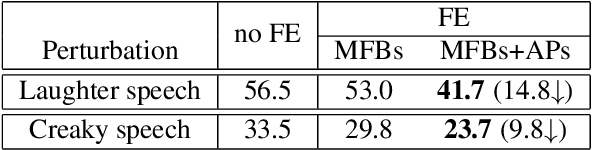
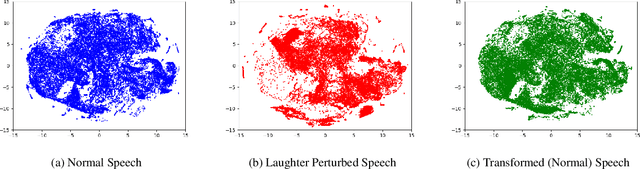
Abstract:Naturally introduced perturbations in audio signal, caused by emotional and physical states of the speaker, can significantly degrade the performance of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems. In this paper, we propose a front-end based on Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Network (CycleGAN) which transforms naturally perturbed speech into normal speech, and hence improves the robustness of an ASR system. The CycleGAN model is trained on non-parallel examples of perturbed and normal speech. Experiments on spontaneous laughter-speech and creaky-speech datasets show that the performance of four different ASR systems improve by using speech obtained from CycleGAN based front-end, as compared to directly using the original perturbed speech. Visualization of the features of the laughter perturbed speech and those generated by the proposed front-end further demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach.
A Novel Approach for Effective Learning in Low Resourced Scenarios
Dec 15, 2017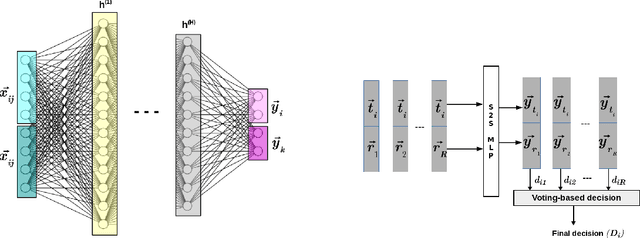
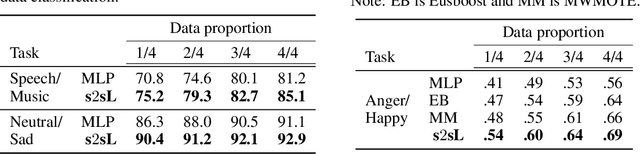
Abstract:Deep learning based discriminative methods, being the state-of-the-art machine learning techniques, are ill-suited for learning from lower amounts of data. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, called simultaneous two sample learning (s2sL), to effectively learn the class discriminative characteristics, even from very low amount of data. In s2sL, more than one sample (here, two samples) are simultaneously considered to both, train and test the classifier. We demonstrate our approach for speech/music discrimination and emotion classification through experiments. Further, we also show the effectiveness of s2sL approach for classification in low-resource scenario, and for imbalanced data.
k-FFNN: A priori knowledge infused Feed-forward Neural Networks
Apr 24, 2017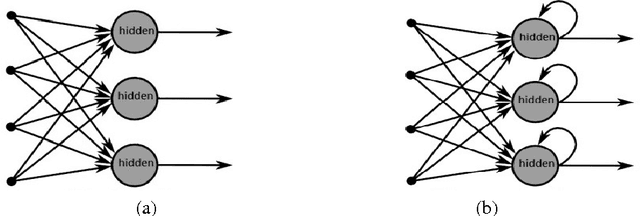
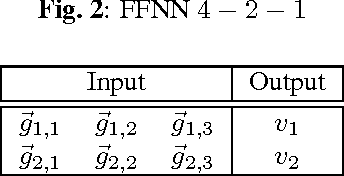
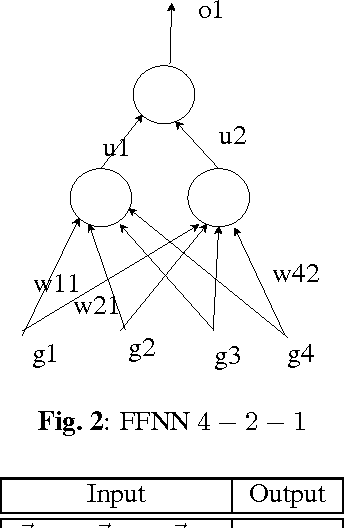
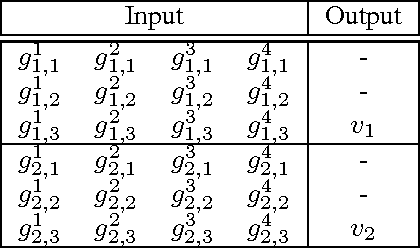
Abstract:Recurrent neural network (RNN) are being extensively used over feed-forward neural networks (FFNN) because of their inherent capability to capture temporal relationships that exist in the sequential data such as speech. This aspect of RNN is advantageous especially when there is no a priori knowledge about the temporal correlations within the data. However, RNNs require large amount of data to learn these temporal correlations, limiting their advantage in low resource scenarios. It is not immediately clear (a) how a priori temporal knowledge can be used in a FFNN architecture (b) how a FFNN performs when provided with this knowledge about temporal correlations (assuming available) during training. The objective of this paper is to explore k-FFNN, namely a FFNN architecture that can incorporate the a priori knowledge of the temporal relationships within the data sequence during training and compare k-FFNN performance with RNN in a low resource scenario. We evaluate the performance of k-FFNN and RNN by extensive experimentation on MediaEval 2016 audio data ("Emotional Impact of Movies" task). Experimental results show that the performance of k-FFNN is comparable to RNN, and in some scenarios k-FFNN performs better than RNN when temporal knowledge is injected into FFNN architecture. The main contributions of this paper are (a) fusing a priori knowledge into FFNN architecture to construct a k-FFNN and (b) analyzing the performance of k-FFNN with respect to RNN for different size of training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge