Sunil Kumar Kopparapu
Signal Transformation for Effective Multi-Channel Signal Processing
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) is an non-invasive method to record the electrical activity of the brain. The EEG signals are low bandwidth and recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously in a time synchronized manner. Typical EEG signal processing involves extracting features from all the individual channels separately and then fusing these features for downstream applications. In this paper, we propose a signal transformation, using basic signal processing, to combine the individual channels of a low-bandwidth signal, like the EEG into a single-channel high-bandwidth signal, like audio. Further this signal transformation is bi-directional, namely the high-bandwidth single-channel can be transformed to generate the individual low-bandwidth signals without any loss of information. Such a transformation when applied to EEG signals overcomes the need to process multiple signals and allows for a single-channel processing. The advantage of this signal transformation is that it allows the use of pre-trained single-channel pre-trained models, for multi-channel signal processing and analysis. We further show the utility of the signal transformation on publicly available EEG dataset.
Spoken Grammar Assessment Using LLM
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Spoken language assessment (SLA) systems restrict themselves to evaluating the pronunciation and oral fluency of a speaker by analysing the read and spontaneous spoken utterances respectively. The assessment of language grammar or vocabulary is relegated to written language assessment (WLA) systems. Most WLA systems present a set of sentences from a curated finite-size database of sentences thereby making it possible to anticipate the test questions and train oneself. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end SLA system to assess language grammar from spoken utterances thus making WLA systems redundant; additionally, we make the assessment largely unteachable by employing a large language model (LLM) to bring in variations in the test. We further demonstrate that a hybrid automatic speech recognition (ASR) with a custom-built language model outperforms the state-of-the-art ASR engine for spoken grammar assessment.
A Novel Scheme to classify Read and Spontaneous Speech
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has led to an increased use of remote telephonic interviews, making it important to distinguish between scripted and spontaneous speech in audio recordings. In this paper, we propose a novel scheme for identifying read and spontaneous speech. Our approach uses a pre-trained DeepSpeech audio-to-alphabet recognition engine to generate a sequence of alphabets from the audio. From these alphabets, we derive features that allow us to discriminate between read and spontaneous speech. Our experimental results show that even a small set of self-explanatory features can effectively classify the two types of speech very effectively.
Text-to-Audio Grounding Based Novel Metric for Evaluating Audio Caption Similarity
Oct 03, 2022
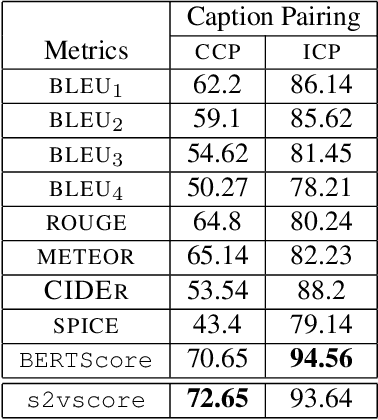
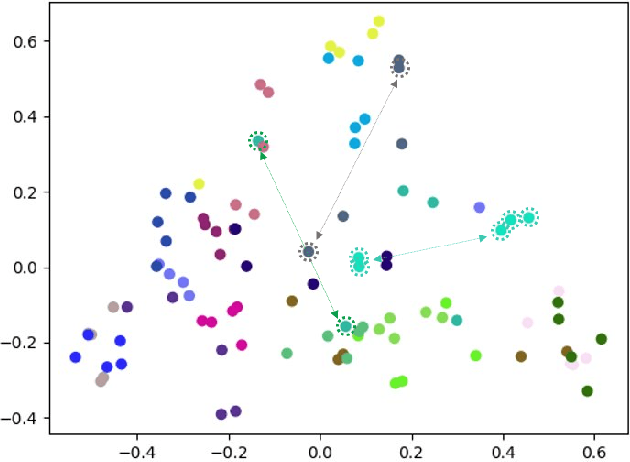
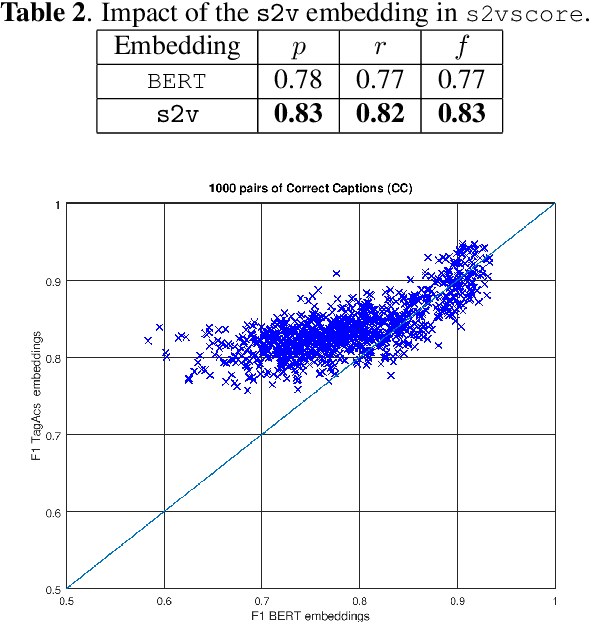
Abstract:Automatic Audio Captioning (AAC) refers to the task of translating an audio sample into a natural language (NL) text that describes the audio events, source of the events and their relationships. Unlike NL text generation tasks, which rely on metrics like BLEU, ROUGE, METEOR based on lexical semantics for evaluation, the AAC evaluation metric requires an ability to map NL text (phrases) that correspond to similar sounds in addition lexical semantics. Current metrics used for evaluation of AAC tasks lack an understanding of the perceived properties of sound represented by text. In this paper, wepropose a novel metric based on Text-to-Audio Grounding (TAG), which is, useful for evaluating cross modal tasks like AAC. Experiments on publicly available AAC data-set shows our evaluation metric to perform better compared to existing metrics used in NL text and image captioning literature.
Computing Optimal Location of Microphone for Improved Speech Recognition
Mar 24, 2022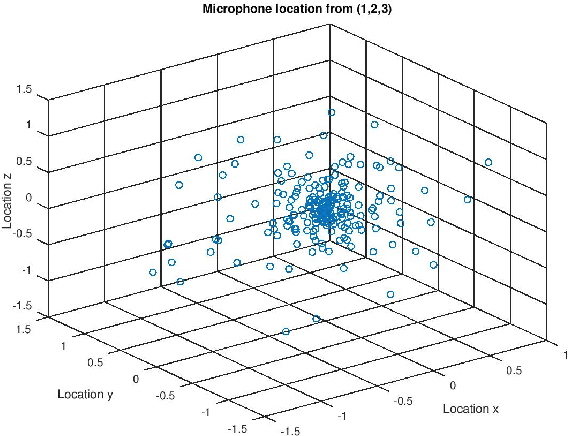
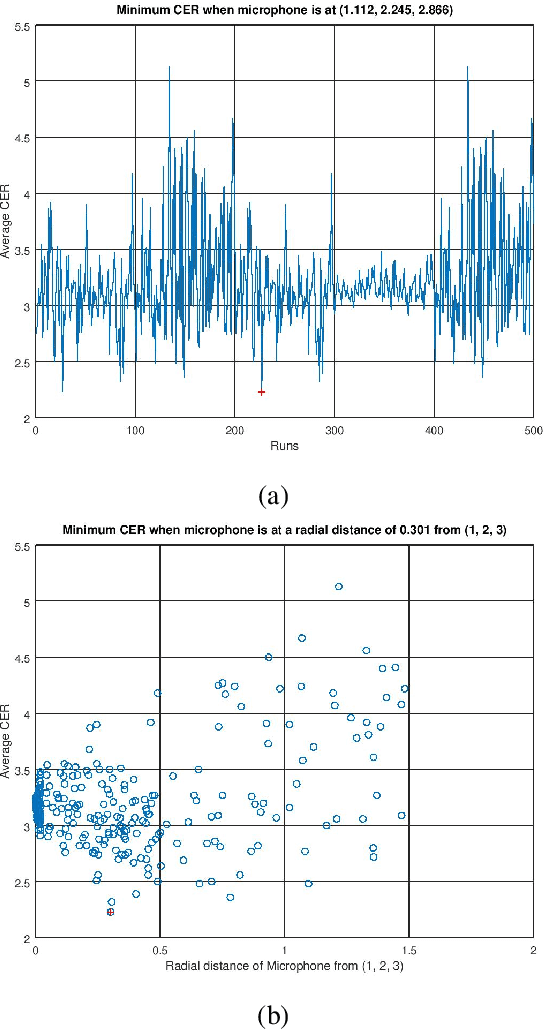
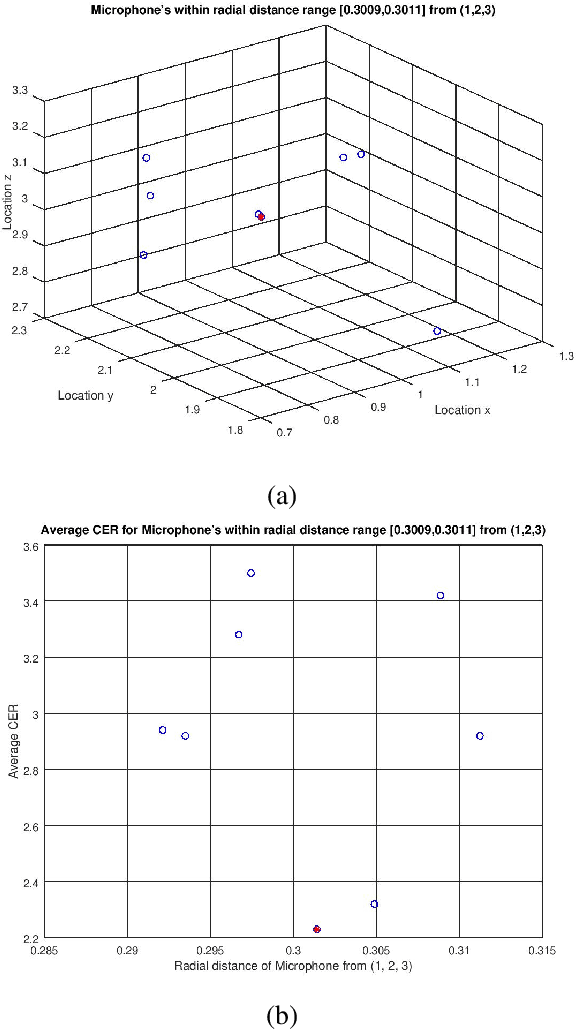
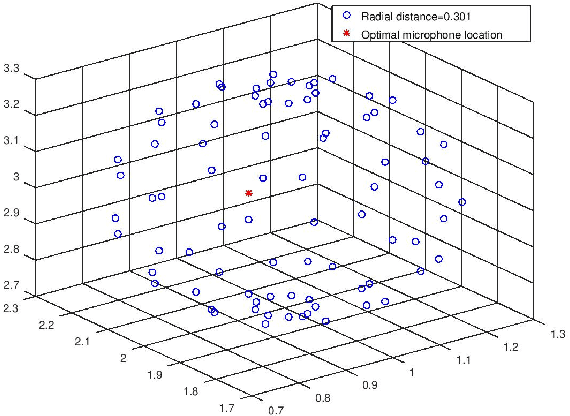
Abstract:It was shown in our earlier work that the measurement error in the microphone position affected the room impulse response (RIR) which in turn affected the single-channel close microphone and multi-channel distant microphone speech recognition. In this paper, as an extension, we systematically study to identify the optimal location of the microphone, given an approximate and hence erroneous location of the microphone in 3D space. The primary idea is to use Monte-Carlo technique to generate a large number of random microphone positions around the erroneous microphone position and select the microphone position that results in the best performance of a general purpose automatic speech recognition (gp-asr). We experiment with clean and noisy speech and show that the optimal location of the microphone is unique and is affected by noise.
Spectro Temporal EEG Biomarkers For Binary Emotion Classification
Feb 02, 2022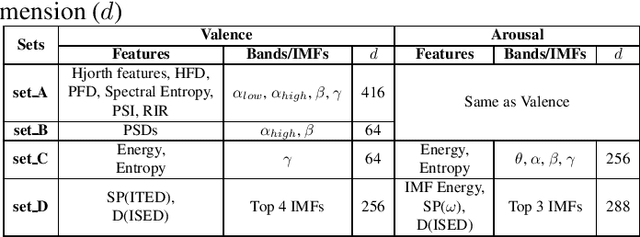
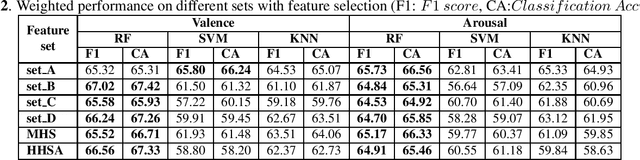
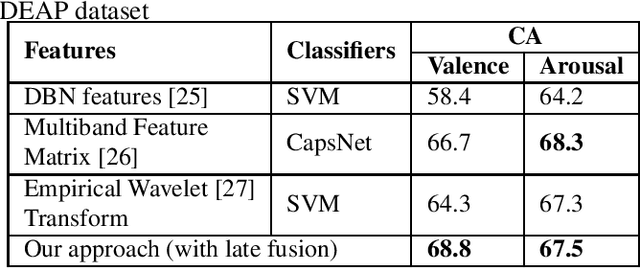
Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG) is one of the most reliable physiological signal for emotion detection. Being non-stationary in nature, EEGs are better analysed by spectro temporal representations. Standard features like Discrete Wavelet Transformation (DWT) can represent temporal changes in spectral dynamics of an EEG, but is insufficient to extract information other way around, i.e. spectral changes in temporal dynamics. On the other hand, Empirical mode decomposition (EMD) based features can be useful to bridge the above mentioned gap. Towards this direction, we extract two novel features on top of EMD, namely, (a) marginal hilbert spectrum (MHS) and (b) Holo-Hilbert spectral analysis (HHSA) based on EMD, to better represent emotions in 2D arousal-valence (A-V) space. The usefulness of these features for EEG emotion classification is investigated through extensive experiments using state-of-the-art classifiers. In addition, experiments conducted on DEAP dataset for binary emotion classification in both A-V space, reveal the efficacy of the proposed features over the standard set of temporal and spectral features.
Automatic Audio Captioning using Attention weighted Event based Embeddings
Jan 28, 2022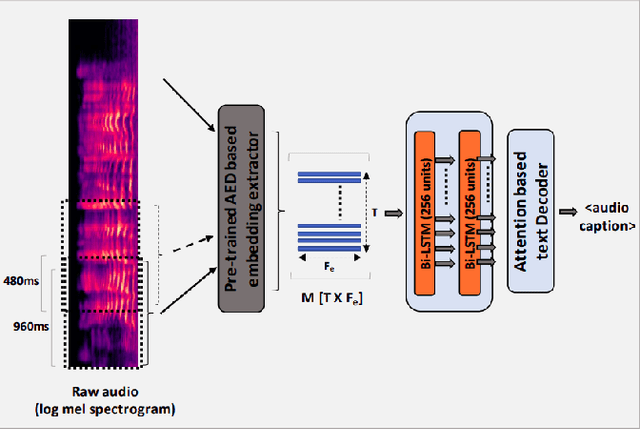
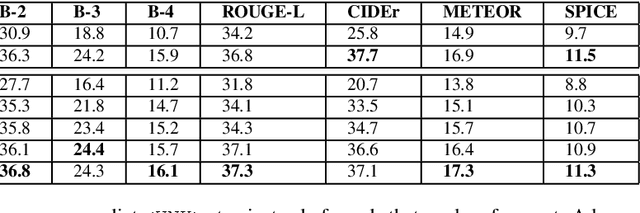
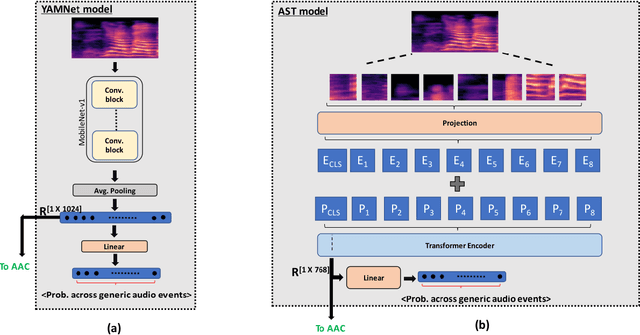
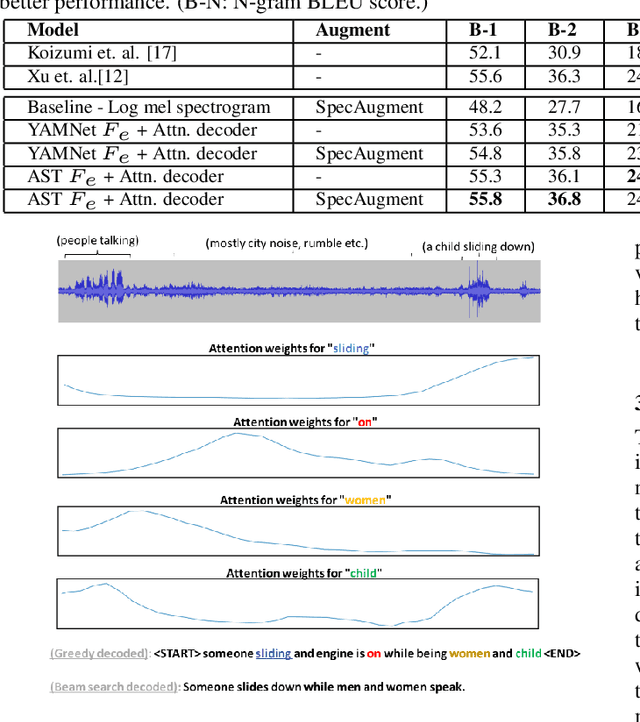
Abstract:Automatic Audio Captioning (AAC) refers to the task of translating audio into a natural language that describes the audio events, source of the events and their relationships. The limited samples in AAC datasets at present, has set up a trend to incorporate transfer learning with Audio Event Detection (AED) as a parent task. Towards this direction, in this paper, we propose an encoder-decoder architecture with light-weight (i.e. with lesser learnable parameters) Bi-LSTM recurrent layers for AAC and compare the performance of two state-of-the-art pre-trained AED models as embedding extractors. Our results show that an efficient AED based embedding extractor combined with temporal attention and augmentation techniques is able to surpass existing literature with computationally intensive architectures. Further, we provide evidence of the ability of the non-uniform attention weighted encoding generated as a part of our model to facilitate the decoder glance over specific sections of the audio while generating each token.
Synthetic speech detection using meta-learning with prototypical loss
Jan 24, 2022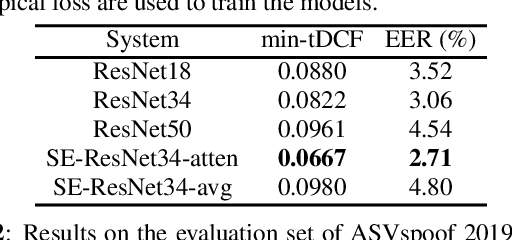
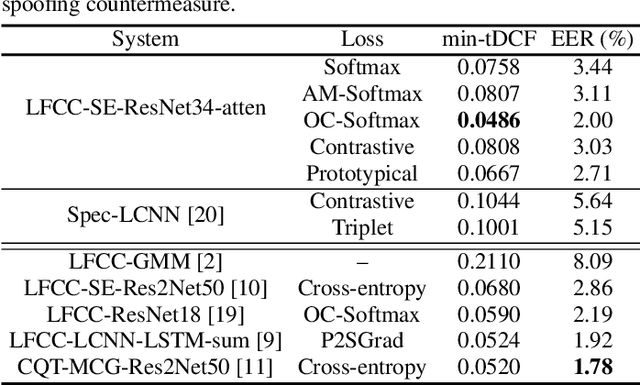
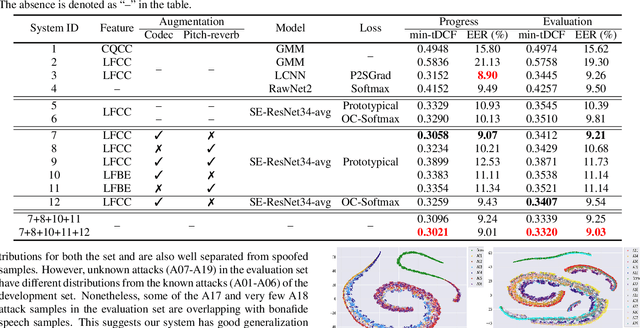
Abstract:Recent works on speech spoofing countermeasures still lack generalization ability to unseen spoofing attacks. This is one of the key issues of ASVspoof challenges especially with the rapid development of diverse and high-quality spoofing algorithms. In this work, we address the generalizability of spoofing detection by proposing prototypical loss under the meta-learning paradigm to mimic the unseen test scenario during training. Prototypical loss with metric-learning objectives can learn the embedding space directly and emerges as a strong alternative to prevailing classification loss functions. We propose an anti-spoofing system based on squeeze-excitation Residual network (SE-ResNet) architecture with prototypical loss. We demonstrate that the proposed single system without any data augmentation can achieve competitive performance to the recent best anti-spoofing systems on ASVspoof 2019 logical access (LA) task. Furthermore, the proposed system with data augmentation outperforms the ASVspoof 2021 challenge best baseline both in the progress and evaluation phase of the LA task. On ASVspoof 2019 and 2021 evaluation set LA scenario, we attain a relative 68.4% and 3.6% improvement in min-tDCF compared to the challenge best baselines, respectively.
A Novel Adaptive Minority Oversampling Technique for Improved Classification in Data Imbalanced Scenarios
Mar 26, 2021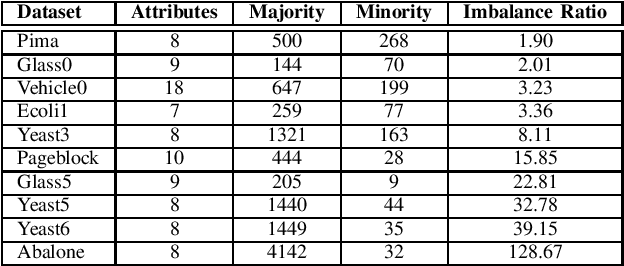
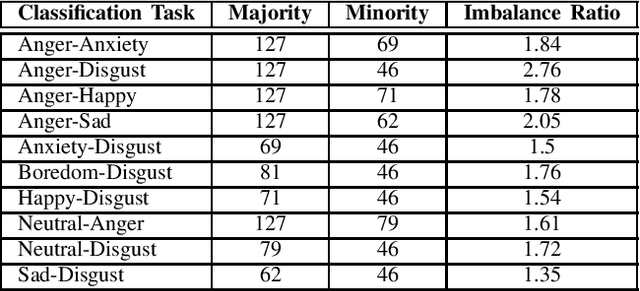
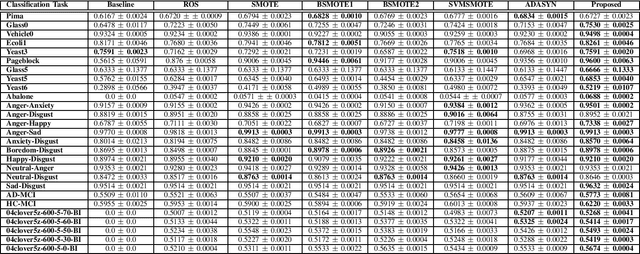
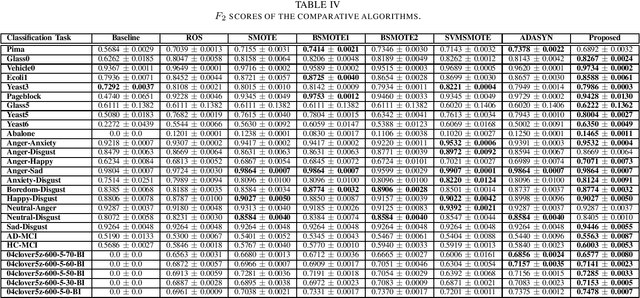
Abstract:Imbalance in the proportion of training samples belonging to different classes often poses performance degradation of conventional classifiers. This is primarily due to the tendency of the classifier to be biased towards the majority classes in the imbalanced dataset. In this paper, we propose a novel three step technique to address imbalanced data. As a first step we significantly oversample the minority class distribution by employing the traditional Synthetic Minority OverSampling Technique (SMOTE) algorithm using the neighborhood of the minority class samples and in the next step we partition the generated samples using a Gaussian-Mixture Model based clustering algorithm. In the final step synthetic data samples are chosen based on the weight associated with the cluster, the weight itself being determined by the distribution of the majority class samples. Extensive experiments on several standard datasets from diverse domains shows the usefulness of the proposed technique in comparison with the original SMOTE and its state-of-the-art variants algorithms.
* 8 pages
Automatic Speaker Independent Dysarthric Speech Intelligibility Assessment System
Mar 10, 2021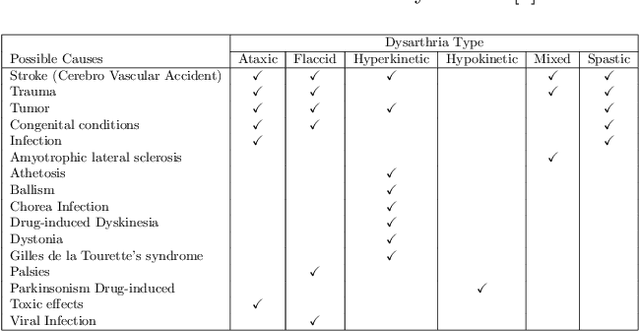
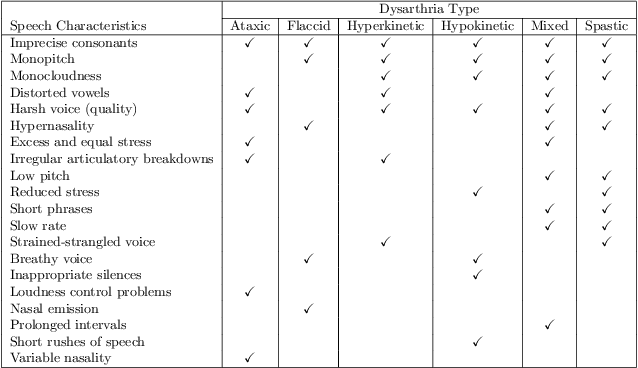
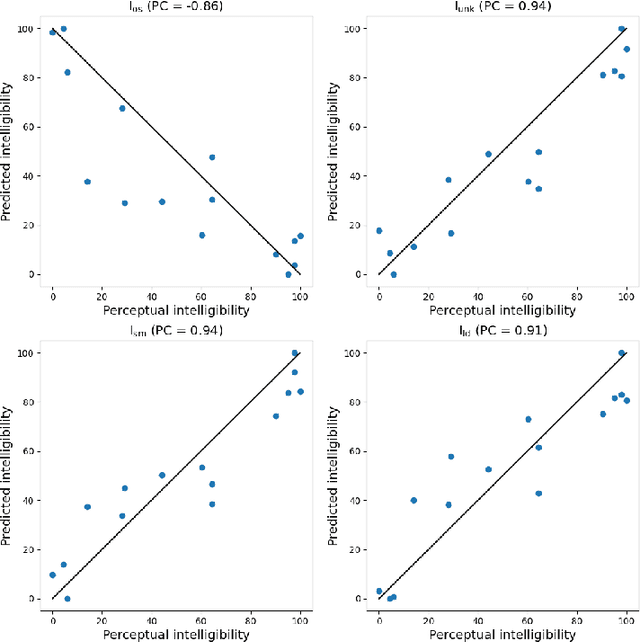
Abstract:Dysarthria is a condition which hampers the ability of an individual to control the muscles that play a major role in speech delivery. The loss of fine control over muscles that assist the movement of lips, vocal chords, tongue and diaphragm results in abnormal speech delivery. One can assess the severity level of dysarthria by analyzing the intelligibility of speech spoken by an individual. Continuous intelligibility assessment helps speech language pathologists not only study the impact of medication but also allows them to plan personalized therapy. It helps the clinicians immensely if the intelligibility assessment system is reliable, automatic, simple for (a) patients to undergo and (b) clinicians to interpret. Lack of availability of dysarthric data has resulted in development of speaker dependent automatic intelligibility assessment systems which requires patients to speak a large number of utterances. In this paper, we propose (a) a cost minimization procedure to select an optimal (small) number of utterances that need to be spoken by the dysarthric patient, (b) four different speaker independent intelligibility assessment systems which require the patient to speak a small number of words, and (c) the assessment score is close to the perceptual score that the Speech Language Pathologist (SLP) can relate to. The need for small number of utterances to be spoken by the patient and the score being relatable to the SLP benefits both the dysarthric patient and the clinician from usability perspective.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge