Ruofan Liu
Image2Garment: Simulation-ready Garment Generation from a Single Image
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Estimating physically accurate, simulation-ready garments from a single image is challenging due to the absence of image-to-physics datasets and the ill-posed nature of this problem. Prior methods either require multi-view capture and expensive differentiable simulation or predict only garment geometry without the material properties required for realistic simulation. We propose a feed-forward framework that sidesteps these limitations by first fine-tuning a vision-language model to infer material composition and fabric attributes from real images, and then training a lightweight predictor that maps these attributes to the corresponding physical fabric parameters using a small dataset of material-physics measurements. Our approach introduces two new datasets (FTAG and T2P) and delivers simulation-ready garments from a single image without iterative optimization. Experiments show that our estimator achieves superior accuracy in material composition estimation and fabric attribute prediction, and by passing them through our physics parameter estimator, we further achieve higher-fidelity simulations compared to state-of-the-art image-to-garment methods.
FGO-ILNS: Tightly Coupled Multi-Sensor Integrated Navigation System Based on Factor Graph Optimization for Autonomous Underwater Vehicle
Oct 22, 2023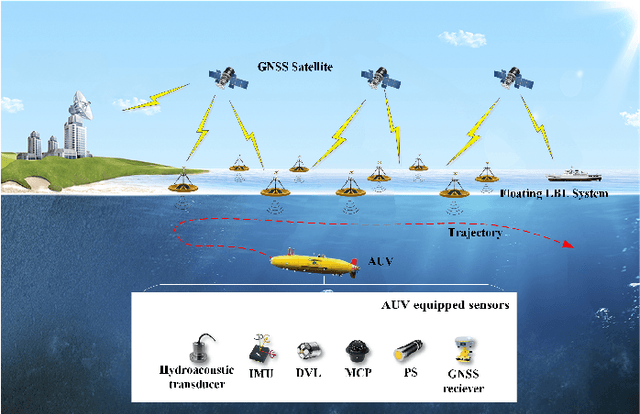
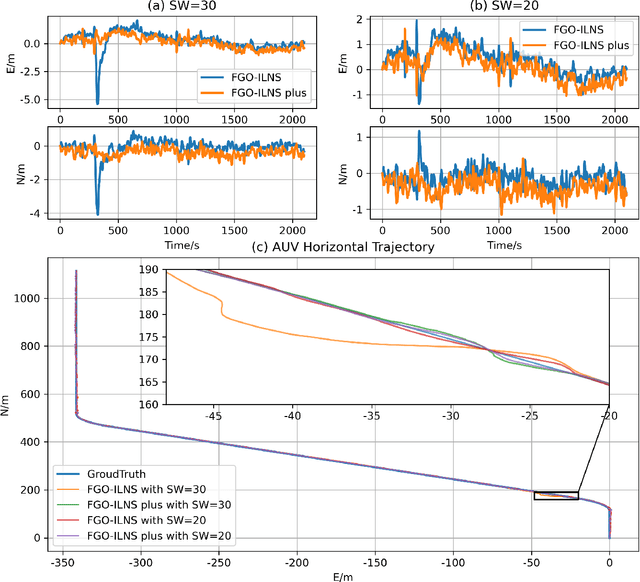
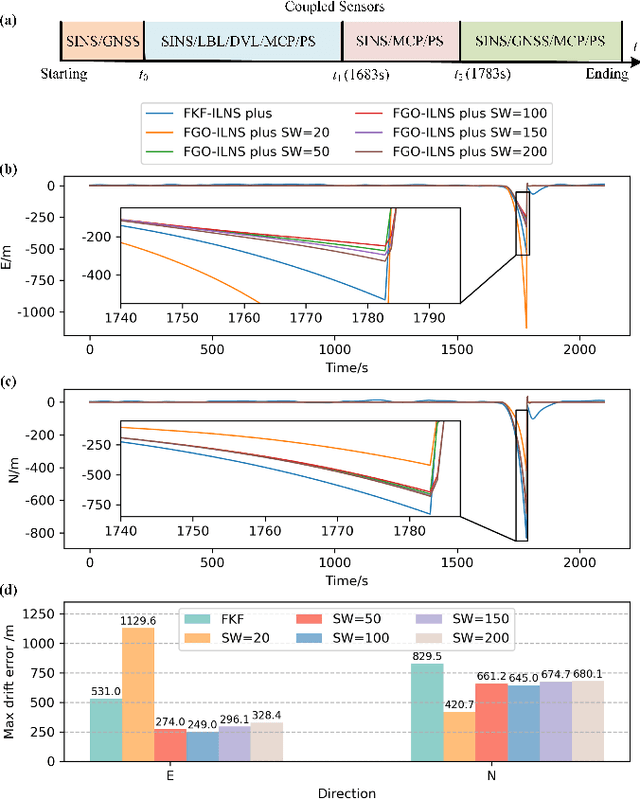
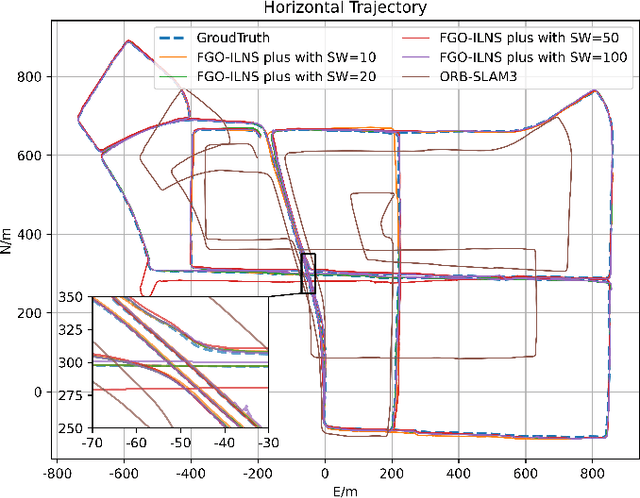
Abstract:Multi-sensor fusion is an effective way to enhance the positioning performance of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs). However, underwater multi-sensor fusion faces challenges such as heterogeneous frequency and dynamic availability of sensors. Traditional filter-based algorithms suffer from low accuracy and robustness when sensors become unavailable. The factor graph optimization (FGO) can enable multi-sensor plug-and-play despite data frequency. Therefore, we present an FGO-based strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS) and long baseline location (LBL) system tightly coupled navigation system (FGO-ILNS). Sensors such as Doppler velocity log (DVL), magnetic compass pilot (MCP), pressure sensor (PS), and global navigation satellite system (GNSS) can be tightly coupled with FGO-ILNS to satisfy different navigation scenarios. In this system, we propose a floating LBL slant range difference factor model tightly coupled with IMU preintegration factor to achieve unification of global position above and below water. Furthermore, to address the issue of sensor measurements not being synchronized with the LBL during fusion, we employ forward-backward IMU preintegration to construct sensor factors such as GNSS and DVL. Moreover, we utilize the marginalization method to reduce the computational load of factor graph optimization. Simulation and public KAIST dataset experiments have verified that, compared to filter-based algorithms like the extended Kalman filter and federal Kalman filter, as well as the state-of-the-art optimization-based algorithm ORB-SLAM3, our proposed FGO-ILNS leads in accuracy and robustness.
DeepVisualInsight: Time-Travelling Visualization for Spatio-Temporal Causality of Deep Classification Training
Dec 31, 2021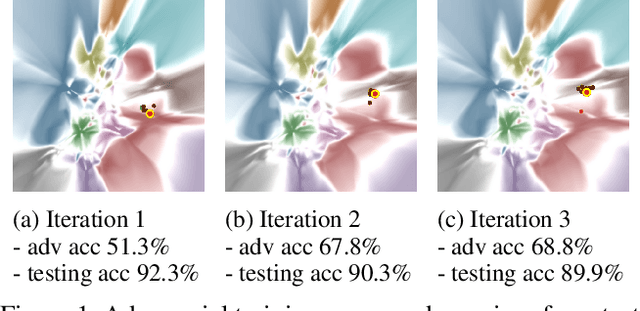
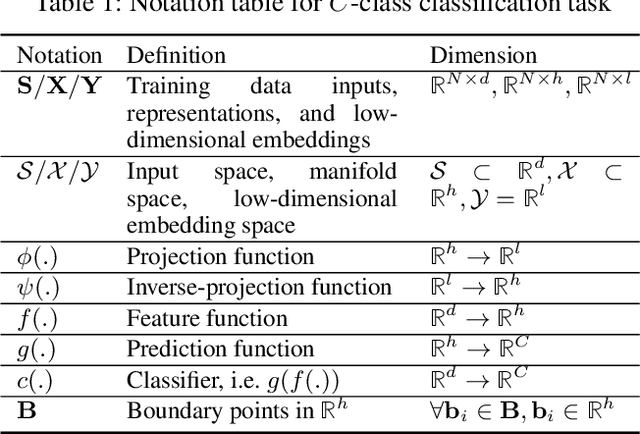
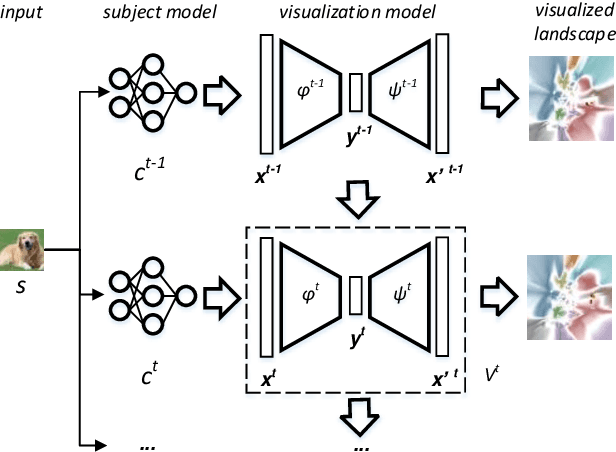
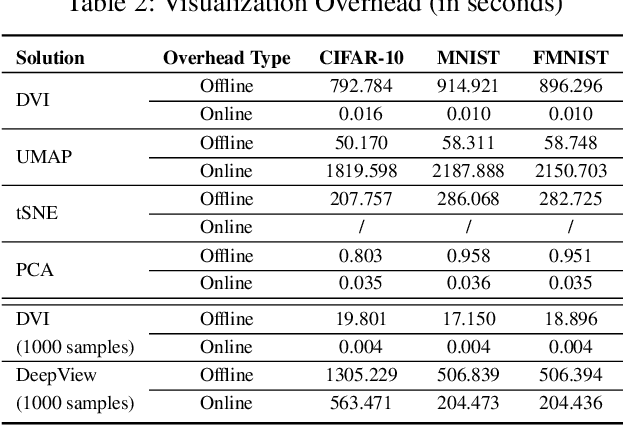
Abstract:Understanding how the predictions of deep learning models are formed during the training process is crucial to improve model performance and fix model defects, especially when we need to investigate nontrivial training strategies such as active learning, and track the root cause of unexpected training results such as performance degeneration. In this work, we propose a time-travelling visual solution DeepVisualInsight (DVI), aiming to manifest the spatio-temporal causality while training a deep learning image classifier. The spatio-temporal causality demonstrates how the gradient-descent algorithm and various training data sampling techniques can influence and reshape the layout of learnt input representation and the classification boundaries in consecutive epochs. Such causality allows us to observe and analyze the whole learning process in the visible low dimensional space. Technically, we propose four spatial and temporal properties and design our visualization solution to satisfy them. These properties preserve the most important information when inverse-)projecting input samples between the visible low-dimensional and the invisible high-dimensional space, for causal analyses. Our extensive experiments show that, comparing to baseline approaches, we achieve the best visualization performance regarding the spatial/temporal properties and visualization efficiency. Moreover, our case study shows that our visual solution can well reflect the characteristics of various training scenarios, showing good potential of DVI as a debugging tool for analyzing deep learning training processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge