Runxuan Yang
A Fast and Lightweight Model for Causal Audio-Visual Speech Separation
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Audio-visual speech separation (AVSS) aims to extract a target speech signal from a mixed signal by leveraging both auditory and visual (lip movement) cues. However, most existing AVSS methods exhibit complex architectures and rely on future context, operating offline, which renders them unsuitable for real-time applications. Inspired by the pipeline of RTFSNet, we propose a novel streaming AVSS model, named Swift-Net, which enhances the causal processing capabilities required for real-time applications. Swift-Net adopts a lightweight visual feature extraction module and an efficient fusion module for audio-visual integration. Additionally, Swift-Net employs Grouped SRUs to integrate historical information across different feature spaces, thereby improving the utilization efficiency of historical information. We further propose a causal transformation template to facilitate the conversion of non-causal AVSS models into causal counterparts. Experiments on three standard benchmark datasets (LRS2, LRS3, and VoxCeleb2) demonstrated that under causal conditions, our proposed Swift-Net exhibited outstanding performance, highlighting the potential of this method for processing speech in complex environments.
Time-Frequency-Based Attention Cache Memory Model for Real-Time Speech Separation
May 19, 2025Abstract:Existing causal speech separation models often underperform compared to non-causal models due to difficulties in retaining historical information. To address this, we propose the Time-Frequency Attention Cache Memory (TFACM) model, which effectively captures spatio-temporal relationships through an attention mechanism and cache memory (CM) for historical information storage. In TFACM, an LSTM layer captures frequency-relative positions, while causal modeling is applied to the time dimension using local and global representations. The CM module stores past information, and the causal attention refinement (CAR) module further enhances time-based feature representations for finer granularity. Experimental results showed that TFACM achieveed comparable performance to the SOTA TF-GridNet-Causal model, with significantly lower complexity and fewer trainable parameters. For more details, visit the project page: https://cslikai.cn/TFACM/.
SonicSim: A customizable simulation platform for speech processing in moving sound source scenarios
Oct 02, 2024
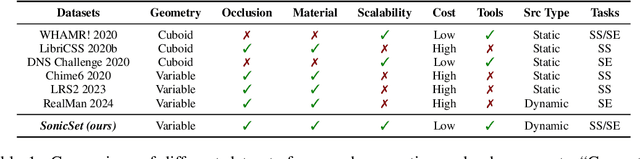

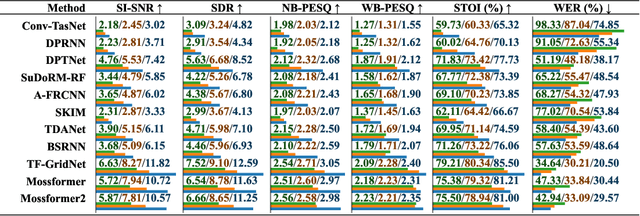
Abstract:The systematic evaluation of speech separation and enhancement models under moving sound source conditions typically requires extensive data comprising diverse scenarios. However, real-world datasets often contain insufficient data to meet the training and evaluation requirements of models. Although synthetic datasets offer a larger volume of data, their acoustic simulations lack realism. Consequently, neither real-world nor synthetic datasets effectively fulfill practical needs. To address these issues, we introduce SonicSim, a synthetic toolkit de-designed to generate highly customizable data for moving sound sources. SonicSim is developed based on the embodied AI simulation platform, Habitat-sim, supporting multi-level adjustments, including scene-level, microphone-level, and source-level, thereby generating more diverse synthetic data. Leveraging SonicSim, we constructed a moving sound source benchmark dataset, SonicSet, using the Librispeech, the Freesound Dataset 50k (FSD50K) and Free Music Archive (FMA), and 90 scenes from the Matterport3D to evaluate speech separation and enhancement models. Additionally, to validate the differences between synthetic data and real-world data, we randomly selected 5 hours of raw data without reverberation from the SonicSet validation set to record a real-world speech separation dataset, which was then compared with the corresponding synthetic datasets. Similarly, we utilized the real-world speech enhancement dataset RealMAN to validate the acoustic gap between other synthetic datasets and the SonicSet dataset for speech enhancement. The results indicate that the synthetic data generated by SonicSim can effectively generalize to real-world scenarios. Demo and code are publicly available at https://cslikai.cn/SonicSim/.
SCANet: A Self- and Cross-Attention Network for Audio-Visual Speech Separation
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:The integration of different modalities, such as audio and visual information, plays a crucial role in human perception of the surrounding environment. Recent research has made significant progress in designing fusion modules for audio-visual speech separation. However, they predominantly focus on multi-modal fusion architectures situated either at the top or bottom positions, rather than comprehensively considering multi-modal fusion at various hierarchical positions within the network. In this paper, we propose a novel model called self- and cross-attention network (SCANet), which leverages the attention mechanism for efficient audio-visual feature fusion. SCANet consists of two types of attention blocks: self-attention (SA) and cross-attention (CA) blocks, where the CA blocks are distributed at the top (TCA), middle (MCA) and bottom (BCA) of SCANet. These blocks maintain the ability to learn modality-specific features and enable the extraction of different semantics from audio-visual features. Comprehensive experiments on three standard audio-visual separation benchmarks (LRS2, LRS3, and VoxCeleb2) demonstrate the effectiveness of SCANet, outperforming existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods while maintaining comparable inference time.
An efficient encoder-decoder architecture with top-down attention for speech separation
Oct 07, 2022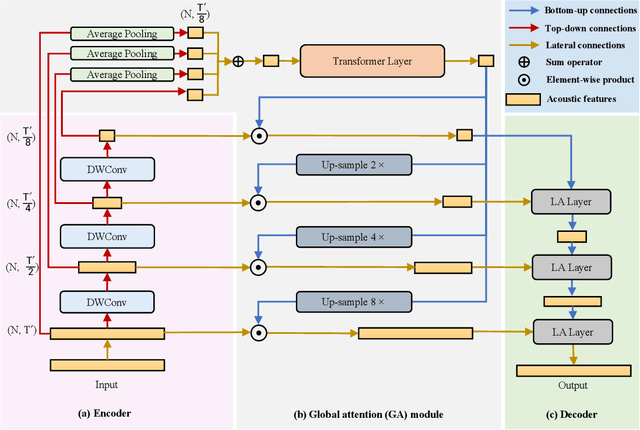
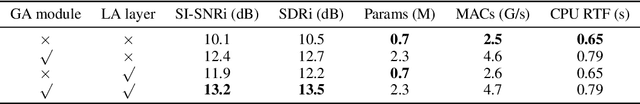
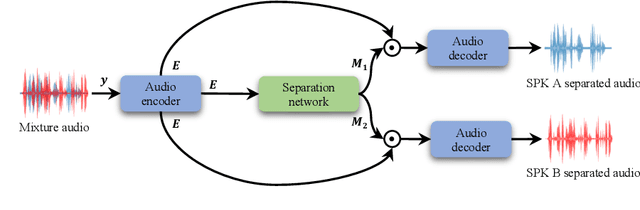
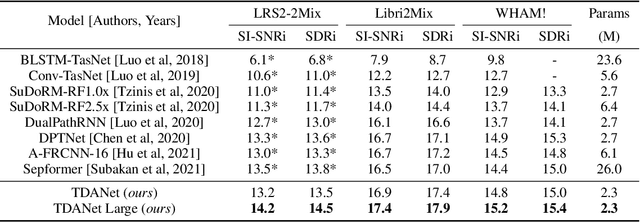
Abstract:Deep neural networks have shown excellent prospects in speech separation tasks. However, obtaining good results while keeping a low model complexity remains challenging in real-world applications. In this paper, we provide a bio-inspired efficient encoder-decoder architecture by mimicking the brain's top-down attention, called TDANet, with decreased model complexity without sacrificing performance. The top-down attention in TDANet is extracted by the global attention (GA) module and the cascaded local attention (LA) layers. The GA module takes multi-scale acoustic features as input to extract global attention signal, which then modulates features of different scales by direct top-down connections. The LA layers use features of adjacent layers as input to extract the local attention signal, which is used to modulate the lateral input in a top-down manner. On three benchmark datasets, TDANet consistently achieved competitive separation performance to previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods with higher efficiency. Specifically, TDANet's multiply-accumulate operations (MACs) are only 5\% of Sepformer, one of the previous SOTA models, and CPU inference time is only 10\% of Sepformer. In addition, a large-size version of TDANet obtained SOTA results on three datasets, with MACs still only 10\% of Sepformer and the CPU inference time only 24\% of Sepformer. Our study suggests that top-down attention can be a more efficient strategy for speech separation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge