Runjie Yan
Consistent Flow Distillation for Text-to-3D Generation
Jan 09, 2025
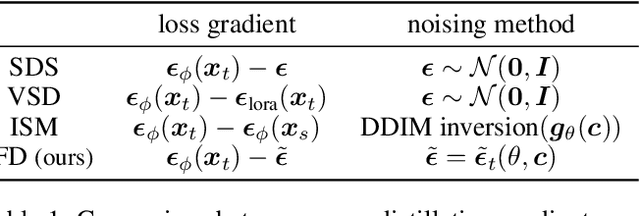
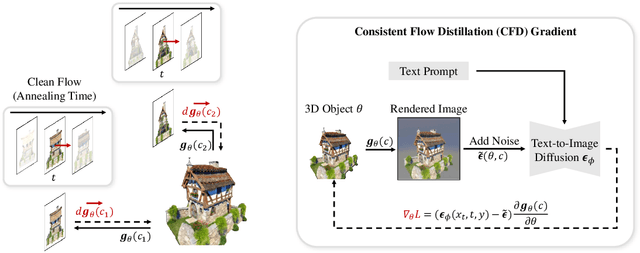
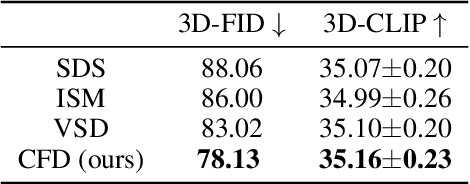
Abstract:Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) has made significant strides in distilling image-generative models for 3D generation. However, its maximum-likelihood-seeking behavior often leads to degraded visual quality and diversity, limiting its effectiveness in 3D applications. In this work, we propose Consistent Flow Distillation (CFD), which addresses these limitations. We begin by leveraging the gradient of the diffusion ODE or SDE sampling process to guide the 3D generation. From the gradient-based sampling perspective, we find that the consistency of 2D image flows across different viewpoints is important for high-quality 3D generation. To achieve this, we introduce multi-view consistent Gaussian noise on the 3D object, which can be rendered from various viewpoints to compute the flow gradient. Our experiments demonstrate that CFD, through consistent flows, significantly outperforms previous methods in text-to-3D generation.
Unique3D: High-Quality and Efficient 3D Mesh Generation from a Single Image
May 30, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we introduce Unique3D, a novel image-to-3D framework for efficiently generating high-quality 3D meshes from single-view images, featuring state-of-the-art generation fidelity and strong generalizability. Previous methods based on Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) can produce diversified 3D results by distilling 3D knowledge from large 2D diffusion models, but they usually suffer from long per-case optimization time with inconsistent issues. Recent works address the problem and generate better 3D results either by finetuning a multi-view diffusion model or training a fast feed-forward model. However, they still lack intricate textures and complex geometries due to inconsistency and limited generated resolution. To simultaneously achieve high fidelity, consistency, and efficiency in single image-to-3D, we propose a novel framework Unique3D that includes a multi-view diffusion model with a corresponding normal diffusion model to generate multi-view images with their normal maps, a multi-level upscale process to progressively improve the resolution of generated orthographic multi-views, as well as an instant and consistent mesh reconstruction algorithm called ISOMER, which fully integrates the color and geometric priors into mesh results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our Unique3D significantly outperforms other image-to-3D baselines in terms of geometric and textural details.
Flow Score Distillation for Diverse Text-to-3D Generation
May 16, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in Text-to-3D generation have yielded remarkable progress, particularly through methods that rely on Score Distillation Sampling (SDS). While SDS exhibits the capability to create impressive 3D assets, it is hindered by its inherent maximum-likelihood-seeking essence, resulting in limited diversity in generation outcomes. In this paper, we discover that the Denoise Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIM) generation process (\ie PF-ODE) can be succinctly expressed using an analogue of SDS loss. One step further, one can see SDS as a generalized DDIM generation process. Following this insight, we show that the noise sampling strategy in the noise addition stage significantly restricts the diversity of generation results. To address this limitation, we present an innovative noise sampling approach and introduce a novel text-to-3D method called Flow Score Distillation (FSD). Our validation experiments across various text-to-image Diffusion Models demonstrate that FSD substantially enhances generation diversity without compromising quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge