Ruiye Ming
SR-LIO++: Efficient LiDAR-Inertial Odometry and Quantized Mapping with Sweep Reconstruction
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Addressing the inherent low acquisition frequency limitation of 3D LiDAR to achieve high-frequency output has become a critical research focus in the LiDAR-Inertial Odometry (LIO) domain. To ensure real-time performance, frequency-enhanced LIO systems must process each sweep within significantly reduced timeframe, which presents substantial challenges for deployment on low-computational-power platforms. To address these limitations, we introduce SR-LIO++, an innovative LIO system capable of achieving doubled output frequency relative to input frequency on resource-constrained hardware platforms, including the Raspberry Pi 4B. Our system employs a sweep reconstruction methodology to enhance LiDAR sweep frequency, generating high-frequency reconstructed sweeps. Building upon this foundation, we propose a caching mechanism for intermediate results (i.e., surface parameters) of the most recent segments, effectively minimizing redundant processing of common segments in adjacent reconstructed sweeps. This method decouples processing time from the traditionally linear dependence on reconstructed sweep frequency. Furthermore, we present a quantized map point management based on index table mapping, significantly reducing memory usage by converting global 3D point storage from 64-bit double precision to 8-bit char representation. This method also converts the computationally intensive Euclidean distance calculations in nearest neighbor searches from 64-bit double precision to 16-bit short and 32-bit integer formats, significantly reducing both memory and computational cost. Extensive experimental evaluations across three distinct computing platforms and four public datasets demonstrate that SR-LIO++ maintains state-of-the-art accuracy while substantially enhancing efficiency. Notably, our system successfully achieves 20Hz state output on Raspberry Pi 4B hardware.
IFTD: Image Feature Triangle Descriptor for Loop Detection in Driving Scenes
Jun 12, 2024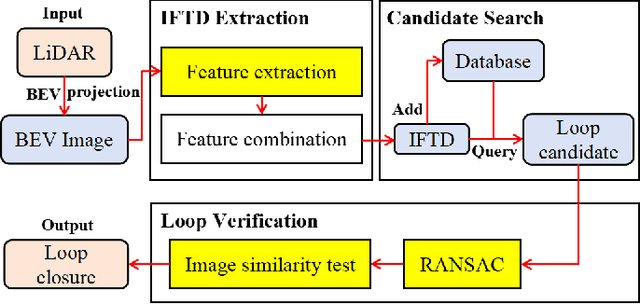
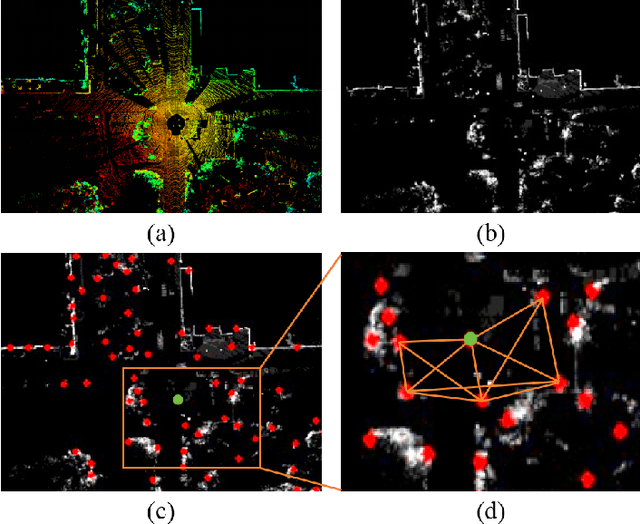
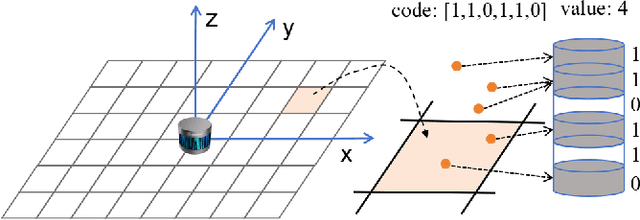

Abstract:In this work, we propose a fast and robust Image Feature Triangle Descriptor (IFTD) based on the STD method, aimed at improving the efficiency and accuracy of place recognition in driving scenarios. We extract keypoints from BEV projection image of point cloud and construct these keypoints into triangle descriptors. By matching these feature triangles, we achieved precise place recognition and calculated the 4-DOF pose estimation between two keyframes. Furthermore, we employ image similarity inspection to perform the final place recognition. Experimental results on three public datasets demonstrate that our IFTD can achieve greater robustness and accuracy than state-of-the-art methods with low computational overhead.
SR-LIVO: LiDAR-Inertial-Visual Odometry and Mapping with Sweep Reconstruction
Dec 28, 2023Abstract:Existing LiDAR-inertial-visual odometry and mapping (LIV-SLAM) systems mainly utilize the LiDAR-inertial odometry (LIO) module for structure reconstruction and the visual-inertial odometry (VIO) module for color rendering. However, the accuracy of VIO is often compromised by photometric changes, weak textures and motion blur, unlike the more robust LIO. This paper introduces SR-LIVO, an advanced and novel LIV-SLAM system employing sweep reconstruction to align reconstructed sweeps with image timestamps. This allows the LIO module to accurately determine states at all imaging moments, enhancing pose accuracy and processing efficiency. Experimental results on two public datasets demonstrate that: 1) our SRLIVO outperforms existing state-of-the-art LIV-SLAM systems in both pose accuracy and time efficiency; 2) our LIO-based pose estimation prove more accurate than VIO-based ones in several mainstream LIV-SLAM systems (including ours). We have released our source code to contribute to the community development in this field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge