Ruixuan Yan
Neuro-symbolic Models for Interpretable Time Series Classification using Temporal Logic Description
Sep 15, 2022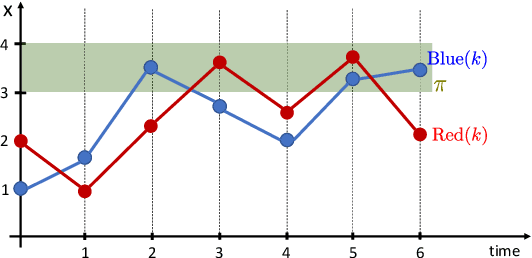
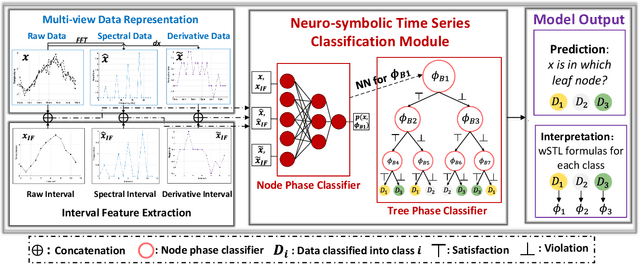
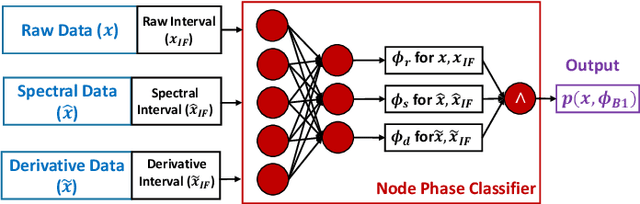
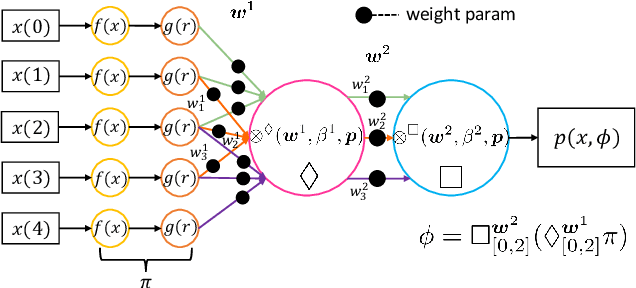
Abstract:Most existing Time series classification (TSC) models lack interpretability and are difficult to inspect. Interpretable machine learning models can aid in discovering patterns in data as well as give easy-to-understand insights to domain specialists. In this study, we present Neuro-Symbolic Time Series Classification (NSTSC), a neuro-symbolic model that leverages signal temporal logic (STL) and neural network (NN) to accomplish TSC tasks using multi-view data representation and expresses the model as a human-readable, interpretable formula. In NSTSC, each neuron is linked to a symbolic expression, i.e., an STL (sub)formula. The output of NSTSC is thus interpretable as an STL formula akin to natural language, describing temporal and logical relations hidden in the data. We propose an NSTSC-based classifier that adopts a decision-tree approach to learn formula structures and accomplish a multiclass TSC task. The proposed smooth activation functions for wSTL allow the model to be learned in an end-to-end fashion. We test NSTSC on a real-world wound healing dataset from mice and benchmark datasets from the UCR time-series repository, demonstrating that NSTSC achieves comparable performance with the state-of-the-art models. Furthermore, NSTSC can generate interpretable formulas that match with domain knowledge.
Weighted Graph-Based Signal Temporal Logic Inference Using Neural Networks
Sep 16, 2021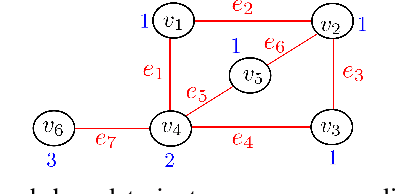
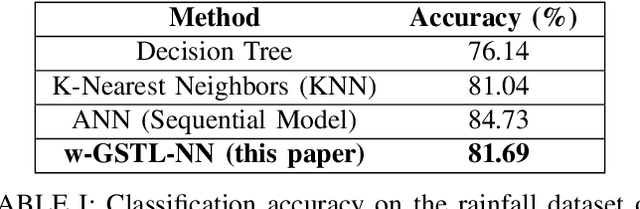
Abstract:Extracting spatial-temporal knowledge from data is useful in many applications. It is important that the obtained knowledge is human-interpretable and amenable to formal analysis. In this paper, we propose a method that trains neural networks to learn spatial-temporal properties in the form of weighted graph-based signal temporal logic (wGSTL) formulas. For learning wGSTL formulas, we introduce a flexible wGSTL formula structure in which the user's preference can be applied in the inferred wGSTL formulas. In the proposed framework, each neuron of the neural networks corresponds to a subformula in a flexible wGSTL formula structure. We initially train a neural network to learn the wGSTL operators and then train a second neural network to learn the parameters in a flexible wGSTL formula structure. We use a COVID-19 dataset and a rain prediction dataset to evaluate the performance of the proposed framework and algorithms. We compare the performance of the proposed framework with three baseline classification methods including K-nearest neighbors, decision trees, and artificial neural networks. The classification accuracy obtained by the proposed framework is comparable with the baseline classification methods.
Neural Network for Weighted Signal Temporal Logic
Apr 08, 2021

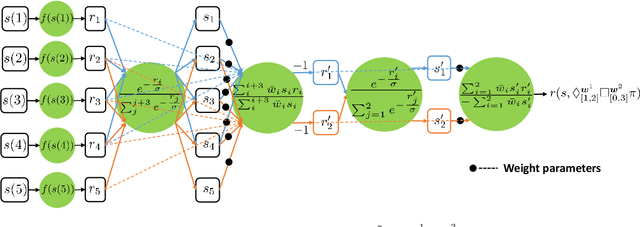
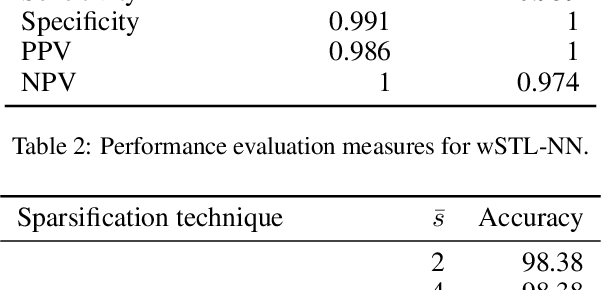
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a neuro-symbolic framework called weighted Signal Temporal Logic Neural Network (wSTL-NN) that combines the characteristics of neural networks and temporal logics. Weighted Signal Temporal Logic (wSTL) formulas are recursively composed of subformulas that are combined using logical and temporal operators. The quantitative semantics of wSTL is defined such that the quantitative satisfaction of subformulas with higher weights has more influence on the quantitative satisfaction of the overall wSTL formula. In the wSTL-NN, each neuron corresponds to a wSTL subformula, and its output corresponds to the quantitative satisfaction of the formula. We use wSTL-NN to represent wSTL formulas as features to classify time series data. STL features are more explainable than those used in classical methods. The wSTL-NN is end-to-end differentiable, which allows learning of wSTL formulas to be done using back-propagation. To reduce the number of weights, we introduce two techniques to sparsify the wSTL-NN.We apply our framework to an occupancy detection time-series dataset to learn a classifier that predicts the occupancy status of an office room.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge