Ruijie Meng
To Defend Against Cyber Attacks, We Must Teach AI Agents to Hack
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:For over a decade, cybersecurity has relied on human labor scarcity to limit attackers to high-value targets manually or generic automated attacks at scale. Building sophisticated exploits requires deep expertise and manual effort, leading defenders to assume adversaries cannot afford tailored attacks at scale. AI agents break this balance by automating vulnerability discovery and exploitation across thousands of targets, needing only small success rates to remain profitable. Current developers focus on preventing misuse through data filtering, safety alignment, and output guardrails. Such protections fail against adversaries who control open-weight models, bypass safety controls, or develop offensive capabilities independently. We argue that AI-agent-driven cyber attacks are inevitable, requiring a fundamental shift in defensive strategy. In this position paper, we identify why existing defenses cannot stop adaptive adversaries and demonstrate that defenders must develop offensive security intelligence. We propose three actions for building frontier offensive AI capabilities responsibly. First, construct comprehensive benchmarks covering the full attack lifecycle. Second, advance from workflow-based to trained agents for discovering in-wild vulnerabilities at scale. Third, implement governance restricting offensive agents to audited cyber ranges, staging release by capability tier, and distilling findings into safe defensive-only agents. We strongly recommend treating offensive AI capabilities as essential defensive infrastructure, as containing cybersecurity risks requires mastering them in controlled settings before adversaries do.
EmotionBox: a music-element-driven emotional music generation system using Recurrent Neural Network
Dec 16, 2021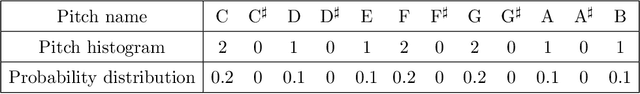
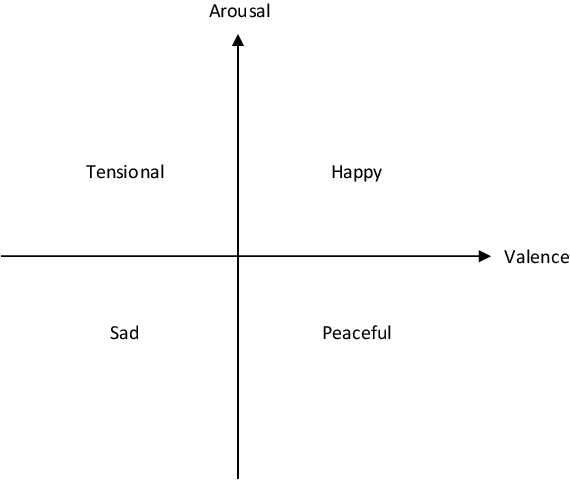
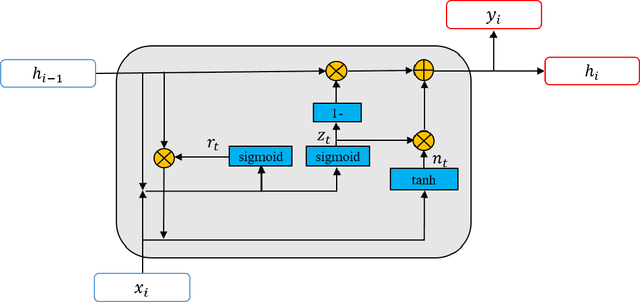
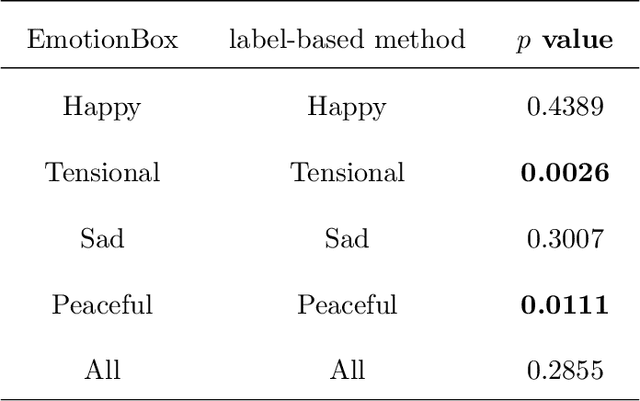
Abstract:With the development of deep neural networks, automatic music composition has made great progress. Although emotional music can evoke listeners' different emotions and it is important for artistic expression, only few researches have focused on generating emotional music. This paper presents EmotionBox -an music-element-driven emotional music generator that is capable of composing music given a specific emotion, where this model does not require a music dataset labeled with emotions. Instead, pitch histogram and note density are extracted as features that represent mode and tempo respectively to control music emotions. The subjective listening tests show that the Emotionbox has a more competitive and balanced performance in arousing a specified emotion than the emotion-label-based method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge