Rohit Prasad
J3DAI: A tiny DNN-Based Edge AI Accelerator for 3D-Stacked CMOS Image Sensor
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:This paper presents J3DAI, a tiny deep neural network-based hardware accelerator for a 3-layer 3D-stacked CMOS image sensor featuring an artificial intelligence (AI) chip integrating a Deep Neural Network (DNN)-based accelerator. The DNN accelerator is designed to efficiently perform neural network tasks such as image classification and segmentation. This paper focuses on the digital system of J3DAI, highlighting its Performance-Power-Area (PPA) characteristics and showcasing advanced edge AI capabilities on a CMOS image sensor. To support hardware, we utilized the Aidge comprehensive software framework, which enables the programming of both the host processor and the DNN accelerator. Aidge supports post-training quantization, significantly reducing memory footprint and computational complexity, making it crucial for deploying models on resource-constrained hardware like J3DAI. Our experimental results demonstrate the versatility and efficiency of this innovative design in the field of edge AI, showcasing its potential to handle both simple and computationally intensive tasks. Future work will focus on further optimizing the architecture and exploring new applications to fully leverage the capabilities of J3DAI. As edge AI continues to grow in importance, innovations like J3DAI will play a crucial role in enabling real-time, low-latency, and energy-efficient AI processing at the edge.
Advancing the State of the Art in Open Domain Dialog Systems through the Alexa Prize
Dec 27, 2018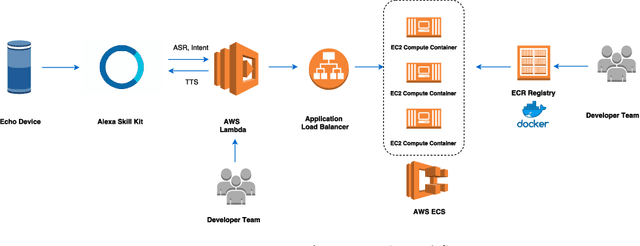
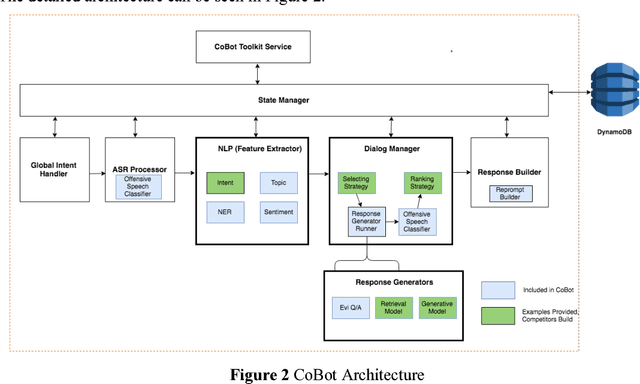
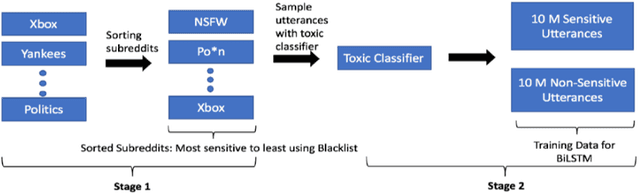
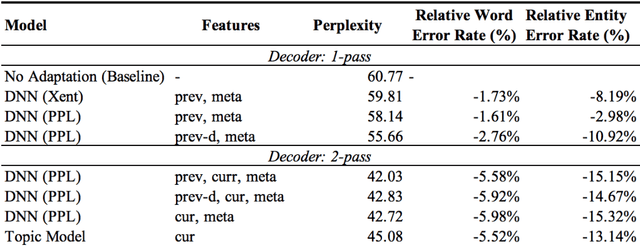
Abstract:Building open domain conversational systems that allow users to have engaging conversations on topics of their choice is a challenging task. Alexa Prize was launched in 2016 to tackle the problem of achieving natural, sustained, coherent and engaging open-domain dialogs. In the second iteration of the competition in 2018, university teams advanced the state of the art by using context in dialog models, leveraging knowledge graphs for language understanding, handling complex utterances, building statistical and hierarchical dialog managers, and leveraging model-driven signals from user responses. The 2018 competition also included the provision of a suite of tools and models to the competitors including the CoBot (conversational bot) toolkit, topic and dialog act detection models, conversation evaluators, and a sensitive content detection model so that the competing teams could focus on building knowledge-rich, coherent and engaging multi-turn dialog systems. This paper outlines the advances developed by the university teams as well as the Alexa Prize team to achieve the common goal of advancing the science of Conversational AI. We address several key open-ended problems such as conversational speech recognition, open domain natural language understanding, commonsense reasoning, statistical dialog management, and dialog evaluation. These collaborative efforts have driven improved experiences by Alexa users to an average rating of 3.61, the median duration of 2 mins 18 seconds, and average turns to 14.6, increases of 14%, 92%, 54% respectively since the launch of the 2018 competition. For conversational speech recognition, we have improved our relative Word Error Rate by 55% and our relative Entity Error Rate by 34% since the launch of the Alexa Prize. Socialbots improved in quality significantly more rapidly in 2018, in part due to the release of the CoBot toolkit.
On Evaluating and Comparing Conversational Agents
Jan 11, 2018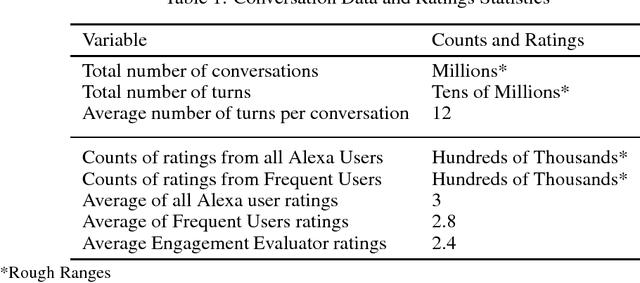
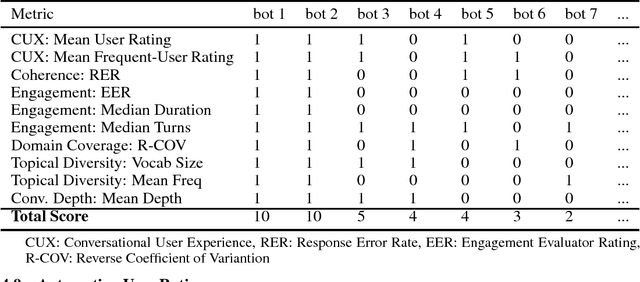
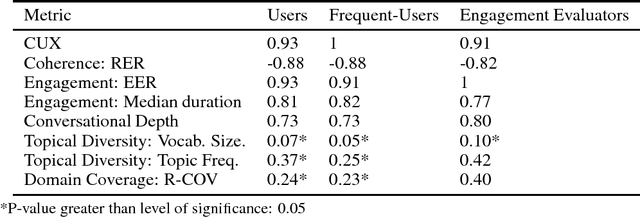

Abstract:Conversational agents are exploding in popularity. However, much work remains in the area of non goal-oriented conversations, despite significant growth in research interest over recent years. To advance the state of the art in conversational AI, Amazon launched the Alexa Prize, a 2.5-million dollar university competition where sixteen selected university teams built conversational agents to deliver the best social conversational experience. Alexa Prize provided the academic community with the unique opportunity to perform research with a live system used by millions of users. The subjectivity associated with evaluating conversations is key element underlying the challenge of building non-goal oriented dialogue systems. In this paper, we propose a comprehensive evaluation strategy with multiple metrics designed to reduce subjectivity by selecting metrics which correlate well with human judgement. The proposed metrics provide granular analysis of the conversational agents, which is not captured in human ratings. We show that these metrics can be used as a reasonable proxy for human judgment. We provide a mechanism to unify the metrics for selecting the top performing agents, which has also been applied throughout the Alexa Prize competition. To our knowledge, to date it is the largest setting for evaluating agents with millions of conversations and hundreds of thousands of ratings from users. We believe that this work is a step towards an automatic evaluation process for conversational AIs.
* 10 pages, 5 tables. NIPS 2017 Conversational AI workshop. http://alborz-geramifard.com/workshops/nips17-Conversational-AI/Main.html
Conversational AI: The Science Behind the Alexa Prize
Jan 11, 2018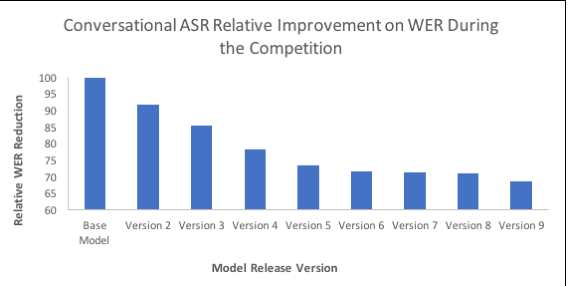
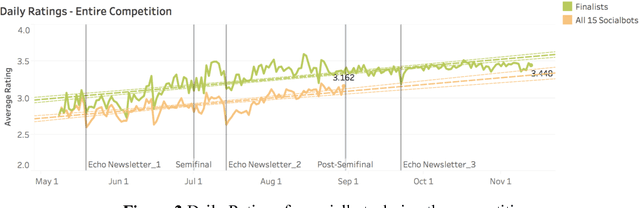
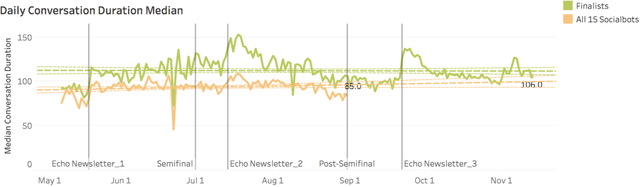
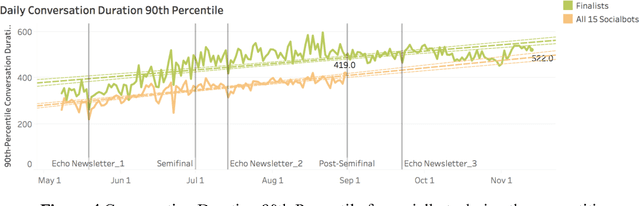
Abstract:Conversational agents are exploding in popularity. However, much work remains in the area of social conversation as well as free-form conversation over a broad range of domains and topics. To advance the state of the art in conversational AI, Amazon launched the Alexa Prize, a 2.5-million-dollar university competition where sixteen selected university teams were challenged to build conversational agents, known as socialbots, to converse coherently and engagingly with humans on popular topics such as Sports, Politics, Entertainment, Fashion and Technology for 20 minutes. The Alexa Prize offers the academic community a unique opportunity to perform research with a live system used by millions of users. The competition provided university teams with real user conversational data at scale, along with the user-provided ratings and feedback augmented with annotations by the Alexa team. This enabled teams to effectively iterate and make improvements throughout the competition while being evaluated in real-time through live user interactions. To build their socialbots, university teams combined state-of-the-art techniques with novel strategies in the areas of Natural Language Understanding, Context Modeling, Dialog Management, Response Generation, and Knowledge Acquisition. To support the efforts of participating teams, the Alexa Prize team made significant scientific and engineering investments to build and improve Conversational Speech Recognition, Topic Tracking, Dialog Evaluation, Voice User Experience, and tools for traffic management and scalability. This paper outlines the advances created by the university teams as well as the Alexa Prize team to achieve the common goal of solving the problem of Conversational AI.
* 18 pages, 5 figures, Alexa Prize Proceedings Paper (https://developer.amazon.com/alexaprize/proceedings), Alexa Prize University Competition to advance Conversational AI
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge