Robert E. Kraut
Examining the Role of Relationship Alignment in Large Language Models
Oct 02, 2024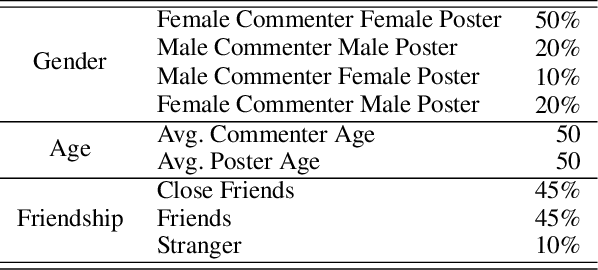
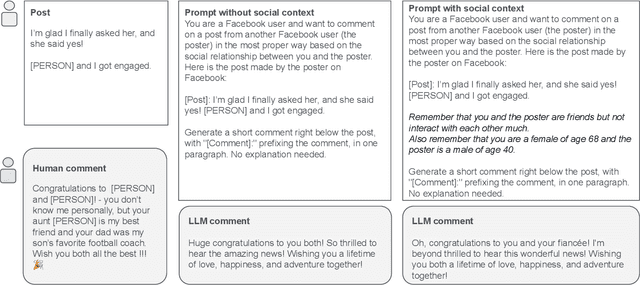
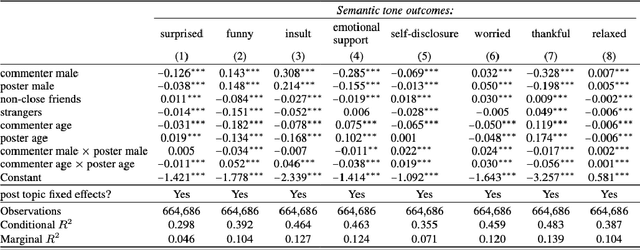
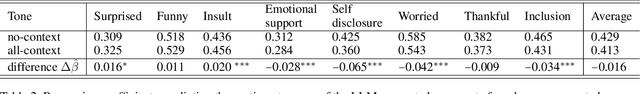
Abstract:The rapid development and deployment of Generative AI in social settings raise important questions about how to optimally personalize them for users while maintaining accuracy and realism. Based on a Facebook public post-comment dataset, this study evaluates the ability of Llama 3.0 (70B) to predict the semantic tones across different combinations of a commenter's and poster's gender, age, and friendship closeness and to replicate these differences in LLM-generated comments. The study consists of two parts: Part I assesses differences in semantic tones across social relationship categories, and Part II examines the similarity between comments generated by Llama 3.0 (70B) and human comments from Part I given public Facebook posts as input. Part I results show that including social relationship information improves the ability of a model to predict the semantic tone of human comments. However, Part II results show that even without including social context information in the prompt, LLM-generated comments and human comments are equally sensitive to social context, suggesting that LLMs can comprehend semantics from the original post alone. When we include all social relationship information in the prompt, the similarity between human comments and LLM-generated comments decreases. This inconsistency may occur because LLMs did not include social context information as part of their training data. Together these results demonstrate the ability of LLMs to comprehend semantics from the original post and respond similarly to human comments, but also highlights their limitations in generalizing personalized comments through prompting alone.
Modeling Motivational Interviewing Strategies On An Online Peer-to-Peer Counseling Platform
Nov 09, 2022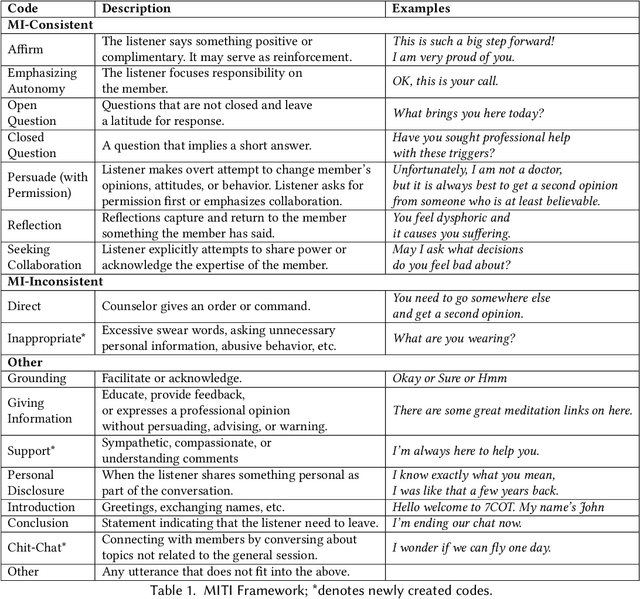



Abstract:Millions of people participate in online peer-to-peer support sessions, yet there has been little prior research on systematic psychology-based evaluations of fine-grained peer-counselor behavior in relation to client satisfaction. This paper seeks to bridge this gap by mapping peer-counselor chat-messages to motivational interviewing (MI) techniques. We annotate 14,797 utterances from 734 chat conversations using 17 MI techniques and introduce four new interviewing codes such as chit-chat and inappropriate to account for the unique conversational patterns observed on online platforms. We automate the process of labeling peer-counselor responses to MI techniques by fine-tuning large domain-specific language models and then use these automated measures to investigate the behavior of the peer counselors via correlational studies. Specifically, we study the impact of MI techniques on the conversation ratings to investigate the techniques that predict clients' satisfaction with their counseling sessions. When counselors use techniques such as reflection and affirmation, clients are more satisfied. Examining volunteer counselors' change in usage of techniques suggest that counselors learn to use more introduction and open questions as they gain experience. This work provides a deeper understanding of the use of motivational interviewing techniques on peer-to-peer counselor platforms and sheds light on how to build better training programs for volunteer counselors on online platforms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge