Robert D. Stevens
The leap to ordinal: functional prognosis after traumatic brain injury using artificial intelligence
Feb 10, 2022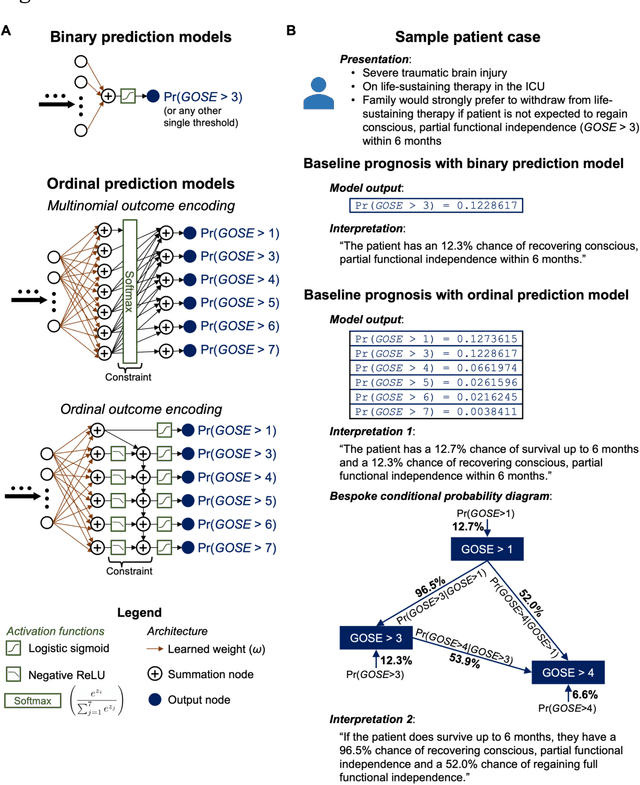
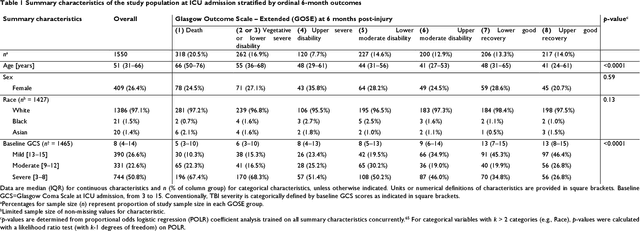
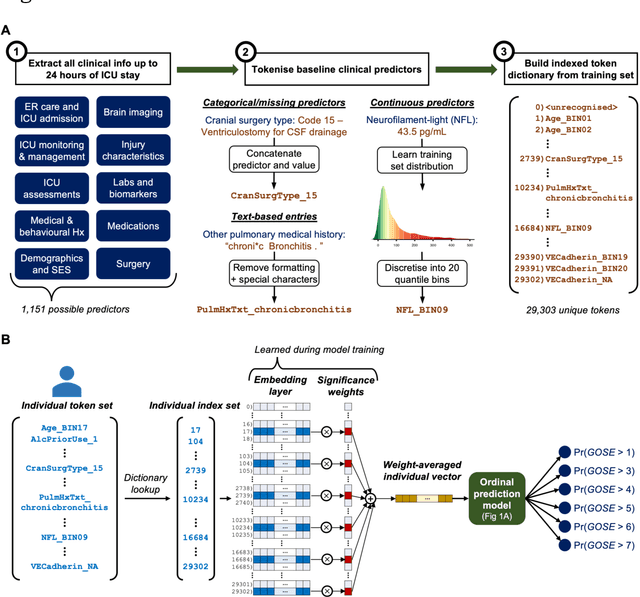
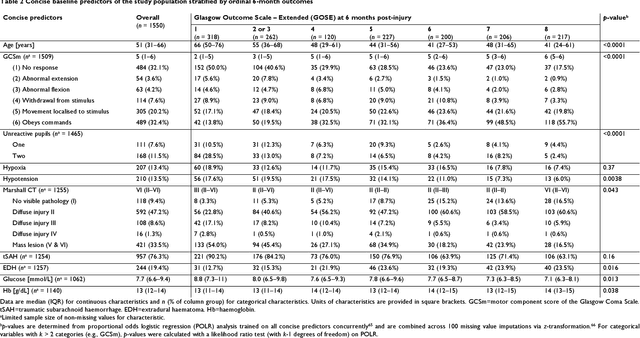
Abstract:When a patient is admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) after a traumatic brain injury (TBI), an early prognosis is essential for baseline risk adjustment and shared decision making. TBI outcomes are commonly categorised by the Glasgow Outcome Scale-Extended (GOSE) into 8, ordered levels of functional recovery at 6 months after injury. Existing ICU prognostic models predict binary outcomes at a certain threshold of GOSE (e.g., prediction of survival [GOSE>1] or functional independence [GOSE>4]). We aimed to develop ordinal prediction models that concurrently predict probabilities of each GOSE score. From a prospective cohort (n=1,550, 65 centres) in the ICU stratum of the Collaborative European NeuroTrauma Effectiveness Research in TBI (CENTER-TBI) patient dataset, we extracted all clinical information within 24 hours of ICU admission (1,151 predictors) and 6-month GOSE scores. We analysed the effect of 2 design elements on ordinal model performance: (1) the baseline predictor set, ranging from a concise set of 10 validated predictors to a token-embedded representation of all possible predictors, and (2) the modelling strategy, from ordinal logistic regression to multinomial deep learning. With repeated k-fold cross-validation, we found that expanding the baseline predictor set significantly improved ordinal prediction performance while increasing analytical complexity did not. Half of these gains could be achieved with the addition of 8 high-impact predictors (2 demographic variables, 4 protein biomarkers, and 2 severity assessments) to the concise set. At best, ordinal models achieved 0.76 (95% CI: 0.74-0.77) ordinal discrimination ability (ordinal c-index) and 57% (95% CI: 54%-60%) explanation of ordinal variation in 6-month GOSE (Somers' D). Our results motivate the search for informative predictors for higher GOSE and the development of ordinal dynamic prediction models.
A Physiology-Driven Computational Model for Post-Cardiac Arrest Outcome Prediction
Feb 11, 2020



Abstract:Patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest (CA) face a high risk of neurological disability and death, however pragmatic methods are lacking for accurate and reliable prognostication. The aim of this study was to build computational models to predict post-CA outcome by leveraging high-dimensional patient data available early after admission to the intensive care unit (ICU). We hypothesized that model performance could be enhanced by integrating physiological time series (PTS) data and by training machine learning (ML) classifiers. We compared three models integrating features extracted from the electronic health records (EHR) alone, features derived from PTS collected in the first 24hrs after ICU admission (PTS24), and models integrating PTS24 and EHR. Outcomes of interest were survival and neurological outcome at ICU discharge. Combined EHR-PTS24 models had higher discrimination (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [AUC]) than models which used either EHR or PTS24 alone, for the prediction of survival (AUC 0.85, 0.80 and 0.68 respectively) and neurological outcome (0.87, 0.83 and 0.78). The best ML classifier achieved higher discrimination than the reference logistic regression model (APACHE III) for survival (AUC 0.85 vs 0.70) and neurological outcome prediction (AUC 0.87 vs 0.75). Feature analysis revealed previously unknown factors to be associated with post-CA recovery. Results attest to the effectiveness of ML models for post-CA predictive modeling and suggest that PTS recorded in very early phase after resuscitation encode short-term outcome probabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge