Rina Kawamura
A Transfer Learning Pipeline for Educational Resource Discovery with Application in Leading Paragraph Generation
Jan 07, 2022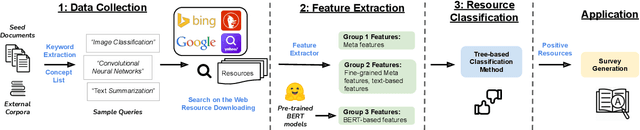
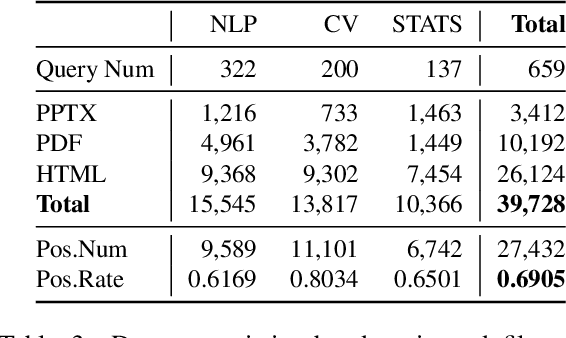

Abstract:Effective human learning depends on a wide selection of educational materials that align with the learner's current understanding of the topic. While the Internet has revolutionized human learning or education, a substantial resource accessibility barrier still exists. Namely, the excess of online information can make it challenging to navigate and discover high-quality learning materials. In this paper, we propose the educational resource discovery (ERD) pipeline that automates web resource discovery for novel domains. The pipeline consists of three main steps: data collection, feature extraction, and resource classification. We start with a known source domain and conduct resource discovery on two unseen target domains via transfer learning. We first collect frequent queries from a set of seed documents and search on the web to obtain candidate resources, such as lecture slides and introductory blog posts. Then we introduce a novel pretrained information retrieval deep neural network model, query-document masked language modeling (QD-MLM), to extract deep features of these candidate resources. We apply a tree-based classifier to decide whether the candidate is a positive learning resource. The pipeline achieves F1 scores of 0.94 and 0.82 when evaluated on two similar but novel target domains. Finally, we demonstrate how this pipeline can benefit an application: leading paragraph generation for surveys. This is the first study that considers various web resources for survey generation, to the best of our knowledge. We also release a corpus of 39,728 manually labeled web resources and 659 queries from NLP, Computer Vision (CV), and Statistics (STATS).
Surfer100: Generating Surveys From Web Resources on Wikipedia-style
Dec 13, 2021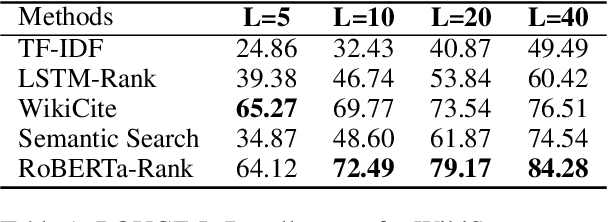
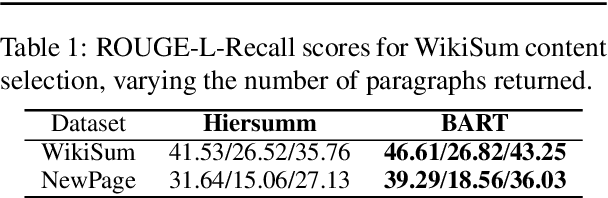
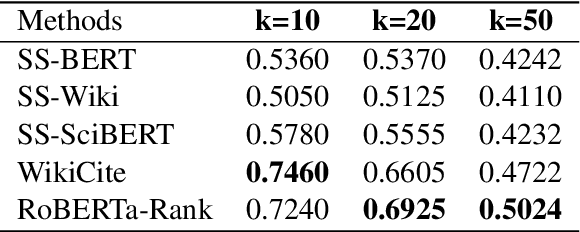
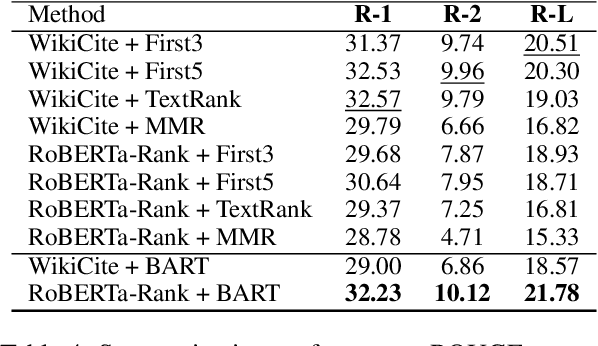
Abstract:Fast-developing fields such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) often outpace the efforts of encyclopedic sources such as Wikipedia, which either do not completely cover recently-introduced topics or lack such content entirely. As a result, methods for automatically producing content are valuable tools to address this information overload. We show that recent advances in pretrained language modeling can be combined for a two-stage extractive and abstractive approach for Wikipedia lead paragraph generation. We extend this approach to generate longer Wikipedia-style summaries with sections and examine how such methods struggle in this application through detailed studies with 100 reference human-collected surveys. This is the first study on utilizing web resources for long Wikipedia-style summaries to the best of our knowledge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge