Richard G. Spencer
Input layer regularization and automated regularization hyperparameter tuning for myelin water estimation using deep learning
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel deep learning method which combines classical regularization with data augmentation for estimating myelin water fraction (MWF) in the brain via biexponential analysis. Our aim is to design an accurate deep learning technique for analysis of signals arising in magnetic resonance relaxometry. In particular, we study the biexponential model, one of the signal models used for MWF estimation. We greatly extend our previous work on \emph{input layer regularization (ILR)} in several ways. We now incorporate optimal regularization parameter selection via a dedicated neural network or generalized cross validation (GCV) on a signal-by-signal, or pixel-by-pixel, basis to form the augmented input signal, and now incorporate estimation of MWF, rather than just exponential time constants, into the analysis. On synthetically generated data, our proposed deep learning architecture outperformed both classical methods and a conventional multi-layer perceptron. On in vivo brain data, our architecture again outperformed other comparison methods, with GCV proving to be somewhat superior to a NN for regularization parameter selection. Thus, ILR improves estimation of MWF within the biexponential model. In addition, classical methods such as GCV may be combined with deep learning to optimize MWF imaging in the human brain.
Hyperspectral Reconstruction of Skin Through Fusion of Scattering Transform Features
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Hyperspectral imagery (HSI) is an established technique with an array of applications, but its use is limited due to both practical and technical issues associated with spectral devices. The goal of the ICASSP 2024 'Hyper-Skin' Challenge is to extract skin HSI from matching RGB images and an infrared band. To address this problem we propose a model using features of the scattering transform - a type of convolutional neural network with predefined filters. Our model matches and inverts those features, rather than the pixel values, reducing the complexity of matching while grouping similar features together, resulting in an improved learning process.
Emergence of the SVD as an interpretable factorization in deep learning for inverse problems
Jan 18, 2023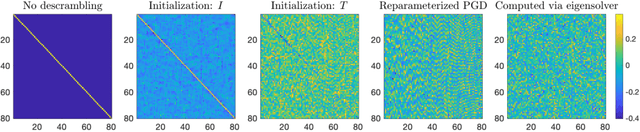

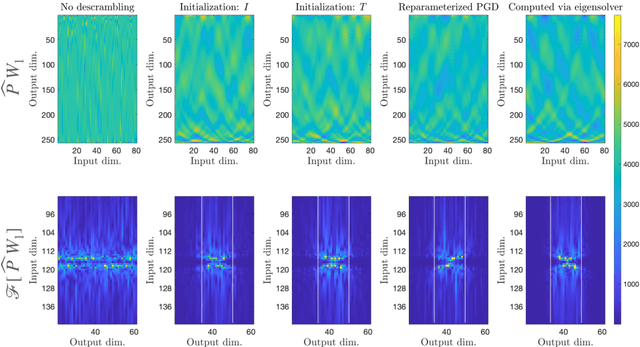
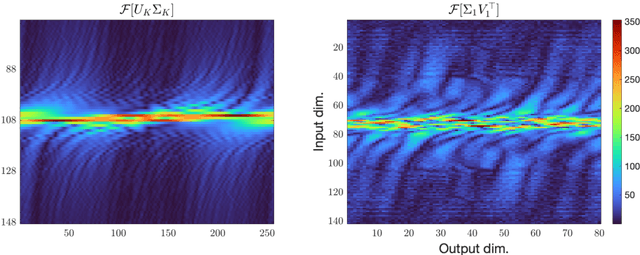
Abstract:We demonstrate the emergence of weight matrix singular value decomposition (SVD) in interpreting neural networks (NNs) for parameter estimation from noisy signals. The SVD appears naturally as a consequence of initial application of a descrambling transform - a recently-developed technique for addressing interpretability in NNs \cite{amey2021neural}. We find that within the class of noisy parameter estimation problems, the SVD may be the means by which networks memorize the signal model. We substantiate our theoretical findings with empirical evidence from both linear and non-linear settings. Our results also illuminate the connections between a mathematical theory of semantic development \cite{saxe2019mathematical} and neural network interpretability.
A Novel Extension to Fuzzy Connectivity for Body Composition Analysis: Applications in Thigh, Brain, and Whole Body Tissue Segmentation
Oct 14, 2018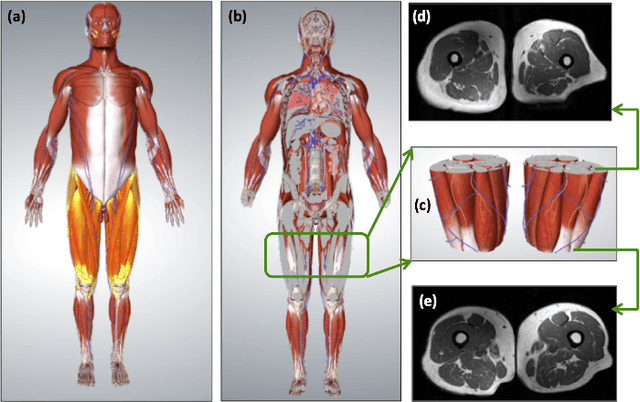
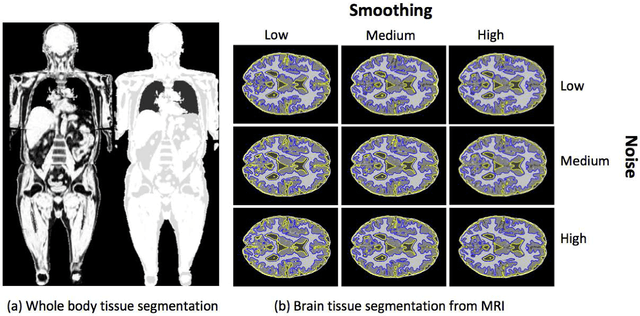
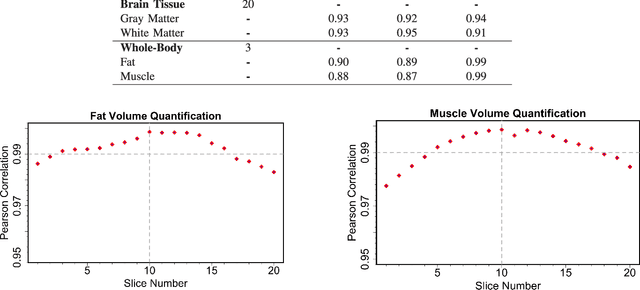
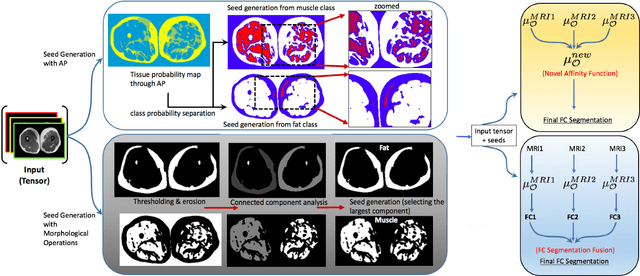
Abstract:Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the non-invasive modality of choice for body tissue composition analysis due to its excellent soft tissue contrast and lack of ionizing radiation. However, quantification of body composition requires an accurate segmentation of fat, muscle and other tissues from MR images, which remains a challenging goal due to the intensity overlap between them. In this study, we propose a fully automated, data-driven image segmentation platform that addresses multiple difficulties in segmenting MR images such as varying inhomogeneity, non-standardness, and noise, while producing high-quality definition of different tissues. In contrast to most approaches in the literature, we perform segmentation operation by combining three different MRI contrasts and a novel segmentation tool which takes into account variability in the data. The proposed system, based on a novel affinity definition within the fuzzy connectivity (FC) image segmentation family, prevents the need for user intervention and reparametrization of the segmentation algorithms. In order to make the whole system fully automated, we adapt an affinity propagation clustering algorithm to roughly identify tissue regions and image background. We perform a thorough evaluation of the proposed algorithm's individual steps as well as comparison with several approaches from the literature for the main application of muscle/fat separation. Furthermore, whole-body tissue composition and brain tissue delineation were conducted to show the generalization ability of the proposed system. This new automated platform outperforms other state-of-the-art segmentation approaches both in accuracy and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge