Rayen Dhahri
Quant-Trim in Practice: Improved Cross-Platform Low-Bit Deployment on Edge NPUs
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Specialized edge accelerators rely on low-bit quantization, but vendor compilers differ in scaling, clipping, and kernel support, often as black boxes. The same floating-point (FP) checkpoint can therefore yield inconsistent accuracy across backends, forcing practitioners to tweak flags or refactor models to vendor-friendly operator subsets. We introduce Quant-Trim, a training-phase method that produces a hardware-neutral checkpoint robust to backend and precision choices. It combines progressive fake quantization to align training with the deployed integer grid and reverse pruning to tame outlier-driven scale inflation while preserving learnability. Quant-Trim is agnostic to quantization schemes (symmetric/asymmetric,per-tensor/per-channel, INT8/INT4) and requires no vendor-specific graph changes.Across models and tasks, it narrows the FP,low-bit gap, reduces dependence on compiler heuristics/calibration, and avoids per-backend retraining. We report accuracy and edge metrics latency, throughput, energy/inference, and cost under static/dynamic activation scaling and varying operator coverage.
Shaving Weights with Occam's Razor: Bayesian Sparsification for Neural Networks Using the Marginal Likelihood
Feb 25, 2024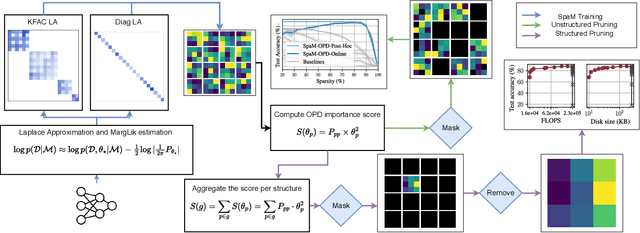
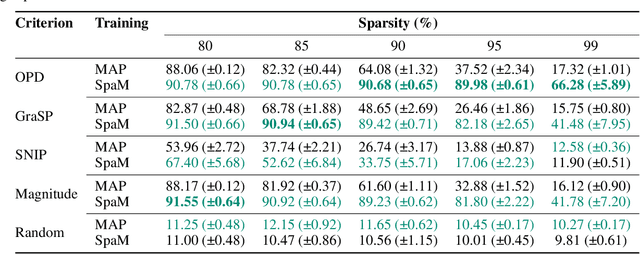
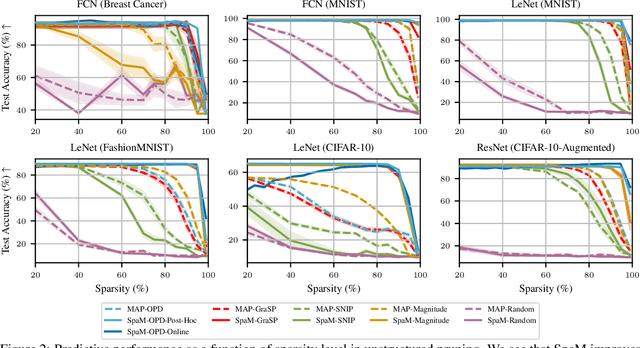
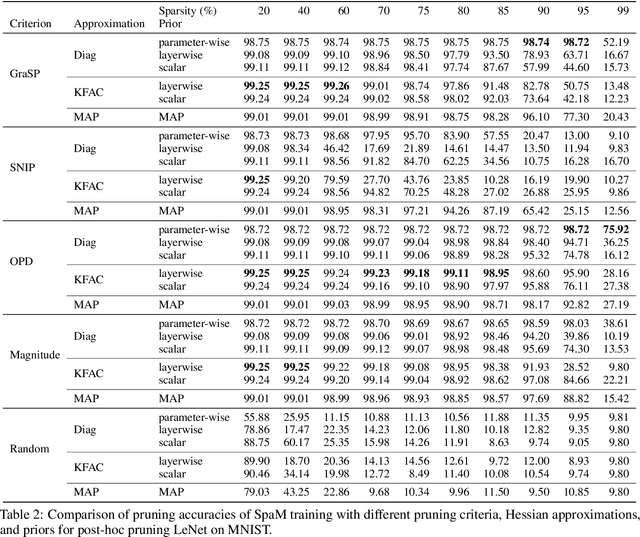
Abstract:Neural network sparsification is a promising avenue to save computational time and memory costs, especially in an age where many successful AI models are becoming too large to na\"ively deploy on consumer hardware. While much work has focused on different weight pruning criteria, the overall sparsifiability of the network, i.e., its capacity to be pruned without quality loss, has often been overlooked. We present Sparsifiability via the Marginal likelihood (SpaM), a pruning framework that highlights the effectiveness of using the Bayesian marginal likelihood in conjunction with sparsity-inducing priors for making neural networks more sparsifiable. Our approach implements an automatic Occam's razor that selects the most sparsifiable model that still explains the data well, both for structured and unstructured sparsification. In addition, we demonstrate that the pre-computed posterior Hessian approximation used in the Laplace approximation can be re-used to define a cheap pruning criterion, which outperforms many existing (more expensive) approaches. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework, especially at high sparsity levels, across a range of different neural network architectures and datasets.
From Judgement's Premises Towards Key Points
Dec 23, 2022Abstract:Key Point Analysis(KPA) is a relatively new task in NLP that combines summarization and classification by extracting argumentative key points (KPs) for a topic from a collection of texts and categorizing their closeness to the different arguments. In our work, we focus on the legal domain and develop methods that identify and extract KPs from premises derived from texts of judgments. The first method is an adaptation to an existing state-of-the-art method, and the two others are new methods that we developed from scratch. We present our methods and examples of their outputs, as well a comparison between them. The full evaluation of our results is done in the matching task -- match between the generated KPs to arguments (premises).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge