Ran Pang
Enhancing AI Diagnostics: Autonomous Lesion Masking via Semi-Supervised Deep Learning
Apr 18, 2024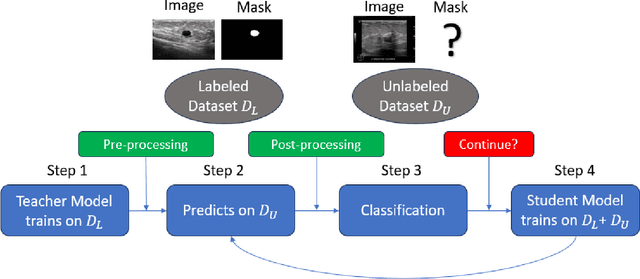
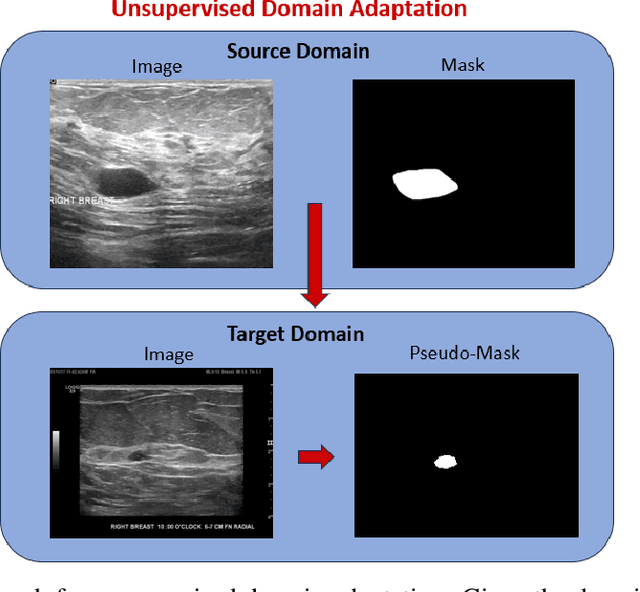

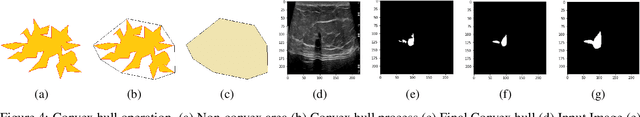
Abstract:This study presents an unsupervised domain adaptation method aimed at autonomously generating image masks outlining regions of interest (ROIs) for differentiating breast lesions in breast ultrasound (US) imaging. Our semi-supervised learning approach utilizes a primitive model trained on a small public breast US dataset with true annotations. This model is then iteratively refined for the domain adaptation task, generating pseudo-masks for our private, unannotated breast US dataset. The dataset, twice the size of the public one, exhibits considerable variability in image acquisition perspectives and demographic representation, posing a domain-shift challenge. Unlike typical domain adversarial training, we employ downstream classification outcomes as a benchmark to guide the updating of pseudo-masks in subsequent iterations. We found the classification precision to be highly correlated with the completeness of the generated ROIs, which promotes the explainability of the deep learning classification model. Preliminary findings demonstrate the efficacy and reliability of this approach in streamlining the ROI annotation process, thereby enhancing the classification and localization of breast lesions for more precise and interpretable diagnoses.
Image Based Appraisal of Real Estate Properties
Jul 27, 2017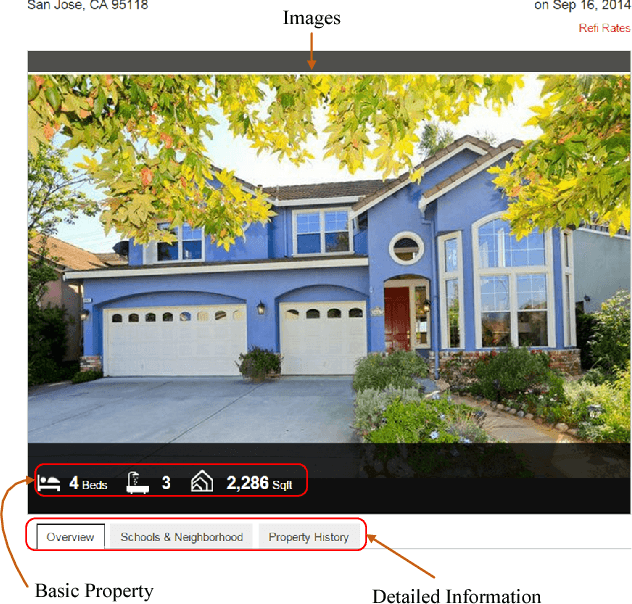
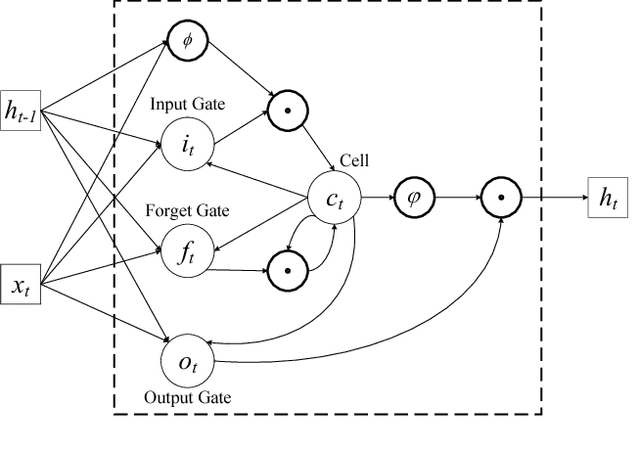
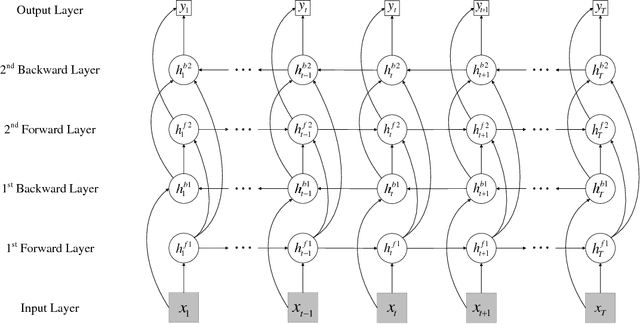
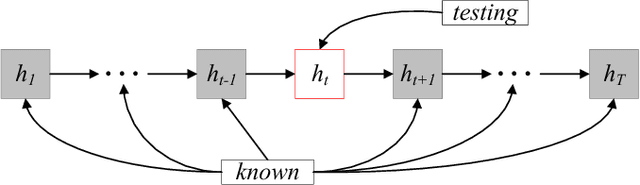
Abstract:Real estate appraisal, which is the process of estimating the price for real estate properties, is crucial for both buys and sellers as the basis for negotiation and transaction. Traditionally, the repeat sales model has been widely adopted to estimate real estate price. However, it depends the design and calculation of a complex economic related index, which is challenging to estimate accurately. Today, real estate brokers provide easy access to detailed online information on real estate properties to their clients. We are interested in estimating the real estate price from these large amounts of easily accessed data. In particular, we analyze the prediction power of online house pictures, which is one of the key factors for online users to make a potential visiting decision. The development of robust computer vision algorithms makes the analysis of visual content possible. In this work, we employ a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) to predict real estate price using the state-of-the-art visual features. The experimental results indicate that our model outperforms several of other state-of-the-art baseline algorithms in terms of both mean absolute error (MAE) and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge