Enhancing AI Diagnostics: Autonomous Lesion Masking via Semi-Supervised Deep Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 18, 2024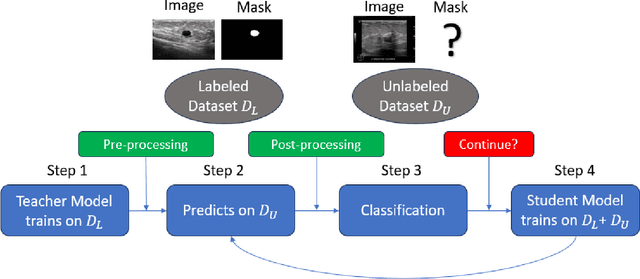
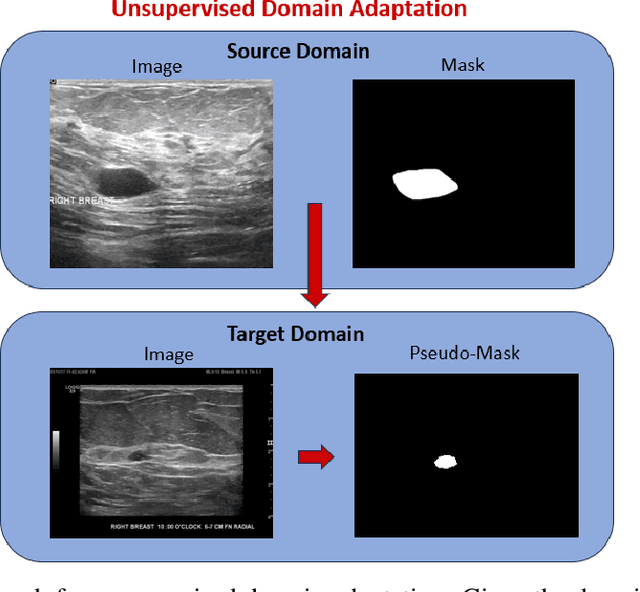

This study presents an unsupervised domain adaptation method aimed at autonomously generating image masks outlining regions of interest (ROIs) for differentiating breast lesions in breast ultrasound (US) imaging. Our semi-supervised learning approach utilizes a primitive model trained on a small public breast US dataset with true annotations. This model is then iteratively refined for the domain adaptation task, generating pseudo-masks for our private, unannotated breast US dataset. The dataset, twice the size of the public one, exhibits considerable variability in image acquisition perspectives and demographic representation, posing a domain-shift challenge. Unlike typical domain adversarial training, we employ downstream classification outcomes as a benchmark to guide the updating of pseudo-masks in subsequent iterations. We found the classification precision to be highly correlated with the completeness of the generated ROIs, which promotes the explainability of the deep learning classification model. Preliminary findings demonstrate the efficacy and reliability of this approach in streamlining the ROI annotation process, thereby enhancing the classification and localization of breast lesions for more precise and interpretable diagnoses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge