Ramanathan Sethuraman
Exploiting Richness of Learned Compressed Representation of Images for Semantic Segmentation
Jul 04, 2023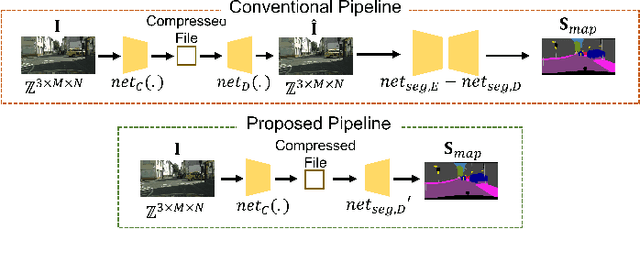
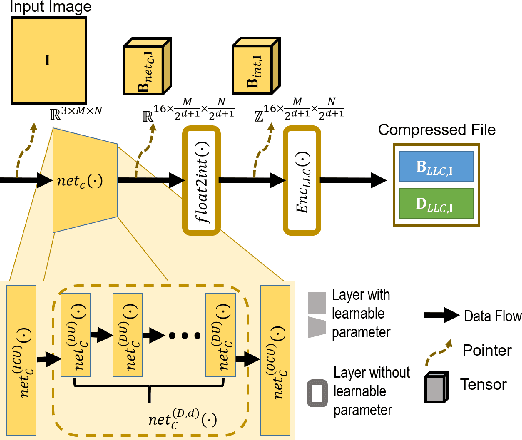
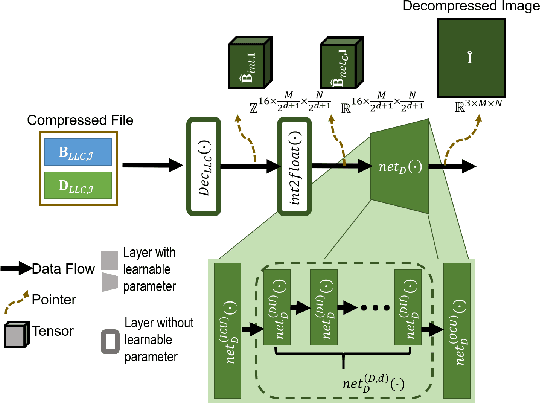
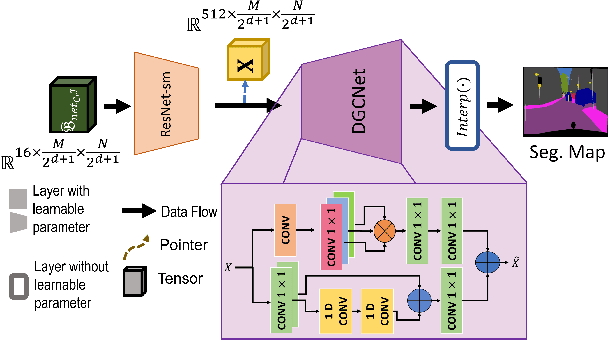
Abstract:Autonomous vehicles and Advanced Driving Assistance Systems (ADAS) have the potential to radically change the way we travel. Many such vehicles currently rely on segmentation and object detection algorithms to detect and track objects around its surrounding. The data collected from the vehicles are often sent to cloud servers to facilitate continual/life-long learning of these algorithms. Considering the bandwidth constraints, the data is compressed before sending it to servers, where it is typically decompressed for training and analysis. In this work, we propose the use of a learning-based compression Codec to reduce the overhead in latency incurred for the decompression operation in the standard pipeline. We demonstrate that the learned compressed representation can also be used to perform tasks like semantic segmentation in addition to decompression to obtain the images. We experimentally validate the proposed pipeline on the Cityscapes dataset, where we achieve a compression factor up to $66 \times$ while preserving the information required to perform segmentation with a dice coefficient of $0.84$ as compared to $0.88$ achieved using decompressed images while reducing the overall compute by $11\%$.
Lung Segmentation and Nodule Detection in Computed Tomography Scan using a Convolutional Neural Network Trained Adversarially using Turing Test Loss
Jun 16, 2020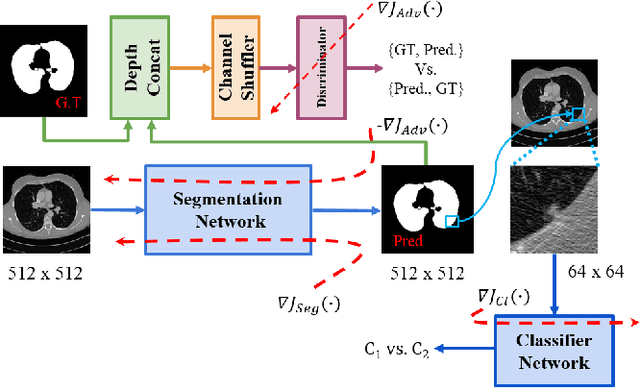
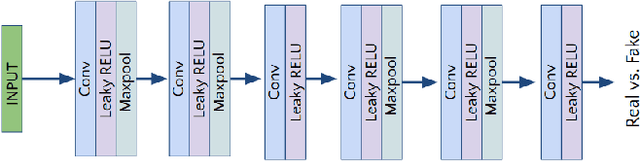
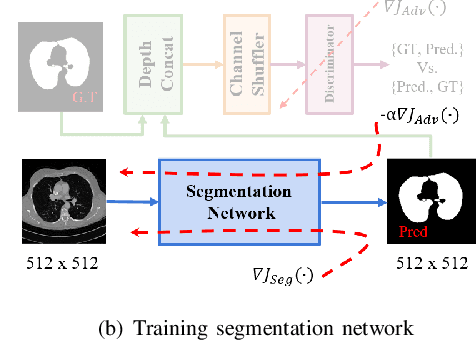
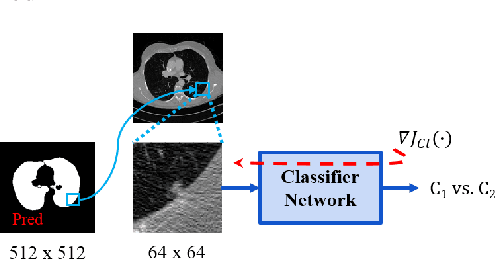
Abstract:Lung cancer is the most common form of cancer found worldwide with a high mortality rate. Early detection of pulmonary nodules by screening with a low-dose computed tomography (CT) scan is crucial for its effective clinical management. Nodules which are symptomatic of malignancy occupy about 0.0125 - 0.025\% of volume in a CT scan of a patient. Manual screening of all slices is a tedious task and presents a high risk of human errors. To tackle this problem we propose a computationally efficient two stage framework. In the first stage, a convolutional neural network (CNN) trained adversarially using Turing test loss segments the lung region. In the second stage, patches sampled from the segmented region are then classified to detect the presence of nodules. The proposed method is experimentally validated on the LUNA16 challenge dataset with a dice coefficient of $0.984\pm0.0007$ for 10-fold cross-validation.
A Two-Stage Multiple Instance Learning Framework for the Detection of Breast Cancer in Mammograms
Apr 24, 2020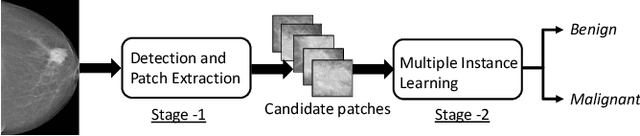
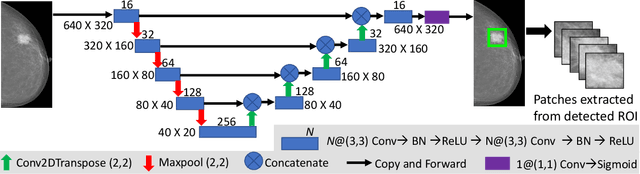
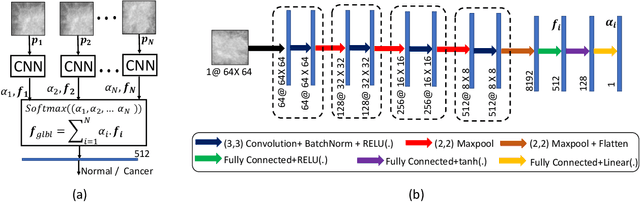
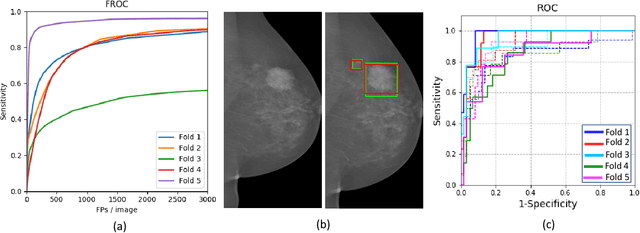
Abstract:Mammograms are commonly employed in the large scale screening of breast cancer which is primarily characterized by the presence of malignant masses. However, automated image-level detection of malignancy is a challenging task given the small size of the mass regions and difficulty in discriminating between malignant, benign mass and healthy dense fibro-glandular tissue. To address these issues, we explore a two-stage Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) framework. A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is trained in the first stage to extract local candidate patches in the mammograms that may contain either a benign or malignant mass. The second stage employs a MIL strategy for an image level benign vs. malignant classification. A global image-level feature is computed as a weighted average of patch-level features learned using a CNN. Our method performed well on the task of localization of masses with an average Precision/Recall of 0.76/0.80 and acheived an average AUC of 0.91 on the imagelevel classification task using a five-fold cross-validation on the INbreast dataset. Restricting the MIL only to the candidate patches extracted in Stage 1 led to a significant improvement in classification performance in comparison to a dense extraction of patches from the entire mammogram.
Learning Decision Ensemble using a Graph Neural Network for Comorbidity Aware Chest Radiograph Screening
Apr 24, 2020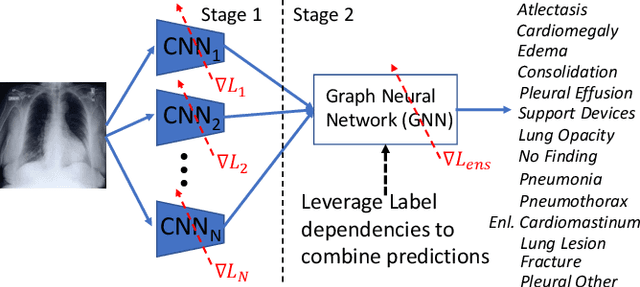
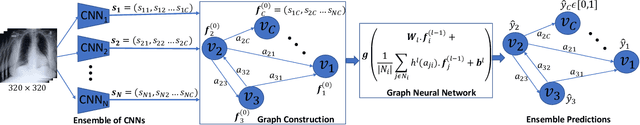
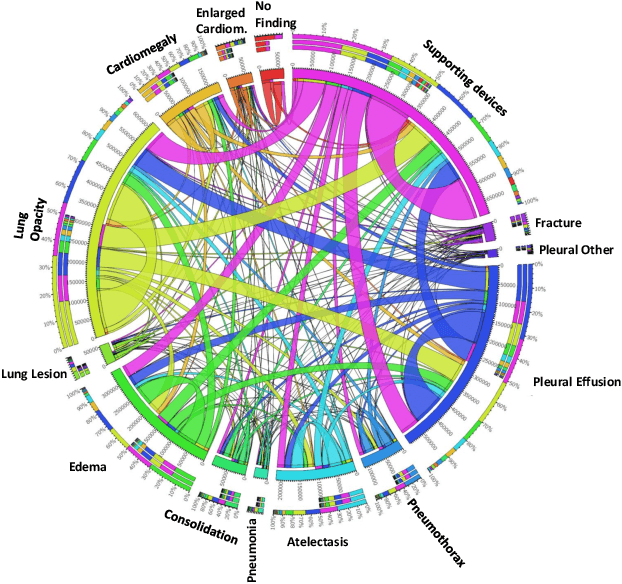
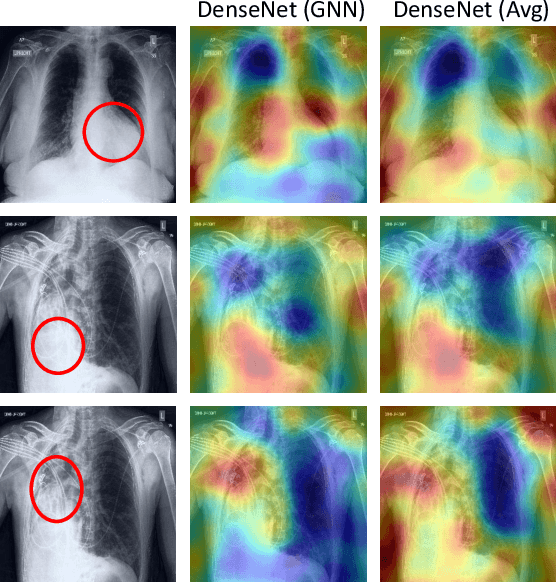
Abstract:Chest radiographs are primarily employed for the screening of cardio, thoracic and pulmonary conditions. Machine learning based automated solutions are being developed to reduce the burden of routine screening on Radiologists, allowing them to focus on critical cases. While recent efforts demonstrate the use of ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks(CNN), they do not take disease comorbidity into consideration, thus lowering their screening performance. To address this issue, we propose a Graph Neural Network (GNN) based solution to obtain ensemble predictions which models the dependencies between different diseases. A comprehensive evaluation of the proposed method demonstrated its potential by improving the performance over standard ensembling technique across a wide range of ensemble constructions. The best performance was achieved using the GNN ensemble of DenseNet121 with an average AUC of 0.821 across thirteen disease comorbidities.
A Systematic Search over Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architectures for Screening Chest Radiographs
Apr 24, 2020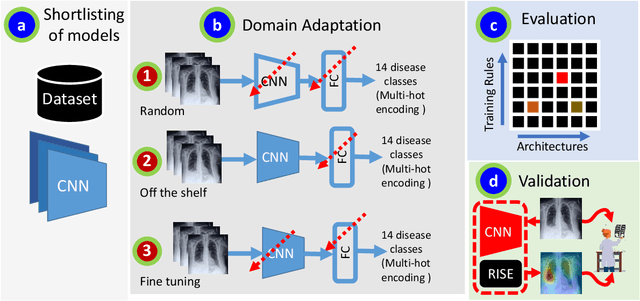
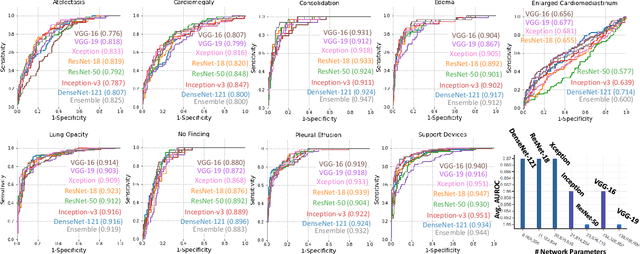
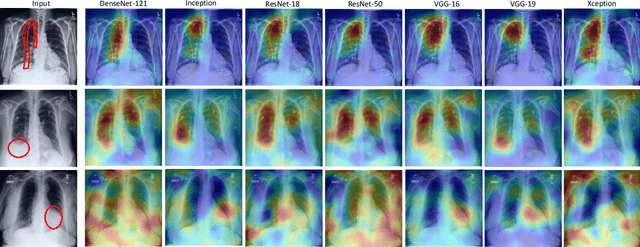
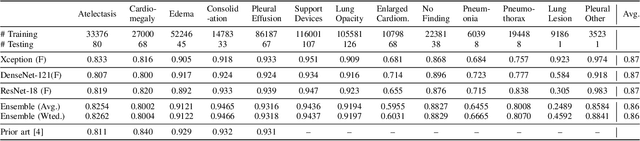
Abstract:Chest radiographs are primarily employed for the screening of pulmonary and cardio-/thoracic conditions. Being undertaken at primary healthcare centers, they require the presence of an on-premise reporting Radiologist, which is a challenge in low and middle income countries. This has inspired the development of machine learning based automation of the screening process. While recent efforts demonstrate a performance benchmark using an ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks (CNN), our systematic search over multiple standard CNN architectures identified single candidate CNN models whose classification performances were found to be at par with ensembles. Over 63 experiments spanning 400 hours, executed on a 11:3 FP32 TensorTFLOPS compute system, we found the Xception and ResNet-18 architectures to be consistent performers in identifying co-existing disease conditions with an average AUC of 0.87 across nine pathologies. We conclude on the reliability of the models by assessing their saliency maps generated using the randomized input sampling for explanation (RISE) method and qualitatively validating them against manual annotations locally sourced from an experienced Radiologist. We also draw a critical note on the limitations of the publicly available CheXpert dataset primarily on account of disparity in class distribution in training vs. testing sets, and unavailability of sufficient samples for few classes, which hampers quantitative reporting due to sample insufficiency.
Fully Convolutional Model for Variable Bit Length and Lossy High Density Compression of Mammograms
May 17, 2018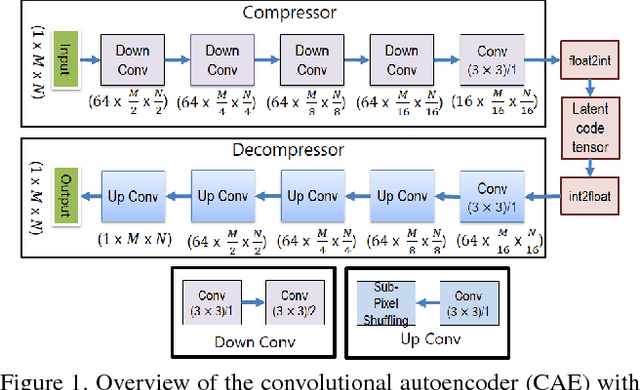
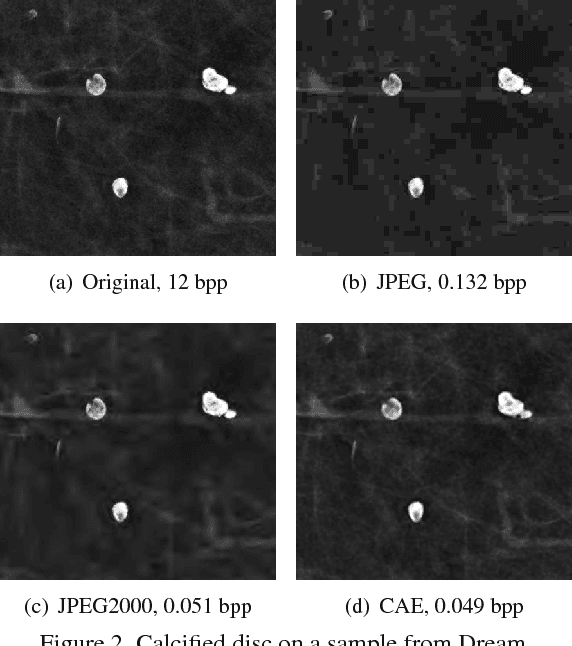
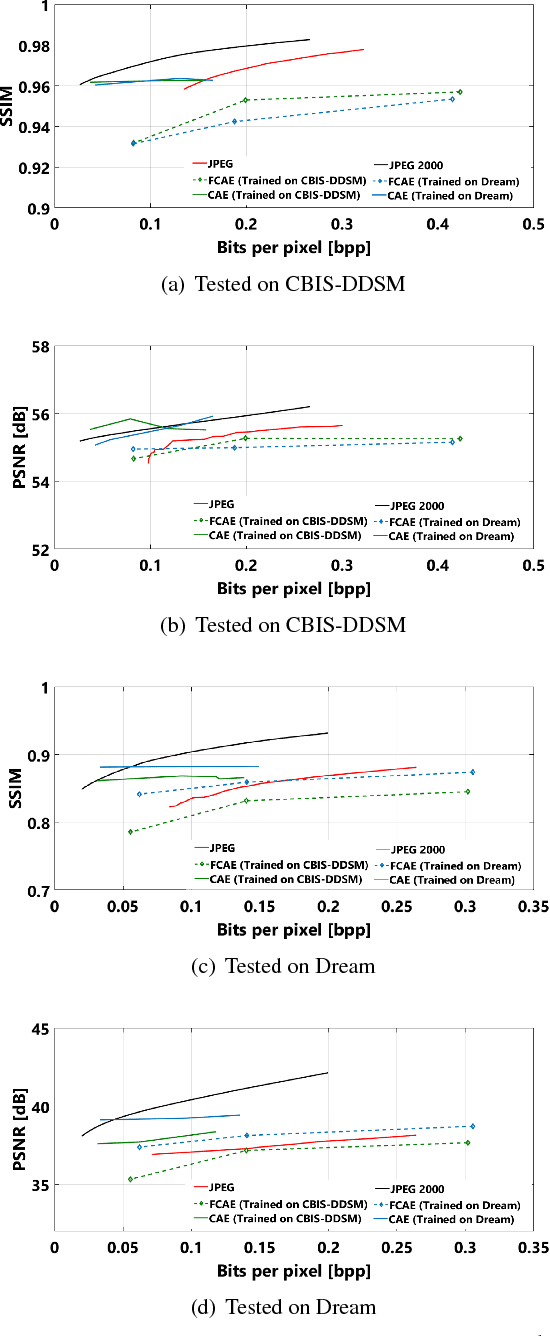
Abstract:Early works on medical image compression date to the 1980's with the impetus on deployment of teleradiology systems for high-resolution digital X-ray detectors. Commercially deployed systems during the period could compress 4,096 x 4,096 sized images at 12 bpp to 2 bpp using lossless arithmetic coding, and over the years JPEG and JPEG2000 were imbibed reaching upto 0.1 bpp. Inspired by the reprise of deep learning based compression for natural images over the last two years, we propose a fully convolutional autoencoder for diagnostically relevant feature preserving lossy compression. This is followed by leveraging arithmetic coding for encapsulating high redundancy of features for further high-density code packing leading to variable bit length. We demonstrate performance on two different publicly available digital mammography datasets using peak signal-to-noise ratio (pSNR), structural similarity (SSIM) index and domain adaptability tests between datasets. At high density compression factors of >300x (~0.04 bpp), our approach rivals JPEG and JPEG2000 as evaluated through a Radiologist's visual Turing test.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge