Arka Mitra
Causality Detection using Multiple Annotation Decision
Oct 26, 2022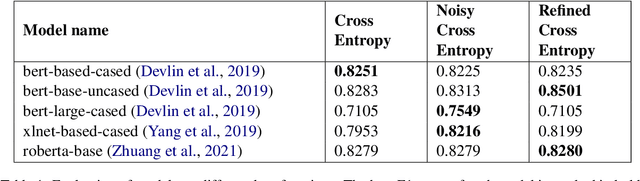
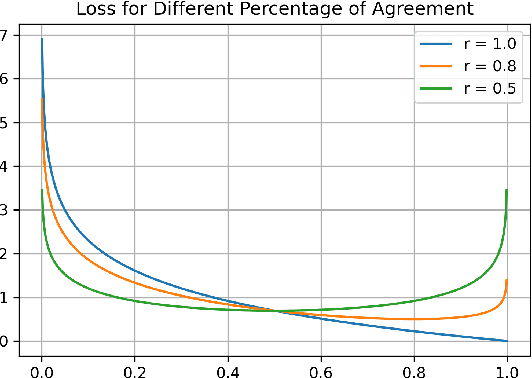
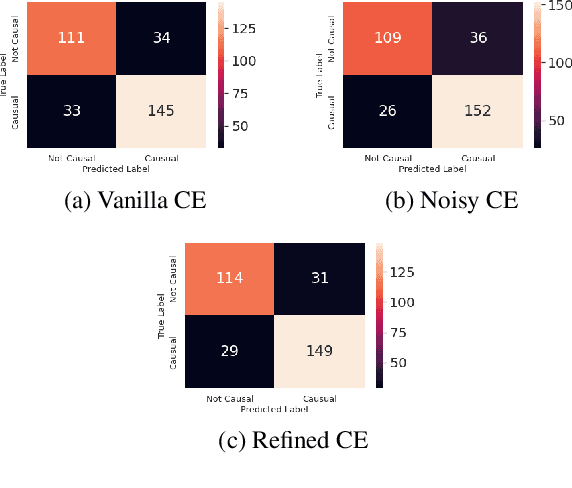
Abstract:The paper describes the work that has been submitted to the 5th workshop on Challenges and Applications of Automated Extraction of socio-political events from text (CASE 2022). The work is associated with Subtask 1 of Shared Task 3 that aims to detect causality in protest news corpus. The authors used different large language models with customized cross-entropy loss functions that exploit annotation information. The experiments showed that bert-based-uncased with refined cross-entropy outperformed the others, achieving a F1 score of 0.8501 on the Causal News Corpus dataset.
Classification on Sentence Embeddings for Legal Assistance
Feb 05, 2022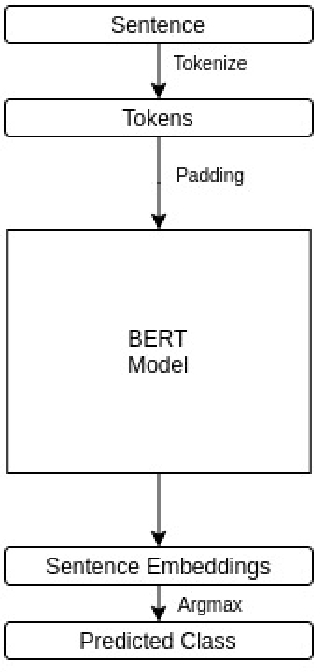
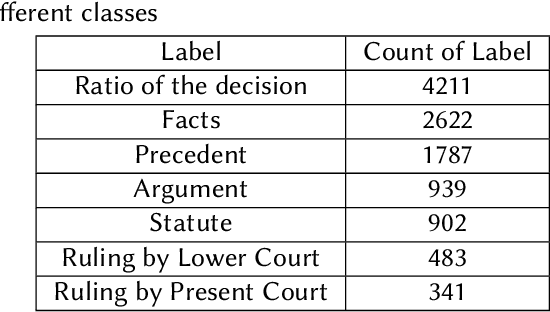
Abstract:Legal proceedings take plenty of time and also cost a lot. The lawyers have to do a lot of work in order to identify the different sections of prior cases and statutes. The paper tries to solve the first tasks in AILA2021 (Artificial Intelligence for Legal Assistance) that will be held in FIRE2021 (Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation). The task is to semantically segment the document into different assigned one of the 7 predefined labels or "rhetorical roles." The paper uses BERT to obtain the sentence embeddings from a sentence, and then a linear classifier is used to output the final prediction. The experiments show that when more weightage is assigned to the class with the highest frequency, the results are better than those when more weightage is given to the class with a lower frequency. In task 1, the team legalNLP obtained a F1 score of 0.22.
Multilingual Hate Speech and Offensive Content Detection using Modified Cross-entropy Loss
Feb 05, 2022


Abstract:The number of increased social media users has led to a lot of people misusing these platforms to spread offensive content and use hate speech. Manual tracking the vast amount of posts is impractical so it is necessary to devise automated methods to identify them quickly. Large language models are trained on a lot of data and they also make use of contextual embeddings. We fine-tune the large language models to help in our task. The data is also quite unbalanced; so we used a modified cross-entropy loss to tackle the issue. We observed that using a model which is fine-tuned in hindi corpora performs better. Our team (HNLP) achieved the macro F1-scores of 0.808, 0.639 in English Subtask A and English Subtask B respectively. For Hindi Subtask A, Hindi Subtask B our team achieved macro F1-scores of 0.737, 0.443 respectively in HASOC 2021.
IIT_kgp at FinCausal 2020, Shared Task 1: Causality Detection using Sentence Embeddings in Financial Reports
Nov 16, 2020

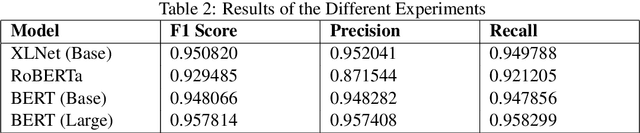
Abstract:The paper describes the work that the team submitted to FinCausal 2020 Shared Task. This work is associated with the first sub-task of identifying causality in sentences. The various models used in the experiments tried to obtain a latent space representation for each of the sentences. Linear regression was performed on these representations to classify whether the sentence is causal or not. The experiments have shown BERT (Large) performed the best, giving a F1 score of 0.958, in the task of detecting the causality of sentences in financial texts and reports. The class imbalance was dealt with a modified loss function to give a better metric score for the evaluation.
A Systematic Search over Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architectures for Screening Chest Radiographs
Apr 24, 2020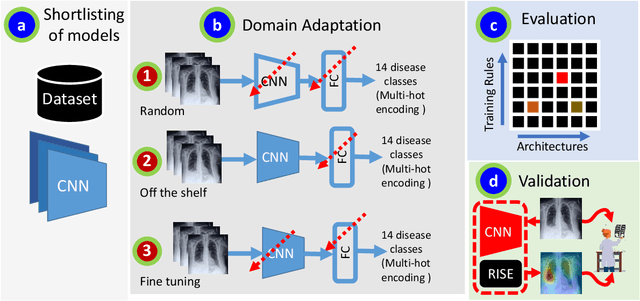
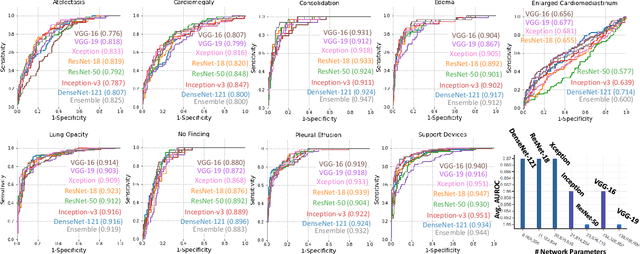
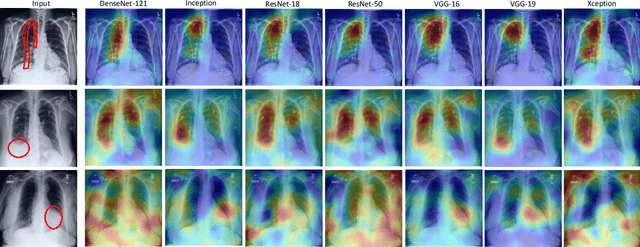
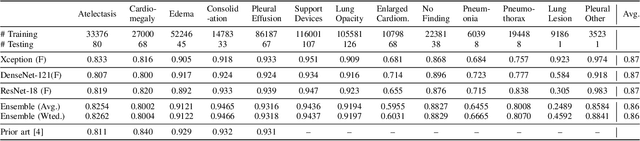
Abstract:Chest radiographs are primarily employed for the screening of pulmonary and cardio-/thoracic conditions. Being undertaken at primary healthcare centers, they require the presence of an on-premise reporting Radiologist, which is a challenge in low and middle income countries. This has inspired the development of machine learning based automation of the screening process. While recent efforts demonstrate a performance benchmark using an ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks (CNN), our systematic search over multiple standard CNN architectures identified single candidate CNN models whose classification performances were found to be at par with ensembles. Over 63 experiments spanning 400 hours, executed on a 11:3 FP32 TensorTFLOPS compute system, we found the Xception and ResNet-18 architectures to be consistent performers in identifying co-existing disease conditions with an average AUC of 0.87 across nine pathologies. We conclude on the reliability of the models by assessing their saliency maps generated using the randomized input sampling for explanation (RISE) method and qualitatively validating them against manual annotations locally sourced from an experienced Radiologist. We also draw a critical note on the limitations of the publicly available CheXpert dataset primarily on account of disparity in class distribution in training vs. testing sets, and unavailability of sufficient samples for few classes, which hampers quantitative reporting due to sample insufficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge