Rūta Binkytė-Sadauskienė
Causal Discovery for Fairness
Jun 14, 2022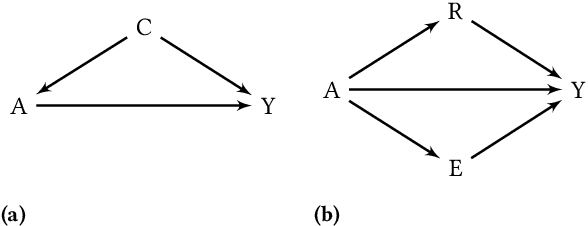
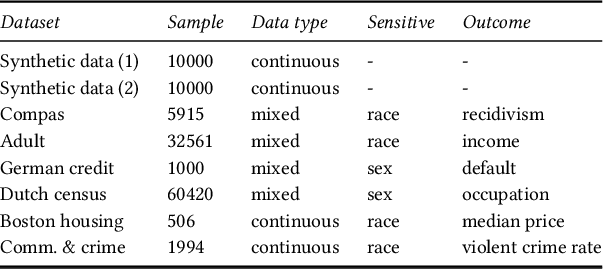
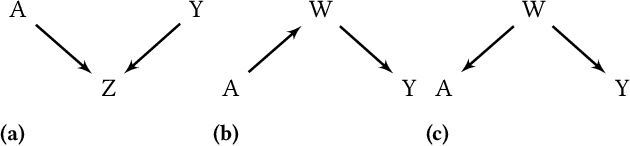
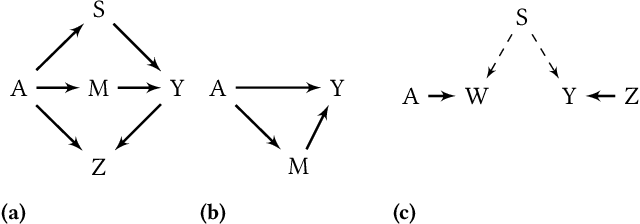
Abstract:It is crucial to consider the social and ethical consequences of AI and ML based decisions for the safe and acceptable use of these emerging technologies. Fairness, in particular, guarantees that the ML decisions do not result in discrimination against individuals or minorities. Identifying and measuring reliably fairness/discrimination is better achieved using causality which considers the causal relation, beyond mere association, between the sensitive attribute (e.g. gender, race, religion, etc.) and the decision (e.g. job hiring, loan granting, etc.). The big impediment to the use of causality to address fairness, however, is the unavailability of the causal model (typically represented as a causal graph). Existing causal approaches to fairness in the literature do not address this problem and assume that the causal model is available. In this paper, we do not make such assumption and we review the major algorithms to discover causal relations from observable data. This study focuses on causal discovery and its impact on fairness. In particular, we show how different causal discovery approaches may result in different causal models and, most importantly, how even slight differences between causal models can have significant impact on fairness/discrimination conclusions. These results are consolidated by empirical analysis using synthetic and standard fairness benchmark datasets. The main goal of this study is to highlight the importance of the causal discovery step to appropriately address fairness using causality.
Questioning causality on sex, gender and COVID-19, and identifying bias in large-scale data-driven analyses: the Bias Priority Recommendations and Bias Catalog for Pandemics
Apr 29, 2021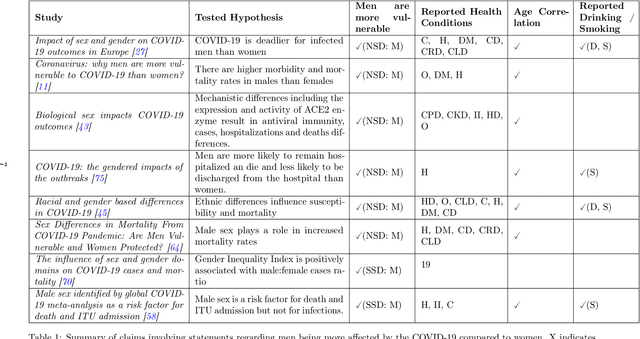
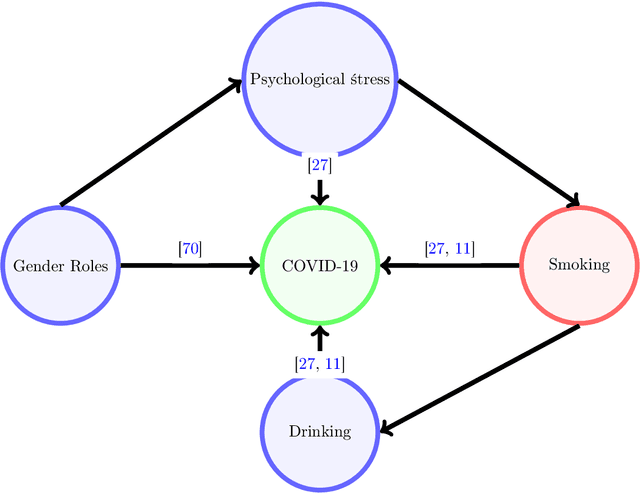
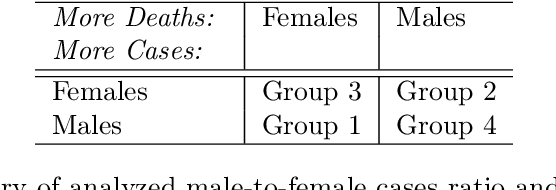
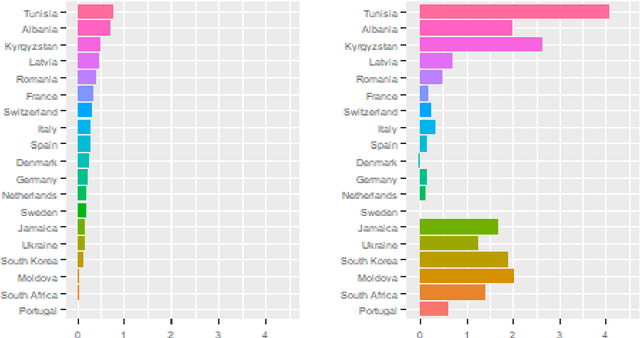
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred a large amount of observational studies reporting linkages between the risk of developing severe COVID-19 or dying from it, and sex and gender. By reviewing a large body of related literature and conducting a fine grained analysis based on sex-disaggregated data of 61 countries spanning 5 continents, we discover several confounding factors that could possibly explain the supposed male vulnerability to COVID-19. We thus highlight the challenge of making causal claims based on available data, given the lack of statistical significance and potential existence of biases. Informed by our findings on potential variables acting as confounders, we contribute a broad overview on the issues bias, explainability and fairness entail in data-driven analyses. Thus, we outline a set of discriminatory policy consequences that could, based on such results, lead to unintended discrimination. To raise awareness on the dimensionality of such foreseen impacts, we have compiled an encyclopedia-like reference guide, the Bias Catalog for Pandemics (BCP), to provide definitions and emphasize realistic examples of bias in general, and within the COVID-19 pandemic context. These are categorized within a division of bias families and a 2-level priority scale, together with preventive steps. In addition, we facilitate the Bias Priority Recommendations on how to best use and apply this catalog, and provide guidelines in order to address real world research questions. The objective is to anticipate and avoid disparate impact and discrimination, by considering causality, explainability, bias and techniques to mitigate the latter. With these, we hope to 1) contribute to designing and conducting fair and equitable data-driven studies and research; and 2) interpret and draw meaningful and actionable conclusions from these.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge