Rúben Almeida
Enhancing Portuguese Variety Identification with Cross-Domain Approaches
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in natural language processing have raised expectations for generative models to produce coherent text across diverse language varieties. In the particular case of the Portuguese language, the predominance of Brazilian Portuguese corpora online introduces linguistic biases in these models, limiting their applicability outside of Brazil. To address this gap and promote the creation of European Portuguese resources, we developed a cross-domain language variety identifier (LVI) to discriminate between European and Brazilian Portuguese. Motivated by the findings of our literature review, we compiled the PtBrVarId corpus, a cross-domain LVI dataset, and study the effectiveness of transformer-based LVI classifiers for cross-domain scenarios. Although this research focuses on two Portuguese varieties, our contribution can be extended to other varieties and languages. We open source the code, corpus, and models to foster further research in this task.
A Legal Framework for Natural Language Processing Model Training in Portugal
May 01, 2024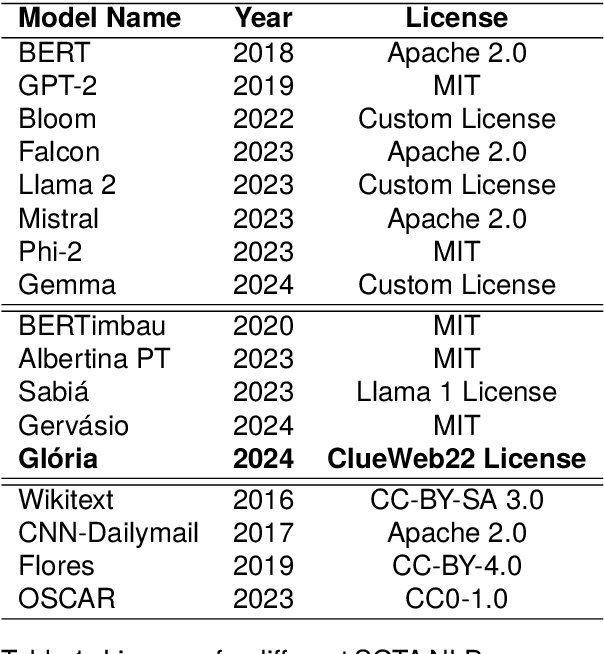
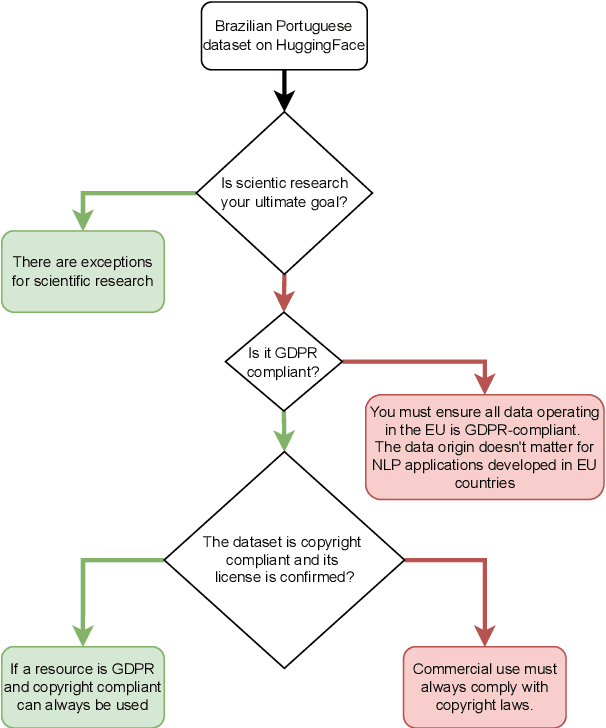
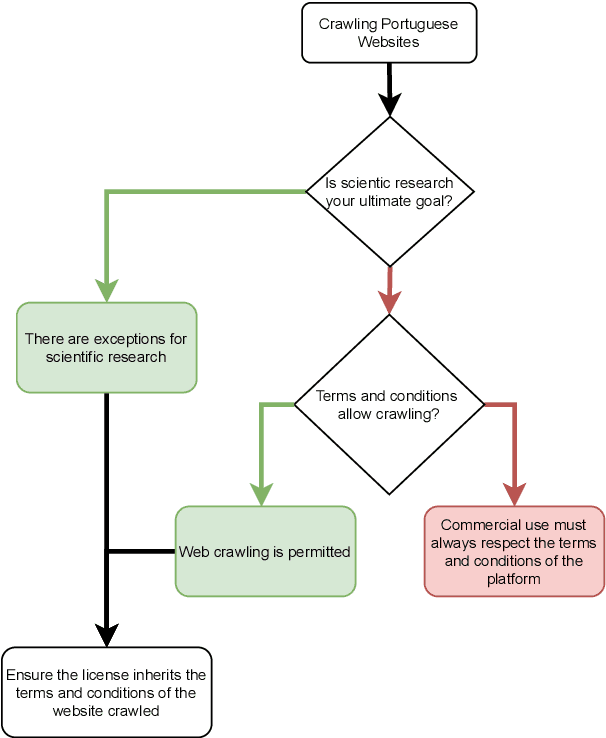
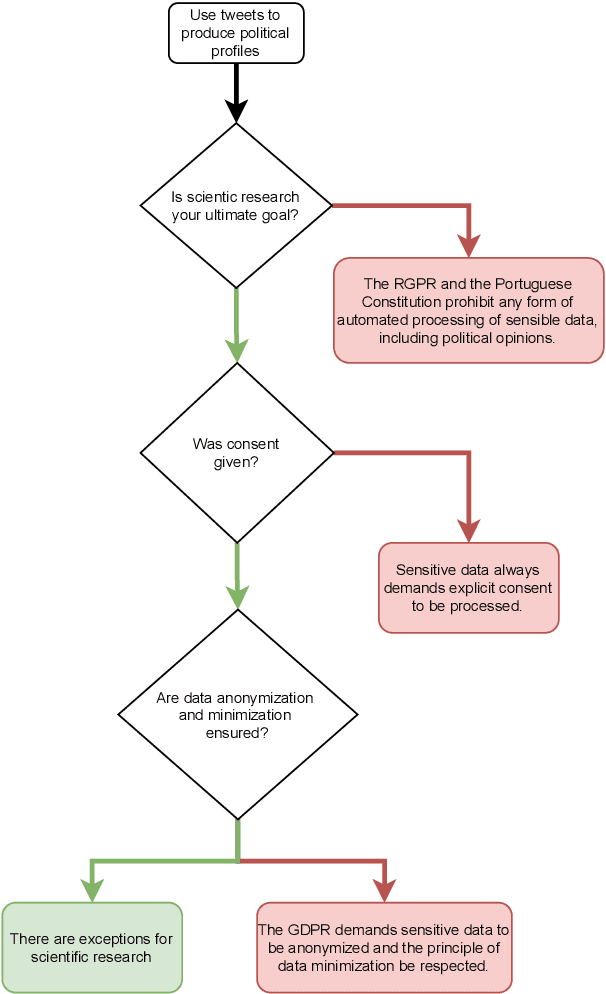
Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning have promoted the advent of many computational systems capable of performing intelligent actions that, until then, were restricted to the human intellect. In the particular case of human languages, these advances allowed the introduction of applications like ChatGPT that are capable of generating coherent text without being explicitly programmed to do so. Instead, these models use large volumes of textual data to learn meaningful representations of human languages. Associated with these advances, concerns about copyright and data privacy infringements caused by these applications have emerged. Despite these concerns, the pace at which new natural language processing applications continued to be developed largely outperformed the introduction of new regulations. Today, communication barriers between legal experts and computer scientists motivate many unintentional legal infringements during the development of such applications. In this paper, a multidisciplinary team intends to bridge this communication gap and promote more compliant Portuguese NLP research by presenting a series of everyday NLP use cases, while highlighting the Portuguese legislation that may arise during its development.
Indexing Portuguese NLP Resources with PT-Pump-Up
Jan 27, 2024Abstract:The recent advances in natural language processing (NLP) are linked to training processes that require vast amounts of corpora. Access to this data is commonly not a trivial process due to resource dispersion and the need to maintain these infrastructures online and up-to-date. New developments in NLP are often compromised due to the scarcity of data or lack of a shared repository that works as an entry point to the community. This is especially true in low and mid-resource languages, such as Portuguese, which lack data and proper resource management infrastructures. In this work, we propose PT-Pump-Up, a set of tools that aim to reduce resource dispersion and improve the accessibility to Portuguese NLP resources. Our proposal is divided into four software components: a) a web platform to list the available resources; b) a client-side Python package to simplify the loading of Portuguese NLP resources; c) an administrative Python package to manage the platform and d) a public GitHub repository to foster future collaboration and contributions. All four components are accessible using: https://linktr.ee/pt_pump_up
* Demo Track, 3 pages
Physio: An LLM-Based Physiotherapy Advisor
Jan 03, 2024Abstract:The capabilities of the most recent language models have increased the interest in integrating them into real-world applications. However, the fact that these models generate plausible, yet incorrect text poses a constraint when considering their use in several domains. Healthcare is a prime example of a domain where text-generative trustworthiness is a hard requirement to safeguard patient well-being. In this paper, we present Physio, a chat-based application for physical rehabilitation. Physio is capable of making an initial diagnosis while citing reliable health sources to support the information provided. Furthermore, drawing upon external knowledge databases, Physio can recommend rehabilitation exercises and over-the-counter medication for symptom relief. By combining these features, Physio can leverage the power of generative models for language processing while also conditioning its response on dependable and verifiable sources. A live demo of Physio is available at https://physio.inesctec.pt.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge