Evelin Amorim
MiNER: A Two-Stage Pipeline for Metadata Extraction from Municipal Meeting Minutes
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Municipal meeting minutes are official documents of local governance, exhibiting heterogeneous formats and writing styles. Effective information retrieval (IR) requires identifying metadata such as meeting number, date, location, participants, and start/end times, elements that are rarely standardized or easy to extract automatically. Existing named entity recognition (NER) models are ill-suited to this task, as they are not adapted to such domain-specific categories. In this paper, we propose a two-stage pipeline for metadata extraction from municipal minutes. First, a question answering (QA) model identifies the opening and closing text segments containing metadata. Transformer-based models (BERTimbau and XLM-RoBERTa with and without a CRF layer) are then applied for fine-grained entity extraction and enhanced through deslexicalization. To evaluate our proposed pipeline, we benchmark both open-weight (Phi) and closed-weight (Gemini) LLMs, assessing predictive performance, inference cost, and carbon footprint. Our results demonstrate strong in-domain performance, better than larger general-purpose LLMs. However, cross-municipality evaluation reveals reduced generalization reflecting the variability and linguistic complexity of municipal records. This work establishes the first benchmark for metadata extraction from municipal meeting minutes, providing a solid foundation for future research in this domain.
A Legal Framework for Natural Language Processing Model Training in Portugal
May 01, 2024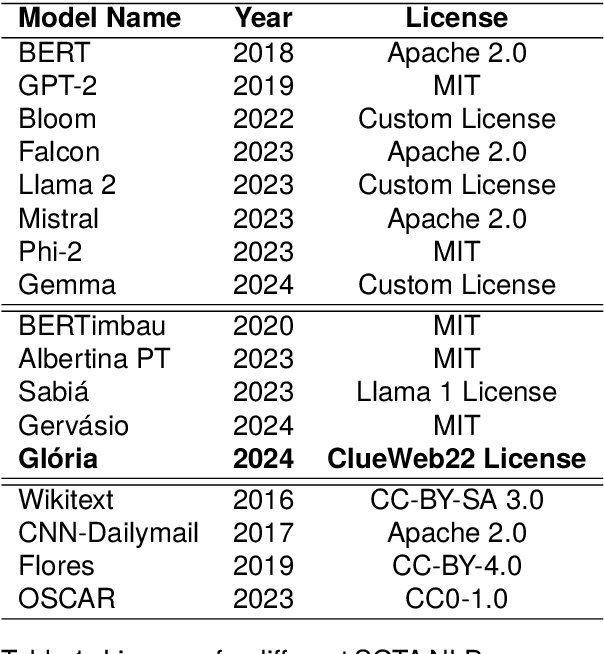
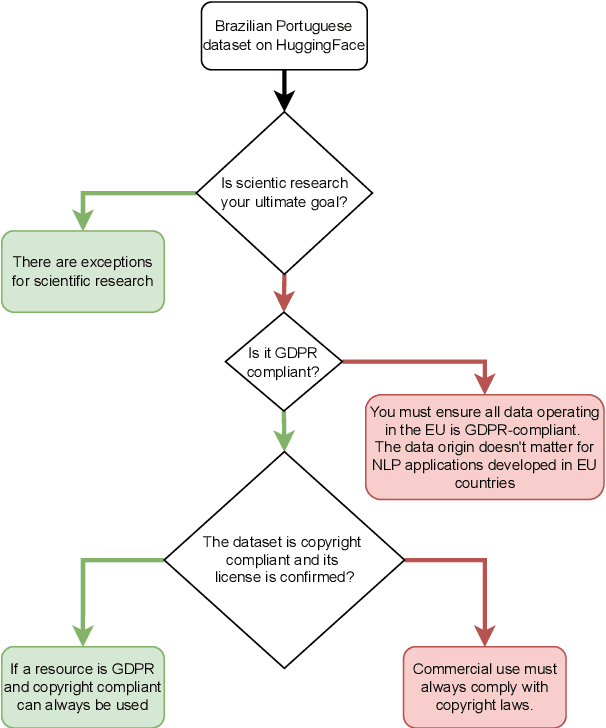
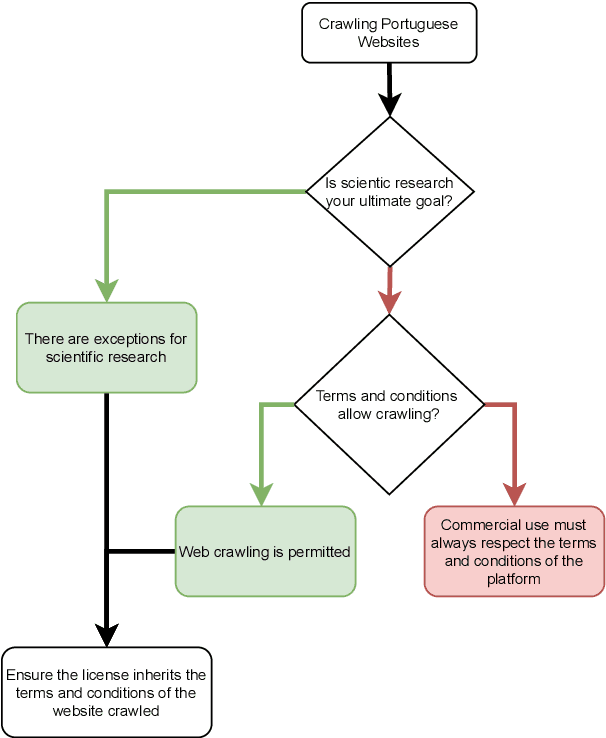
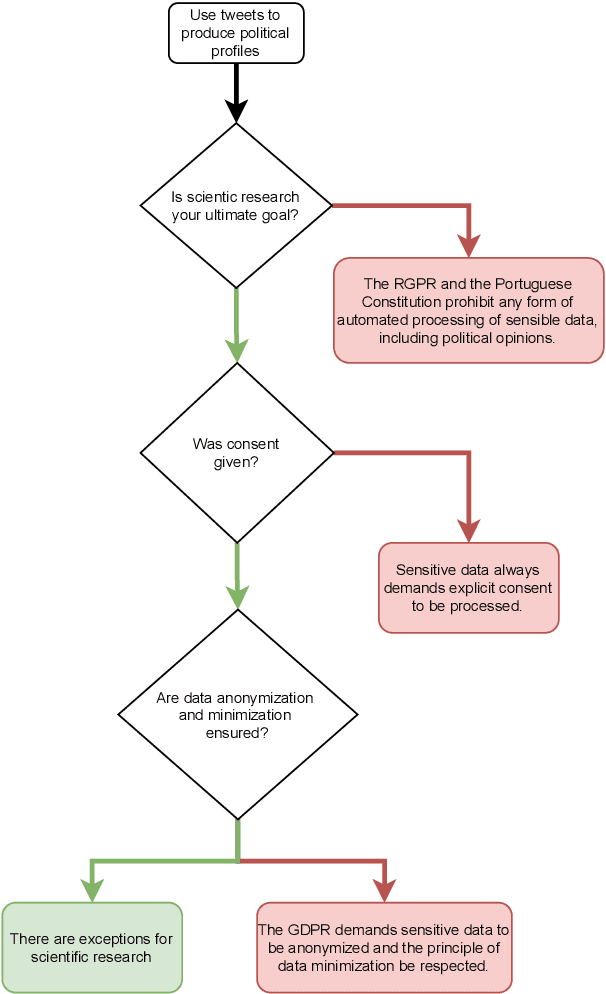
Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning have promoted the advent of many computational systems capable of performing intelligent actions that, until then, were restricted to the human intellect. In the particular case of human languages, these advances allowed the introduction of applications like ChatGPT that are capable of generating coherent text without being explicitly programmed to do so. Instead, these models use large volumes of textual data to learn meaningful representations of human languages. Associated with these advances, concerns about copyright and data privacy infringements caused by these applications have emerged. Despite these concerns, the pace at which new natural language processing applications continued to be developed largely outperformed the introduction of new regulations. Today, communication barriers between legal experts and computer scientists motivate many unintentional legal infringements during the development of such applications. In this paper, a multidisciplinary team intends to bridge this communication gap and promote more compliant Portuguese NLP research by presenting a series of everyday NLP use cases, while highlighting the Portuguese legislation that may arise during its development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge