Qiyuan Shen
Cross-Modal Visual Relocalization in Prior LiDAR Maps Utilizing Intensity Textures
Dec 02, 2024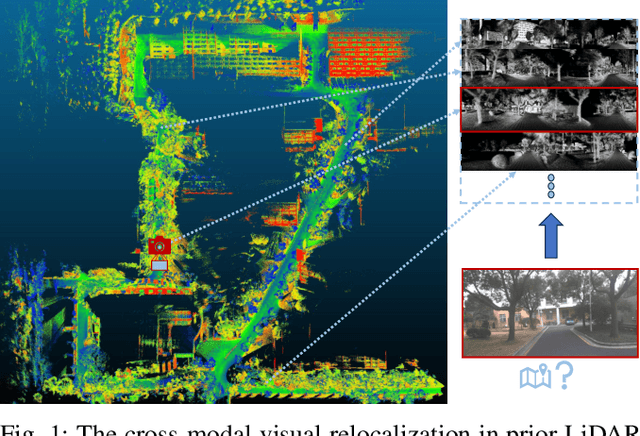
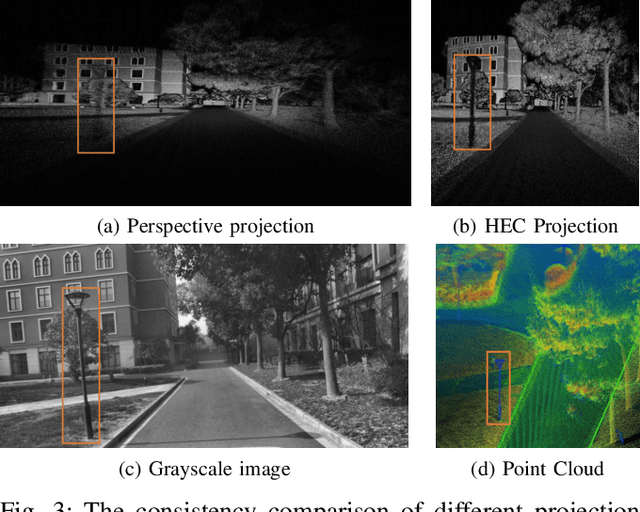


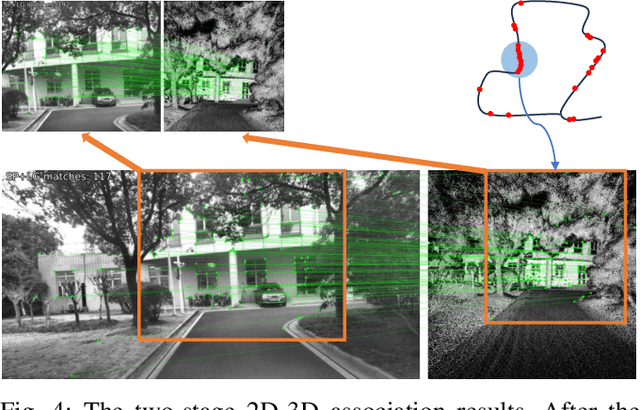
Abstract:Cross-modal localization has drawn increasing attention in recent years, while the visual relocalization in prior LiDAR maps is less studied. Related methods usually suffer from inconsistency between the 2D texture and 3D geometry, neglecting the intensity features in the LiDAR point cloud. In this paper, we propose a cross-modal visual relocalization system in prior LiDAR maps utilizing intensity textures, which consists of three main modules: map projection, coarse retrieval, and fine relocalization. In the map projection module, we construct the database of intensity channel map images leveraging the dense characteristic of panoramic projection. The coarse retrieval module retrieves the top-K most similar map images to the query image from the database, and retains the top-K' results by covisibility clustering. The fine relocalization module applies a two-stage 2D-3D association and a covisibility inlier selection method to obtain robust correspondences for 6DoF pose estimation. The experimental results on our self-collected datasets demonstrate the effectiveness in both place recognition and pose estimation tasks.
A Survey of Simulators for Autonomous Driving: Taxonomy, Challenges, and Evaluation Metrics
Nov 18, 2023Abstract:Simulators have irreplaceable importance for the research and development of autonomous driving. Besides saving resources, labor, and time, simulation is the only feasible way to reproduce many severe accident scenarios. Despite their widespread adoption across academia and industry, there is an absence in the evolutionary trajectory of simulators and critical discourse on their limitations. To bridge the gap in research, this paper conducts an in-depth review of simulators for autonomous driving. It delineates the three-decade development into three stages: specialized development period, gap period, and comprehensive development, from which it detects a trend of implementing comprehensive functionalities and open-source accessibility. Then it classifies the simulators by functions, identifying five categories: traffic flow simulator, vehicle dynamics simulator, scenario editor, sensory data generator, and driving strategy validator. Simulators that amalgamate diverse features are defined as comprehensive simulators. By investigating commercial and open-source simulators, this paper reveals that the critical issues faced by simulators primarily revolve around fidelity and efficiency concerns. This paper justifies that enhancing the realism of adverse weather simulation, automated map reconstruction, and interactive traffic participants will bolster credibility. Concurrently, headless simulation and multiple-speed simulation techniques will exploit the theoretic advantages. Moreover, this paper delves into potential solutions for the identified issues. It explores qualitative and quantitative evaluation metrics to assess the simulator's performance. This paper guides users to find suitable simulators efficiently and provides instructive suggestions for developers to improve simulator efficacy purposefully.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge