Qingxia Liu
Neural Entity Summarization with Joint Encoding and Weak Supervision
May 10, 2020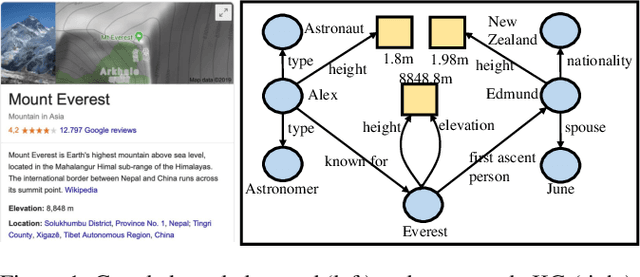

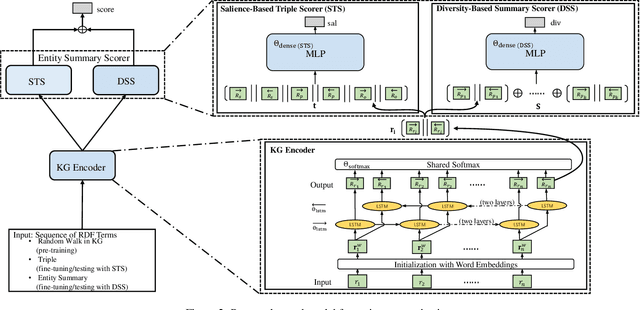
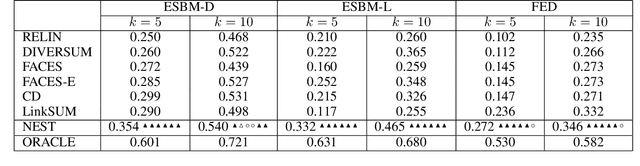
Abstract:In a large-scale knowledge graph (KG), an entity is often described by a large number of triple-structured facts. Many applications require abridged versions of entity descriptions, called entity summaries. Existing solutions to entity summarization are mainly unsupervised. In this paper, we present a supervised approach NEST that is based on our novel neural model to jointly encode graph structure and text in KGs and generate high-quality diversified summaries. Since it is costly to obtain manually labeled summaries for training, our supervision is weak as we train with programmatically labeled data which may contain noise but is free of manual work. Evaluation results show that our approach significantly outperforms the state of the art on two public benchmarks.
DeepLENS: Deep Learning for Entity Summarization
Mar 08, 2020


Abstract:Entity summarization has been a prominent task over knowledge graphs. While existing methods are mainly unsupervised, we present DeepLENS, a simple yet effective deep learning model where we exploit textual semantics for encoding triples and we score each candidate triple based on its interdependence on other triples. DeepLENS significantly outperformed existing methods on a public benchmark.
ESBM: An Entity Summarization BenchMark
Mar 08, 2020



Abstract:Entity summarization is the problem of computing an optimal compact summary for an entity by selecting a size-constrained subset of triples from RDF data. Entity summarization supports a multiplicity of applications and has led to fruitful research. However, there is a lack of evaluation efforts that cover the broad spectrum of existing systems. One reason is a lack of benchmarks for evaluation. Some benchmarks are no longer available, while others are small and have limitations. In this paper, we create an Entity Summarization BenchMark (ESBM) which overcomes the limitations of existing benchmarks and meets standard desiderata for a benchmark. Using this largest available benchmark for evaluating general-purpose entity summarizers, we perform the most extensive experiment to date where 9~existing systems are compared. Considering that all of these systems are unsupervised, we also implement and evaluate a supervised learning based system for reference.
Entity Summarization: State of the Art and Future Challenges
Oct 18, 2019



Abstract:The increasing availability of semantic data, which is commonly represented as entity-property-value triples, has enabled novel information retrieval applications. However, the magnitude of semantic data, in particular the large number of triples describing an entity, could overload users with excessive amounts of information. This has motivated fruitful research on automated generation of summaries for entity descriptions to satisfy users' information needs efficiently and effectively. We focus on this important topic of entity summarization, and present the first comprehensive survey of existing research. We review existing methods and evaluation efforts, and suggest directions for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge