Qi Ou
PolyConf: Unlocking Polymer Conformation Generation through Hierarchical Generative Models
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Polymer conformation generation is a critical task that enables atomic-level studies of diverse polymer materials. While significant advances have been made in designing various conformation generation methods for small molecules and proteins, these methods struggle to generate polymer conformations due to polymers' unique structural characteristics. The scarcity of polymer conformation datasets further limits progress, making this promising area largely unexplored. In this work, we propose PolyConf, a pioneering tailored polymer conformation generation method that leverages hierarchical generative models to unlock new possibilities for this task. Specifically, we decompose the polymer conformation into a series of local conformations (i.e., the conformations of its repeating units), generating these local conformations through an autoregressive model. We then generate corresponding orientation transformations via a diffusion model to assemble these local conformations into the complete polymer conformation. Moreover, we develop the first benchmark with a high-quality polymer conformation dataset derived from molecular dynamics simulations to boost related research in this area. The comprehensive evaluation demonstrates that PolyConf consistently generates high-quality polymer conformations, facilitating advancements in polymer modeling and simulation.
DeePKS+ABACUS as a Bridge between Expensive Quantum Mechanical Models and Machine Learning Potentials
Jun 21, 2022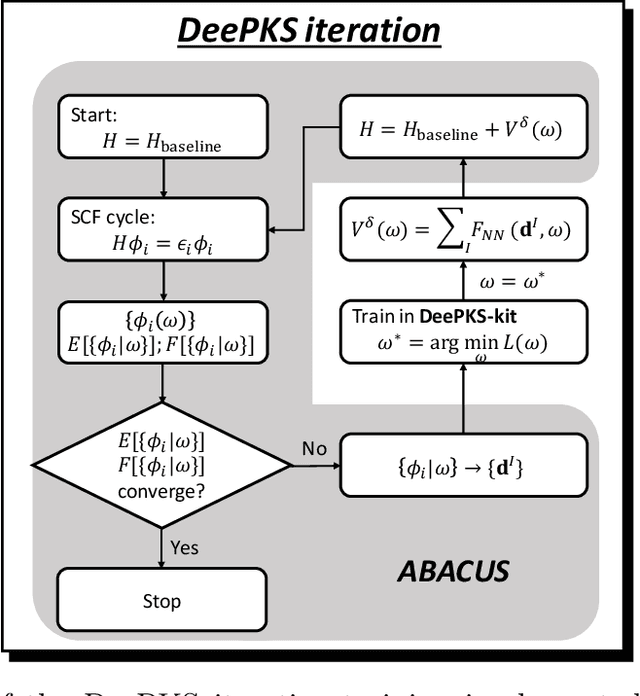
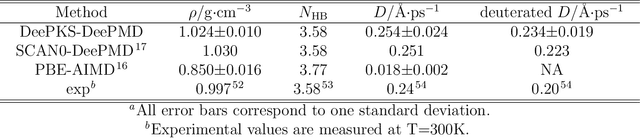
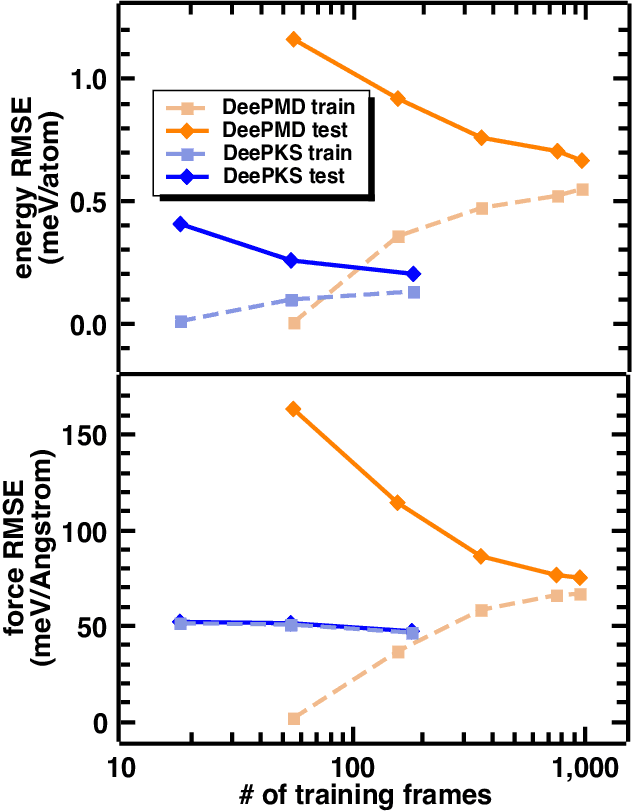
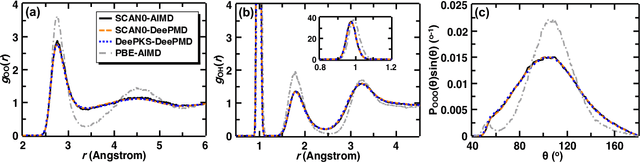
Abstract:Recently, the development of machine learning (ML) potentials has made it possible to perform large-scale and long-time molecular simulations with the accuracy of quantum mechanical (QM) models. However, for high-level QM methods, such as density functional theory (DFT) at the meta-GGA level and/or with exact exchange, quantum Monte Carlo, etc., generating a sufficient amount of data for training a ML potential has remained computationally challenging due to their high cost. In this work, we demonstrate that this issue can be largely alleviated with Deep Kohn-Sham (DeePKS), a ML-based DFT model. DeePKS employs a computationally efficient neural network-based functional model to construct a correction term added upon a cheap DFT model. Upon training, DeePKS offers closely-matched energies and forces compared with high-level QM method, but the number of training data required is orders of magnitude less than that required for training a reliable ML potential. As such, DeePKS can serve as a bridge between expensive QM models and ML potentials: one can generate a decent amount of high-accuracy QM data to train a DeePKS model, and then use the DeePKS model to label a much larger amount of configurations to train a ML potential. This scheme for periodic systems is implemented in a DFT package ABACUS, which is open-source and ready for use in various applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge