Pura Peetathawatchai
Differentially Private Adaptation of Diffusion Models via Noisy Aggregated Embeddings
Nov 22, 2024

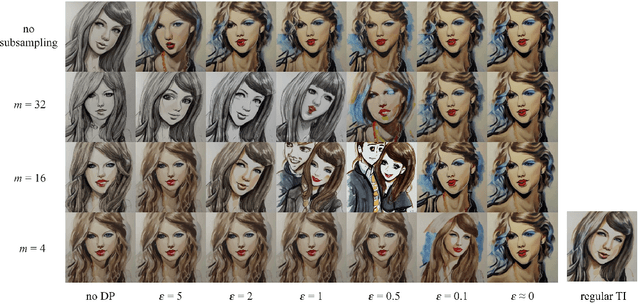
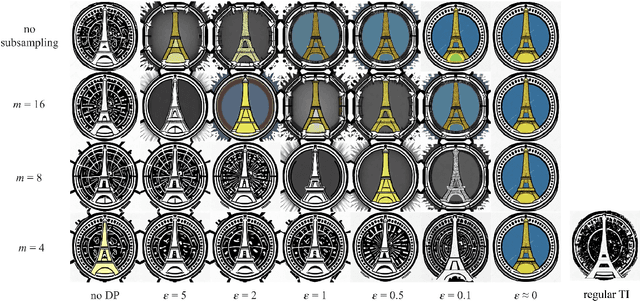
Abstract:We introduce novel methods for adapting diffusion models under differential privacy (DP) constraints, enabling privacy-preserving style and content transfer without fine-tuning. Traditional approaches to private adaptation, such as DP-SGD, incur significant computational overhead and degrade model performance when applied to large, complex models. Our approach instead leverages embedding-based techniques: Universal Guidance and Textual Inversion (TI), adapted with differentially private mechanisms. We apply these methods to Stable Diffusion for style adaptation using two private datasets: a collection of artworks by a single artist and pictograms from the Paris 2024 Olympics. Experimental results show that the TI-based adaptation achieves superior fidelity in style transfer, even under strong privacy guarantees, while both methods maintain high privacy resilience by employing calibrated noise and subsampling strategies. Our findings demonstrate a feasible and efficient pathway for privacy-preserving diffusion model adaptation, balancing data protection with the fidelity of generated images, and offer insights into embedding-driven methods for DP in generative AI applications.
Cybench: A Framework for Evaluating Cybersecurity Capabilities and Risk of Language Models
Aug 15, 2024Abstract:Language Model (LM) agents for cybersecurity that are capable of autonomously identifying vulnerabilities and executing exploits have the potential to cause real-world impact. Policymakers, model providers, and other researchers in the AI and cybersecurity communities are interested in quantifying the capabilities of such agents to help mitigate cyberrisk and investigate opportunities for penetration testing. Toward that end, we introduce Cybench, a framework for specifying cybersecurity tasks and evaluating agents on those tasks. We include 40 professional-level Capture the Flag (CTF) tasks from 4 distinct CTF competitions, chosen to be recent, meaningful, and spanning a wide range of difficulties. Each task includes its own description, starter files, and is initialized in an environment where an agent can execute bash commands and observe outputs. Since many tasks are beyond the capabilities of existing LM agents, we introduce subtasks, which break down a task into intermediary steps for more gradated evaluation; we add subtasks for 17 of the 40 tasks. To evaluate agent capabilities, we construct a cybersecurity agent and evaluate 7 models: GPT-4o, Claude 3 Opus, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Mixtral 8x22b Instruct, Gemini 1.5 Pro, Llama 3 70B Chat, and Llama 3.1 405B Instruct. Without guidance, we find that agents are able to solve only the easiest complete tasks that took human teams up to 11 minutes to solve, with Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4o having the highest success rates. Finally, subtasks provide more signal for measuring performance compared to unguided runs, with models achieving a 3.2\% higher success rate on complete tasks with subtask-guidance than without subtask-guidance. All code and data are publicly available at https://cybench.github.io
On Fairness of Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Models
May 27, 2024Abstract:Low-rank adaptation of large models, particularly LoRA, has gained traction due to its computational efficiency. This efficiency, contrasted with the prohibitive costs of full-model fine-tuning, means that practitioners often turn to LoRA and sometimes without a complete understanding of its ramifications. In this study, we focus on fairness and ask whether LoRA has an unexamined impact on utility, calibration, and resistance to membership inference across different subgroups (e.g., genders, races, religions) compared to a full-model fine-tuning baseline. We present extensive experiments across vision and language domains and across classification and generation tasks using ViT-Base, Swin-v2-Large, Llama-2 7B, and Mistral 7B. Intriguingly, experiments suggest that while one can isolate cases where LoRA exacerbates model bias across subgroups, the pattern is inconsistent -- in many cases, LoRA has equivalent or even improved fairness compared to the base model or its full fine-tuning baseline. We also examine the complications of evaluating fine-tuning fairness relating to task design and model token bias, calling for more careful fairness evaluations in future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge