Prijith Chandran
Knowledge Distillation for Enhancing Walmart E-commerce Search Relevance Using Large Language Models
May 11, 2025
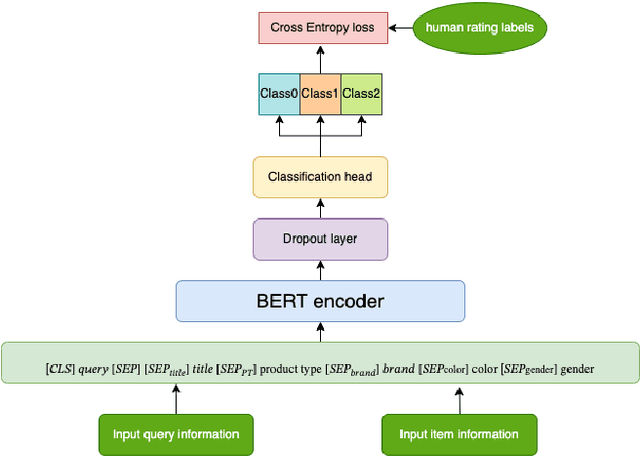
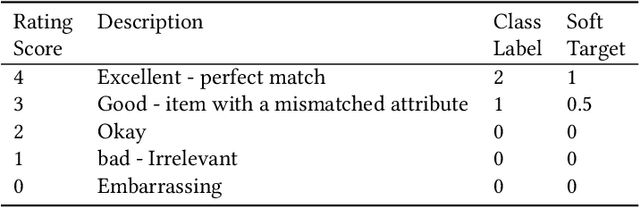
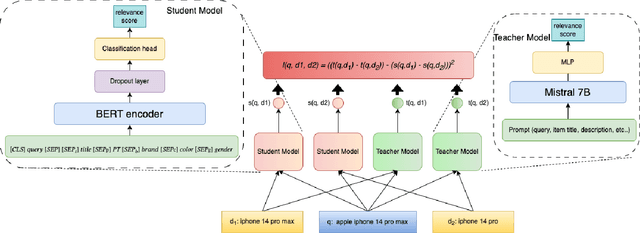
Abstract:Ensuring the products displayed in e-commerce search results are relevant to users queries is crucial for improving the user experience. With their advanced semantic understanding, deep learning models have been widely used for relevance matching in search tasks. While large language models (LLMs) offer superior ranking capabilities, it is challenging to deploy LLMs in real-time systems due to the high-latency requirements. To leverage the ranking power of LLMs while meeting the low-latency demands of production systems, we propose a novel framework that distills a high performing LLM into a more efficient, low-latency student model. To help the student model learn more effectively from the teacher model, we first train the teacher LLM as a classification model with soft targets. Then, we train the student model to capture the relevance margin between pairs of products for a given query using mean squared error loss. Instead of using the same training data as the teacher model, we significantly expand the student model dataset by generating unlabeled data and labeling it with the teacher model predictions. Experimental results show that the student model performance continues to improve as the size of the augmented training data increases. In fact, with enough augmented data, the student model can outperform the teacher model. The student model has been successfully deployed in production at Walmart.com with significantly positive metrics.
* 9 pages, published at WWWW'25
Enhancing Relevance of Embedding-based Retrieval at Walmart
Aug 09, 2024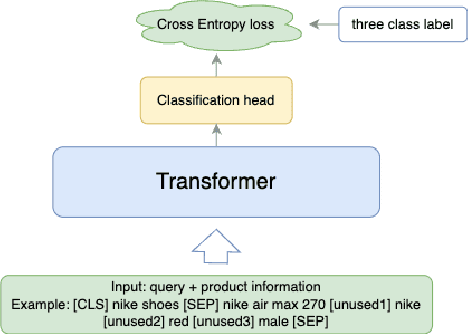

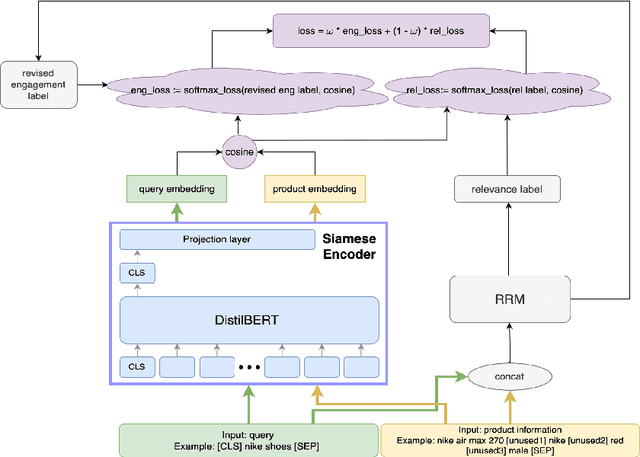
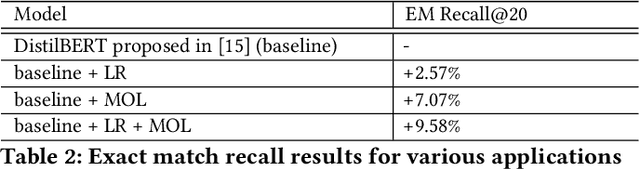
Abstract:Embedding-based neural retrieval (EBR) is an effective search retrieval method in product search for tackling the vocabulary gap between customer search queries and products. The initial launch of our EBR system at Walmart yielded significant gains in relevance and add-to-cart rates [1]. However, despite EBR generally retrieving more relevant products for reranking, we have observed numerous instances of relevance degradation. Enhancing retrieval performance is crucial, as it directly influences product reranking and affects the customer shopping experience. Factors contributing to these degradations include false positives/negatives in the training data and the inability to handle query misspellings. To address these issues, we present several approaches to further strengthen the capabilities of our EBR model in terms of retrieval relevance. We introduce a Relevance Reward Model (RRM) based on human relevance feedback. We utilize RRM to remove noise from the training data and distill it into our EBR model through a multi-objective loss. In addition, we present the techniques to increase the performance of our EBR model, such as typo-aware training, and semi-positive generation. The effectiveness of our EBR is demonstrated through offline relevance evaluation, online AB tests, and successful deployments to live production. [1] Alessandro Magnani, Feng Liu, Suthee Chaidaroon, Sachin Yadav, Praveen Reddy Suram, Ajit Puthenputhussery, Sijie Chen, Min Xie, Anirudh Kashi, Tony Lee, et al. 2022. Semantic retrieval at walmart. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. 3495-3503.
Large Language Models for Relevance Judgment in Product Search
Jun 01, 2024Abstract:High relevance of retrieved and re-ranked items to the search query is the cornerstone of successful product search, yet measuring relevance of items to queries is one of the most challenging tasks in product information retrieval, and quality of product search is highly influenced by the precision and scale of available relevance-labelled data. In this paper, we present an array of techniques for leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) for automating the relevance judgment of query-item pairs (QIPs) at scale. Using a unique dataset of multi-million QIPs, annotated by human evaluators, we test and optimize hyper parameters for finetuning billion-parameter LLMs with and without Low Rank Adaption (LoRA), as well as various modes of item attribute concatenation and prompting in LLM finetuning, and consider trade offs in item attribute inclusion for quality of relevance predictions. We demonstrate considerable improvement over baselines of prior generations of LLMs, as well as off-the-shelf models, towards relevance annotations on par with the human relevance evaluators. Our findings have immediate implications for the growing field of relevance judgment automation in product search.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge