Poikavila Ullaskrishnan
A Non-contrast Head CT Foundation Model for Comprehensive Neuro-Trauma Triage
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in AI and medical imaging offer transformative potential in emergency head CT interpretation for reducing assessment times and improving accuracy in the face of an increasing request of such scans and a global shortage in radiologists. This study introduces a 3D foundation model for detecting diverse neuro-trauma findings with high accuracy and efficiency. Using large language models (LLMs) for automatic labeling, we generated comprehensive multi-label annotations for critical conditions. Our approach involved pretraining neural networks for hemorrhage subtype segmentation and brain anatomy parcellation, which were integrated into a pretrained comprehensive neuro-trauma detection network through multimodal fine-tuning. Performance evaluation against expert annotations and comparison with CT-CLIP demonstrated strong triage accuracy across major neuro-trauma findings, such as hemorrhage and midline shift, as well as less frequent critical conditions such as cerebral edema and arterial hyperdensity. The integration of neuro-specific features significantly enhanced diagnostic capabilities, achieving an average AUC of 0.861 for 16 neuro-trauma conditions. This work advances foundation models in medical imaging, serving as a benchmark for future AI-assisted neuro-trauma diagnostics in emergency radiology.
General-Purpose vs. Domain-Adapted Large Language Models for Extraction of Data from Thoracic Radiology Reports
Dec 01, 2023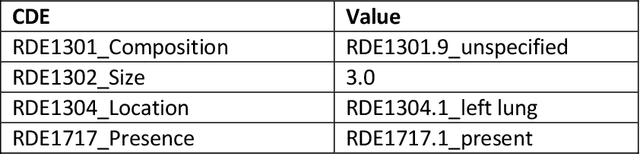
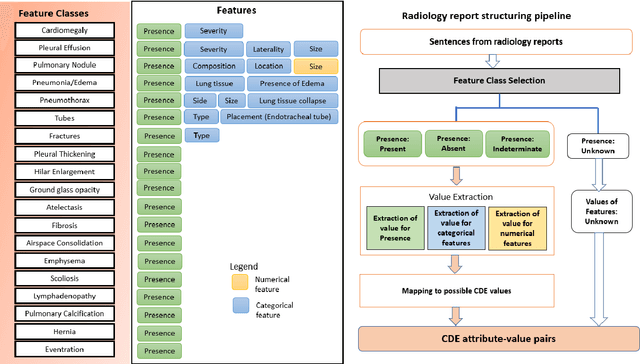
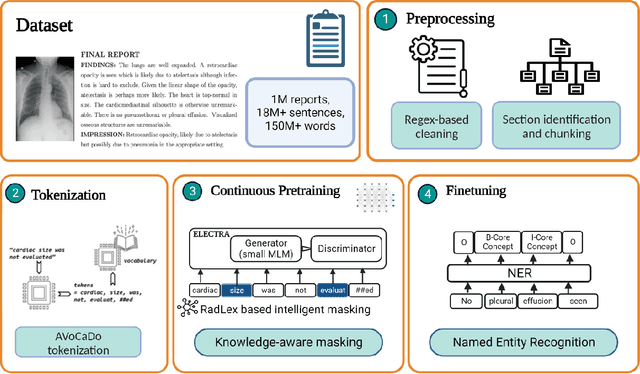
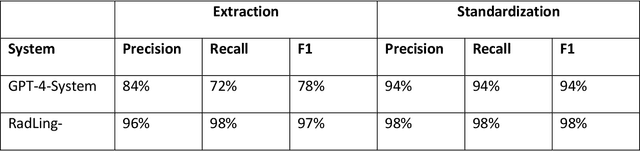
Abstract:Radiologists produce unstructured data that could be valuable for clinical care when consumed by information systems. However, variability in style limits usage. Study compares performance of system using domain-adapted language model (RadLing) and general-purpose large language model (GPT-4) in extracting common data elements (CDE) from thoracic radiology reports. Three radiologists annotated a retrospective dataset of 1300 thoracic reports (900 training, 400 test) and mapped to 21 pre-selected relevant CDEs. RadLing was used to generate embeddings for sentences and identify CDEs using cosine-similarity, which were mapped to values using light-weight mapper. GPT-4 system used OpenAI's general-purpose embeddings to identify relevant CDEs and used GPT-4 to map to values. The output CDE:value pairs were compared to the reference standard; an identical match was considered true positive. Precision (positive predictive value) was 96% (2700/2824) for RadLing and 99% (2034/2047) for GPT-4. Recall (sensitivity) was 94% (2700/2876) for RadLing and 70% (2034/2887) for GPT-4; the difference was statistically significant (P<.001). RadLing's domain-adapted embeddings were more sensitive in CDE identification (95% vs 71%) and its light-weight mapper had comparable precision in value assignment (95.4% vs 95.0%). RadLing system exhibited higher performance than GPT-4 system in extracting CDEs from radiology reports. RadLing system's domain-adapted embeddings outperform general-purpose embeddings from OpenAI in CDE identification and its light-weight value mapper achieves comparable precision to large GPT-4. RadLing system offers operational advantages including local deployment and reduced runtime costs. Domain-adapted RadLing system surpasses GPT-4 system in extracting common data elements from radiology reports, while providing benefits of local deployment and lower costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge