Philipp Christmann
Traceable Drug Recommendation over Medical Knowledge Graphs
Oct 31, 2025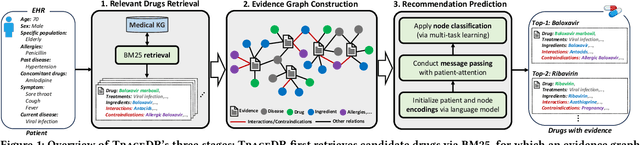
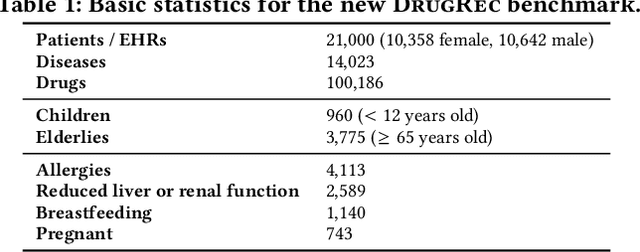
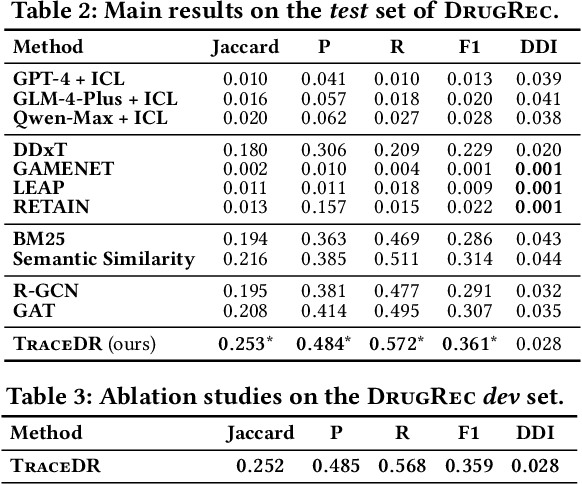

Abstract:Drug recommendation (DR) systems aim to support healthcare professionals in selecting appropriate medications based on patients' medical conditions. State-of-the-art approaches utilize deep learning techniques for improving DR, but fall short in providing any insights on the derivation process of recommendations -- a critical limitation in such high-stake applications. We propose TraceDR, a novel DR system operating over a medical knowledge graph (MKG), which ensures access to large-scale and high-quality information. TraceDR simultaneously predicts drug recommendations and related evidence within a multi-task learning framework, enabling traceability of medication recommendations. For covering a more diverse set of diseases and drugs than existing works, we devise a framework for automatically constructing patient health records and release DrugRec, a new large-scale testbed for DR.
The ReQAP System for Question Answering over Personal Information
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Personal information is abundant on users' devices, from structured data in calendar, shopping records or fitness tools, to unstructured contents in mail and social media posts. This works presents the ReQAP system that supports users with answers for complex questions that involve filters, joins and aggregation over heterogeneous sources. The unique trait of ReQAP is that it recursively decomposes questions and incrementally builds an operator tree for execution. Both the question interpretation and the individual operators make smart use of light-weight language models, with judicious fine-tuning. The demo showcases the rich functionality for advanced user questions, and also offers detailed tracking of how the answers are computed by the operators in the execution tree. Being able to trace answers back to the underlying sources is vital for human comprehensibility and user trust in the system.
Recursive Question Understanding for Complex Question Answering over Heterogeneous Personal Data
May 17, 2025Abstract:Question answering over mixed sources, like text and tables, has been advanced by verbalizing all contents and encoding it with a language model. A prominent case of such heterogeneous data is personal information: user devices log vast amounts of data every day, such as calendar entries, workout statistics, shopping records, streaming history, and more. Information needs range from simple look-ups to queries of analytical nature. The challenge is to provide humans with convenient access with small footprint, so that all personal data stays on the user devices. We present ReQAP, a novel method that creates an executable operator tree for a given question, via recursive decomposition. Operators are designed to enable seamless integration of structured and unstructured sources, and the execution of the operator tree yields a traceable answer. We further release the PerQA benchmark, with persona-based data and questions, covering a diverse spectrum of realistic user needs.
RAG-based Question Answering over Heterogeneous Data and Text
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:This article presents the QUASAR system for question answering over unstructured text, structured tables, and knowledge graphs, with unified treatment of all sources. The system adopts a RAG-based architecture, with a pipeline of evidence retrieval followed by answer generation, with the latter powered by a moderate-sized language model. Additionally and uniquely, QUASAR has components for question understanding, to derive crisper input for evidence retrieval, and for re-ranking and filtering the retrieved evidence before feeding the most informative pieces into the answer generation. Experiments with three different benchmarks demonstrate the high answering quality of our approach, being on par with or better than large GPT models, while keeping the computational cost and energy consumption orders of magnitude lower.
Retrieving Contextual Information for Long-Form Question Answering using Weak Supervision
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:Long-form question answering (LFQA) aims at generating in-depth answers to end-user questions, providing relevant information beyond the direct answer. However, existing retrievers are typically optimized towards information that directly targets the question, missing out on such contextual information. Furthermore, there is a lack of training data for relevant context. To this end, we propose and compare different weak supervision techniques to optimize retrieval for contextual information. Experiments demonstrate improvements on the end-to-end QA performance on ASQA, a dataset for long-form question answering. Importantly, as more contextual information is retrieved, we improve the relevant page recall for LFQA by 14.7% and the groundedness of generated long-form answers by 12.5%. Finally, we show that long-form answers often anticipate likely follow-up questions, via experiments on a conversational QA dataset.
Faithful Temporal Question Answering over Heterogeneous Sources
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:Temporal question answering (QA) involves time constraints, with phrases such as "... in 2019" or "... before COVID". In the former, time is an explicit condition, in the latter it is implicit. State-of-the-art methods have limitations along three dimensions. First, with neural inference, time constraints are merely soft-matched, giving room to invalid or inexplicable answers. Second, questions with implicit time are poorly supported. Third, answers come from a single source: either a knowledge base (KB) or a text corpus. We propose a temporal QA system that addresses these shortcomings. First, it enforces temporal constraints for faithful answering with tangible evidence. Second, it properly handles implicit questions. Third, it operates over heterogeneous sources, covering KB, text and web tables in a unified manner. The method has three stages: (i) understanding the question and its temporal conditions, (ii) retrieving evidence from all sources, and (iii) faithfully answering the question. As implicit questions are sparse in prior benchmarks, we introduce a principled method for generating diverse questions. Experiments show superior performance over a suite of baselines.
CompMix: A Benchmark for Heterogeneous Question Answering
Jun 23, 2023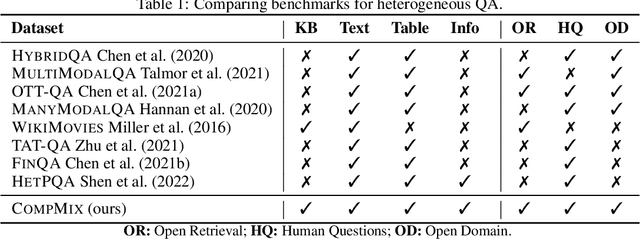
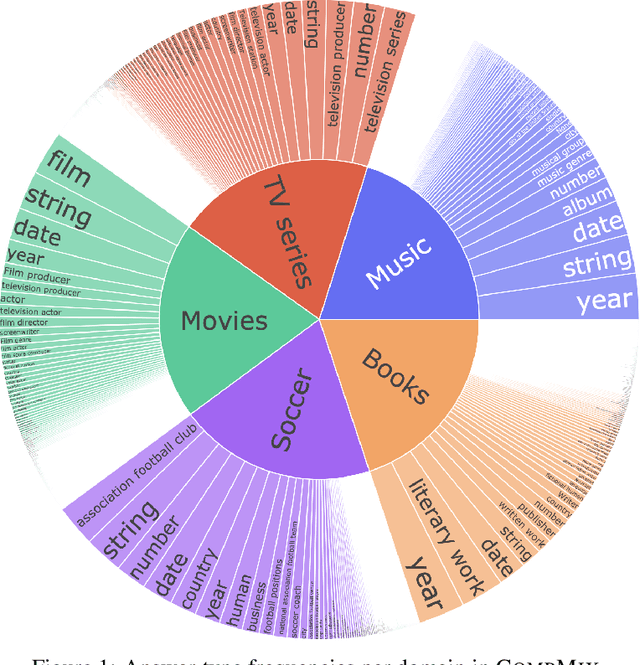
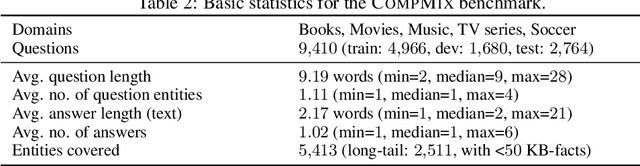
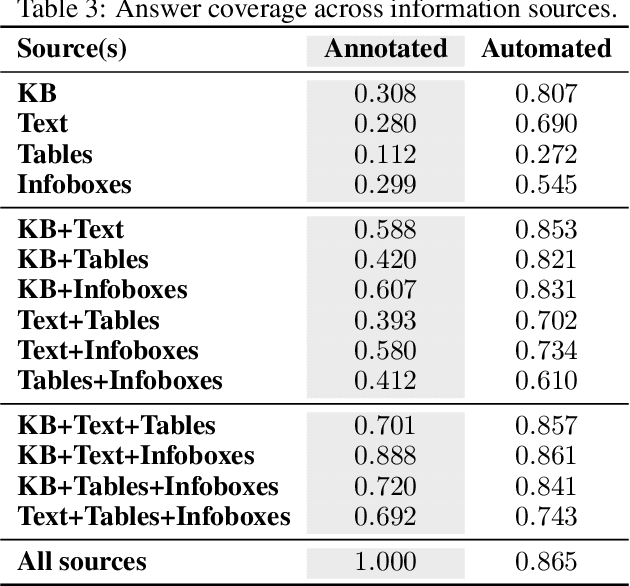
Abstract:Fact-centric question answering (QA) often requires access to multiple, heterogeneous, information sources. By jointly considering several sources like a knowledge base (KB), a text collection, and tables from the web, QA systems can enhance their answer coverage and confidence. However, existing QA benchmarks are mostly constructed with a single source of knowledge in mind. This limits capabilities of these benchmarks to fairly evaluate QA systems that can tap into more than one information repository. To bridge this gap, we release CompMix, a crowdsourced QA benchmark which naturally demands the integration of a mixture of input sources. CompMix has a total of 9,410 questions, and features several complex intents like joins and temporal conditions. Evaluation of a range of QA systems on CompMix highlights the need for further research on leveraging information from heterogeneous sources.
Explainable Conversational Question Answering over Heterogeneous Sources via Iterative Graph Neural Networks
May 02, 2023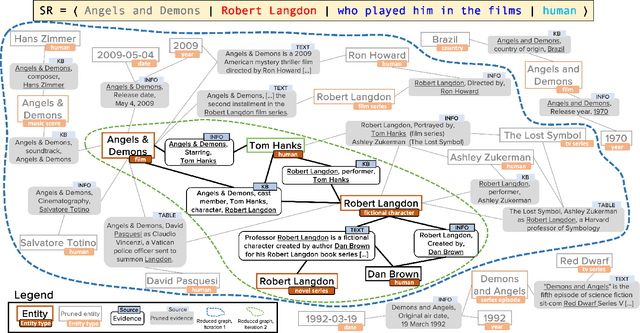
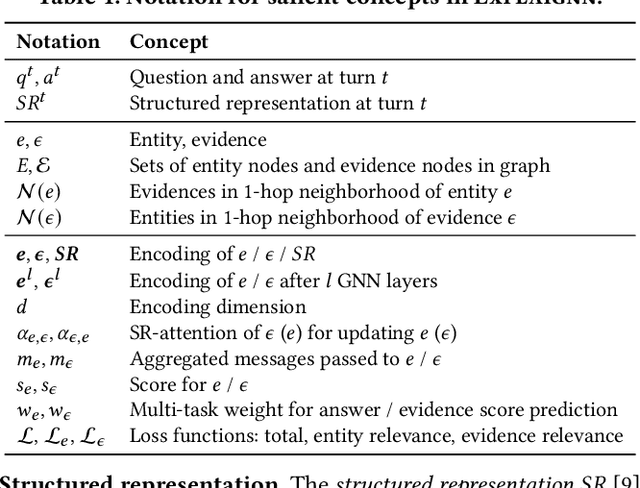
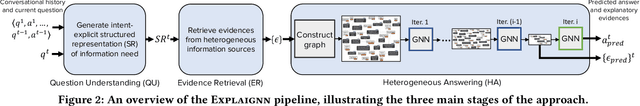
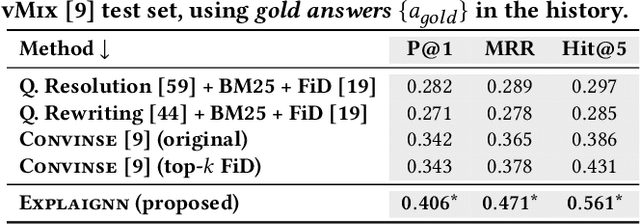
Abstract:In conversational question answering, users express their information needs through a series of utterances with incomplete context. Typical ConvQA methods rely on a single source (a knowledge base (KB), or a text corpus, or a set of tables), thus being unable to benefit from increased answer coverage and redundancy of multiple sources. Our method EXPLAIGNN overcomes these limitations by integrating information from a mixture of sources with user-comprehensible explanations for answers. It constructs a heterogeneous graph from entities and evidence snippets retrieved from a KB, a text corpus, web tables, and infoboxes. This large graph is then iteratively reduced via graph neural networks that incorporate question-level attention, until the best answers and their explanations are distilled. Experiments show that EXPLAIGNN improves performance over state-of-the-art baselines. A user study demonstrates that derived answers are understandable by end users.
Conversational Question Answering on Heterogeneous Sources
Apr 25, 2022
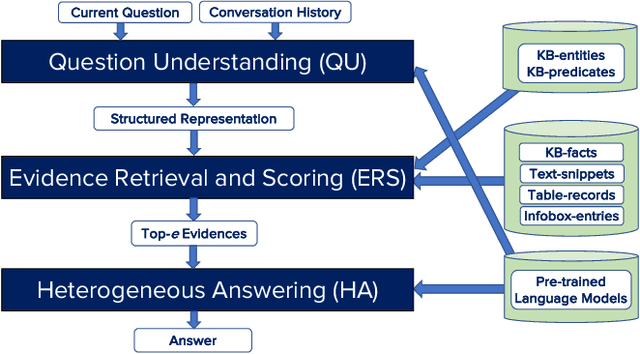
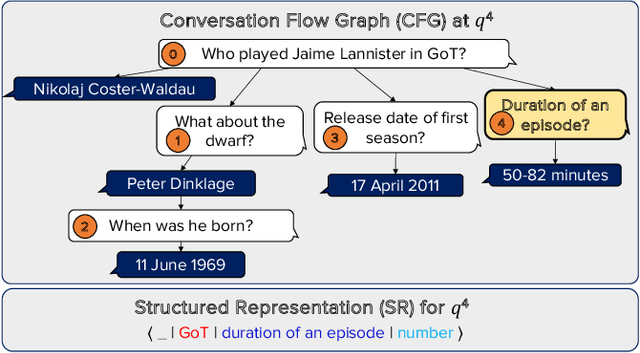

Abstract:Conversational question answering (ConvQA) tackles sequential information needs where contexts in follow-up questions are left implicit. Current ConvQA systems operate over homogeneous sources of information: either a knowledge base (KB), or a text corpus, or a collection of tables. This paper addresses the novel issue of jointly tapping into all of these together, this way boosting answer coverage and confidence. We present CONVINSE, an end-to-end pipeline for ConvQA over heterogeneous sources, operating in three stages: i) learning an explicit structured representation of an incoming question and its conversational context, ii) harnessing this frame-like representation to uniformly capture relevant evidences from KB, text, and tables, and iii) running a fusion-in-decoder model to generate the answer. We construct and release the first benchmark, ConvMix, for ConvQA over heterogeneous sources, comprising 3000 real-user conversations with 16000 questions, along with entity annotations, completed question utterances, and question paraphrases. Experiments demonstrate the viability and advantages of our method, compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
Efficient Contextualization using Top-k Operators for Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs
Aug 21, 2021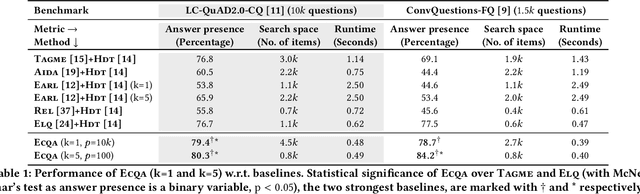
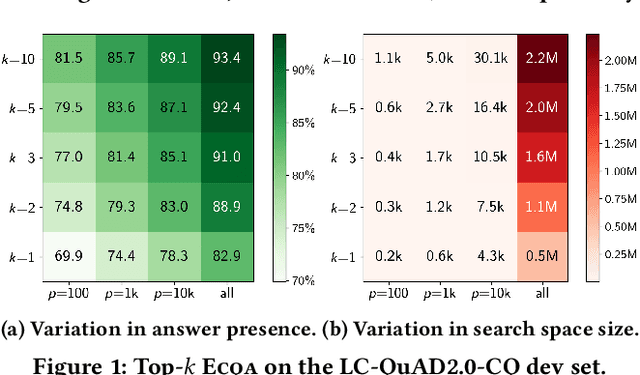
Abstract:Answering complex questions over knowledge bases (KB-QA) faces huge input data with billions of facts, involving millions of entities and thousands of predicates. For efficiency, QA systems first reduce the answer search space by identifying a set of facts that is likely to contain all answers and relevant cues. The most common technique is to apply named entity disambiguation (NED) systems to the question, and retrieve KB facts for the disambiguated entities. This work presents ECQA, an efficient method that prunes irrelevant parts of the search space using KB-aware signals. ECQA is based on top-k query processing over score-ordered lists of KB items that combine signals about lexical matching, relevance to the question, coherence among candidate items, and connectivity in the KB graph. Experiments with two recent QA benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of ECQA over state-of-the-art baselines with respect to answer presence, size of the search space, and runtimes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge