Philip Mathew
Mirror Mirror on the Wall, Have I Forgotten it All? A New Framework for Evaluating Machine Unlearning
May 13, 2025Abstract:Machine unlearning methods take a model trained on a dataset and a forget set, then attempt to produce a model as if it had only been trained on the examples not in the forget set. We empirically show that an adversary is able to distinguish between a mirror model (a control model produced by retraining without the data to forget) and a model produced by an unlearning method across representative unlearning methods from the literature. We build distinguishing algorithms based on evaluation scores in the literature (i.e. membership inference scores) and Kullback-Leibler divergence. We propose a strong formal definition for machine unlearning called computational unlearning. Computational unlearning is defined as the inability for an adversary to distinguish between a mirror model and a model produced by an unlearning method. If the adversary cannot guess better than random (except with negligible probability), then we say that an unlearning method achieves computational unlearning. Our computational unlearning definition provides theoretical structure to prove unlearning feasibility results. For example, our computational unlearning definition immediately implies that there are no deterministic computational unlearning methods for entropic learning algorithms. We also explore the relationship between differential privacy (DP)-based unlearning methods and computational unlearning, showing that DP-based approaches can satisfy computational unlearning at the cost of an extreme utility collapse. These results demonstrate that current methodology in the literature fundamentally falls short of achieving computational unlearning. We conclude by identifying several open questions for future work.
Evaluating Trade-offs in Computer Vision Between Attribute Privacy, Fairness and Utility
Feb 15, 2023



Abstract:This paper investigates to what degree and magnitude tradeoffs exist between utility, fairness and attribute privacy in computer vision. Regarding privacy, we look at this important problem specifically in the context of attribute inference attacks, a less addressed form of privacy. To create a variety of models with different preferences, we use adversarial methods to intervene on attributes relating to fairness and privacy. We see that that certain tradeoffs exist between fairness and utility, privacy and utility, and between privacy and fairness. The results also show that those tradeoffs and interactions are more complex and nonlinear between the three goals than intuition would suggest.
EdgeMixup: Improving Fairness for Skin Disease Classification and Segmentation
Feb 28, 2022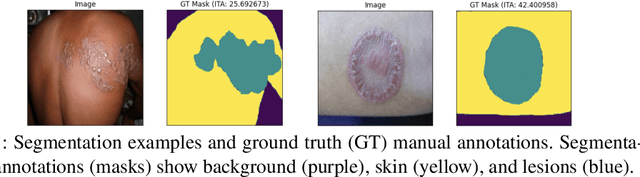
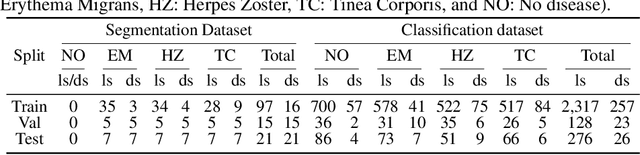

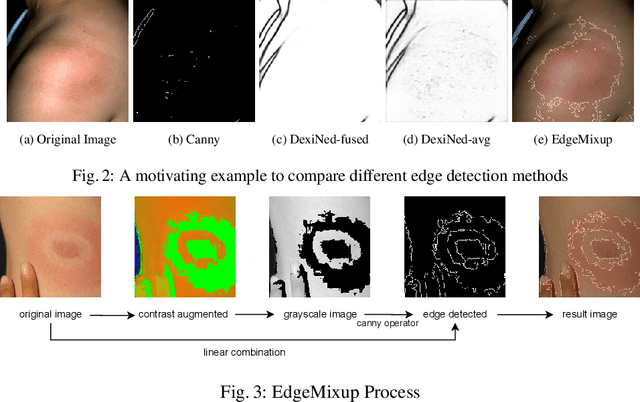
Abstract:Skin lesions can be an early indicator of a wide range of infectious and other diseases. The use of deep learning (DL) models to diagnose skin lesions has great potential in assisting clinicians with prescreening patients. However, these models often learn biases inherent in training data, which can lead to a performance gap in the diagnosis of people with light and/or dark skin tones. To the best of our knowledge, limited work has been done on identifying, let alone reducing, model bias in skin disease classification and segmentation. In this paper, we examine DL fairness and demonstrate the existence of bias in classification and segmentation models for subpopulations with darker skin tones compared to individuals with lighter skin tones, for specific diseases including Lyme, Tinea Corporis and Herpes Zoster. Then, we propose a novel preprocessing, data alteration method, called EdgeMixup, to improve model fairness with a linear combination of an input skin lesion image and a corresponding a predicted edge detection mask combined with color saturation alteration. For the task of skin disease classification, EdgeMixup outperforms much more complex competing methods such as adversarial approaches, achieving a 10.99% reduction in accuracy gap between light and dark skin tone samples, and resulting in 8.4% improved performance for an underrepresented subpopulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge