Phil Chowienczyk
Automated Quality Controlled Analysis of 2D Phase Contrast Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Sep 28, 2022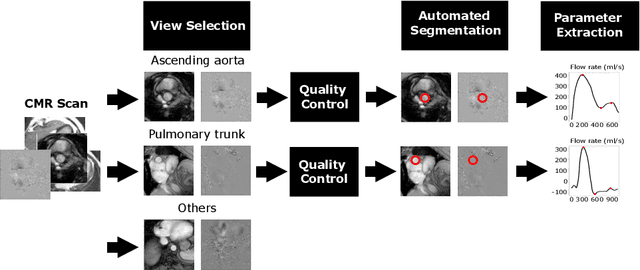
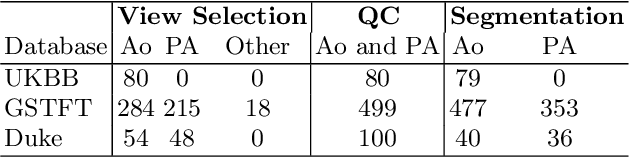
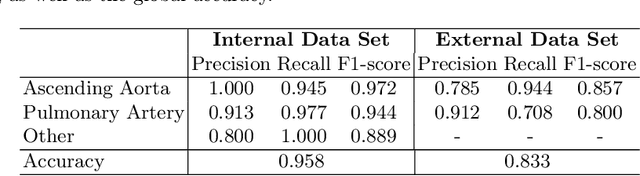
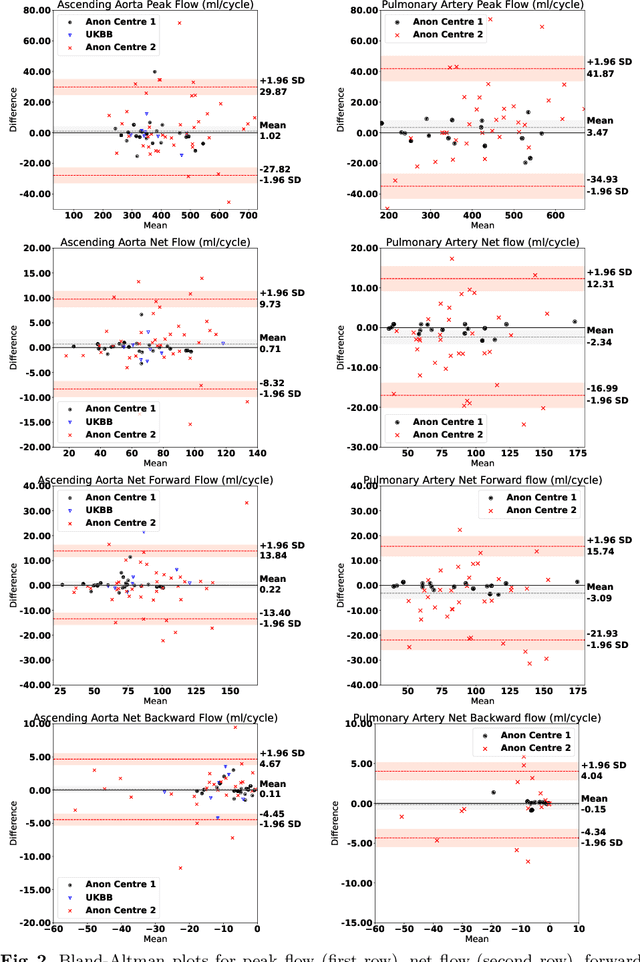
Abstract:Flow analysis carried out using phase contrast cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (PC-CMR) enables the quantification of important parameters that are used in the assessment of cardiovascular function. An essential part of this analysis is the identification of the correct CMR views and quality control (QC) to detect artefacts that could affect the flow quantification. We propose a novel deep learning based framework for the fully-automated analysis of flow from full CMR scans that first carries out these view selection and QC steps using two sequential convolutional neural networks, followed by automatic aorta and pulmonary artery segmentation to enable the quantification of key flow parameters. Accuracy values of 0.958 and 0.914 were obtained for view classification and QC, respectively. For segmentation, Dice scores were $>$0.969 and the Bland-Altman plots indicated excellent agreement between manual and automatic peak flow values. In addition, we tested our pipeline on an external validation data set, with results indicating good robustness of the pipeline. This work was carried out using multivendor clinical data consisting of 986 cases, indicating the potential for the use of this pipeline in a clinical setting.
AI-enabled Assessment of Cardiac Systolic and Diastolic Function from Echocardiography
Mar 21, 2022
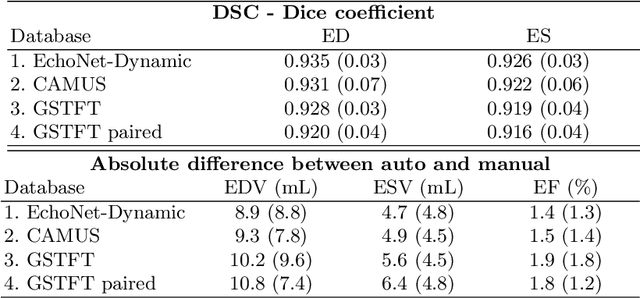
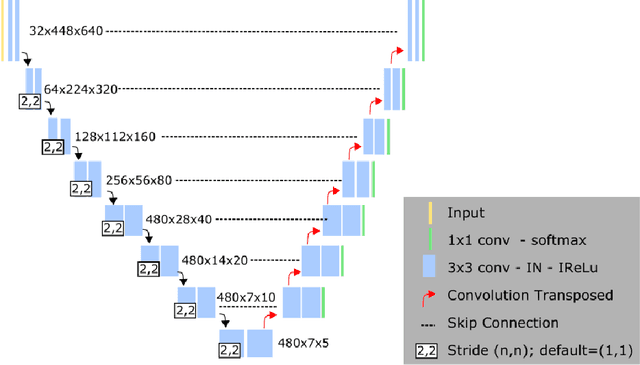
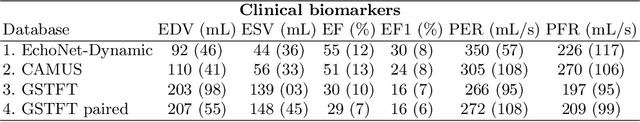
Abstract:Left ventricular (LV) function is an important factor in terms of patient management, outcome, and long-term survival of patients with heart disease. The most recently published clinical guidelines for heart failure recognise that over reliance on only one measure of cardiac function (LV ejection fraction) as a diagnostic and treatment stratification biomarker is suboptimal. Recent advances in AI-based echocardiography analysis have shown excellent results on automated estimation of LV volumes and LV ejection fraction. However, from time-varying 2-D echocardiography acquisition, a richer description of cardiac function can be obtained by estimating functional biomarkers from the complete cardiac cycle. In this work we propose for the first time an AI approach for deriving advanced biomarkers of systolic and diastolic LV function from 2-D echocardiography based on segmentations of the full cardiac cycle. These biomarkers will allow clinicians to obtain a much richer picture of the heart in health and disease. The AI model is based on the 'nn-Unet' framework and was trained and tested using four different databases. Results show excellent agreement between manual and automated analysis and showcase the potential of the advanced systolic and diastolic biomarkers for patient stratification. Finally, for a subset of 50 cases, we perform a correlation analysis between clinical biomarkers derived from echocardiography and CMR and we show excellent agreement between the two modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge