Pengcheng Xia
Multi-modal cross-domain mixed fusion model with dual disentanglement for fault diagnosis under unseen working conditions
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Intelligent fault diagnosis has become an indispensable technique for ensuring machinery reliability. However, existing methods suffer significant performance decline in real-world scenarios where models are tested under unseen working conditions, while domain adaptation approaches are limited to their reliance on target domain samples. Moreover, most existing studies rely on single-modal sensing signals, overlooking the complementary nature of multi-modal information for improving model generalization. To address these limitations, this paper proposes a multi-modal cross-domain mixed fusion model with dual disentanglement for fault diagnosis. A dual disentanglement framework is developed to decouple modality-invariant and modality-specific features, as well as domain-invariant and domain-specific representations, enabling both comprehensive multi-modal representation learning and robust domain generalization. A cross-domain mixed fusion strategy is designed to randomly mix modality information across domains for modality and domain diversity augmentation. Furthermore, a triple-modal fusion mechanism is introduced to adaptively integrate multi-modal heterogeneous information. Extensive experiments are conducted on induction motor fault diagnosis under both unseen constant and time-varying working conditions. The results demonstrate that the proposed method consistently outperforms advanced methods and comprehensive ablation studies further verify the effectiveness of each proposed component and multi-modal fusion. The code is available at: https://github.com/xiapc1996/MMDG.
DAWN: Dynamic Frame Avatar with Non-autoregressive Diffusion Framework for Talking Head Video Generation
Oct 17, 2024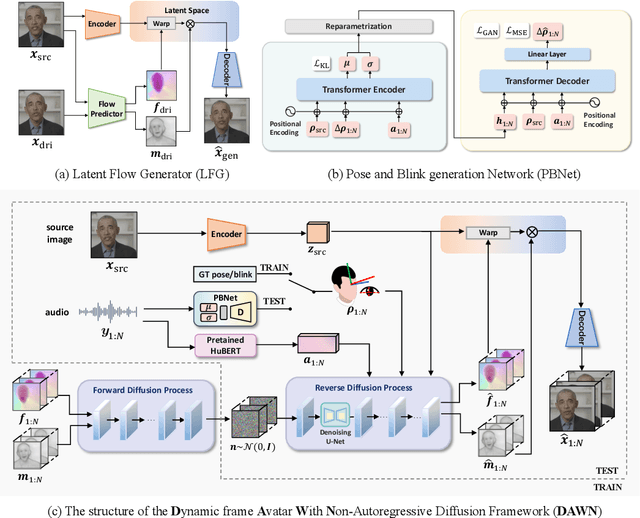
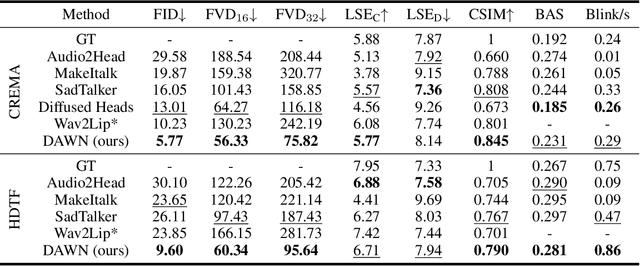


Abstract:Talking head generation intends to produce vivid and realistic talking head videos from a single portrait and speech audio clip. Although significant progress has been made in diffusion-based talking head generation, almost all methods rely on autoregressive strategies, which suffer from limited context utilization beyond the current generation step, error accumulation, and slower generation speed. To address these challenges, we present DAWN (Dynamic frame Avatar With Non-autoregressive diffusion), a framework that enables all-at-once generation of dynamic-length video sequences. Specifically, it consists of two main components: (1) audio-driven holistic facial dynamics generation in the latent motion space, and (2) audio-driven head pose and blink generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method generates authentic and vivid videos with precise lip motions, and natural pose/blink movements. Additionally, with a high generation speed, DAWN possesses strong extrapolation capabilities, ensuring the stable production of high-quality long videos. These results highlight the considerable promise and potential impact of DAWN in the field of talking head video generation. Furthermore, we hope that DAWN sparks further exploration of non-autoregressive approaches in diffusion models. Our code will be publicly at https://github.com/Hanbo-Cheng/DAWN-pytorch.
AutoKary2022: A Large-Scale Densely Annotated Dateset for Chromosome Instance Segmentation
Mar 31, 2023Abstract:Automated chromosome instance segmentation from metaphase cell microscopic images is critical for the diagnosis of chromosomal disorders (i.e., karyotype analysis). However, it is still a challenging task due to lacking of densely annotated datasets and the complicated morphologies of chromosomes, e.g., dense distribution, arbitrary orientations, and wide range of lengths. To facilitate the development of this area, we take a big step forward and manually construct a large-scale densely annotated dataset named AutoKary2022, which contains over 27,000 chromosome instances in 612 microscopic images from 50 patients. Specifically, each instance is annotated with a polygonal mask and a class label to assist in precise chromosome detection and segmentation. On top of it, we systematically investigate representative methods on this dataset and obtain a number of interesting findings, which helps us have a deeper understanding of the fundamental problems in chromosome instance segmentation. We hope this dataset could advance research towards medical understanding. The dataset can be available at: https://github.com/wangjuncongyu/chromosome-instance-segmentation-dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge