Pavithra Srinath
Improving Long-Term Metrics in Recommendation Systems using Short-Horizon Offline RL
Jun 01, 2021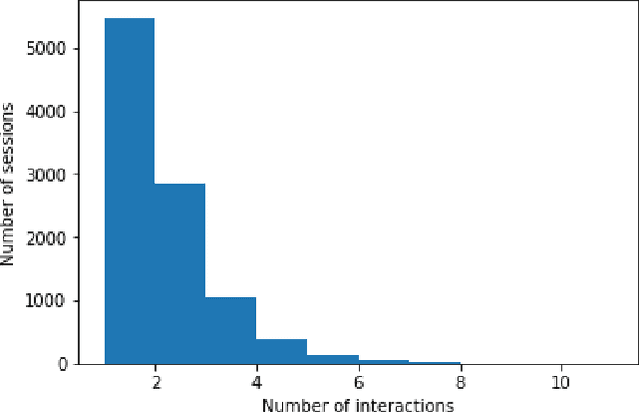
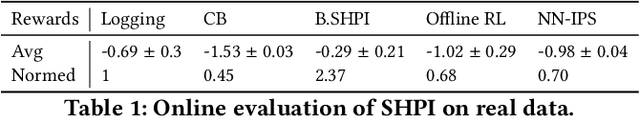
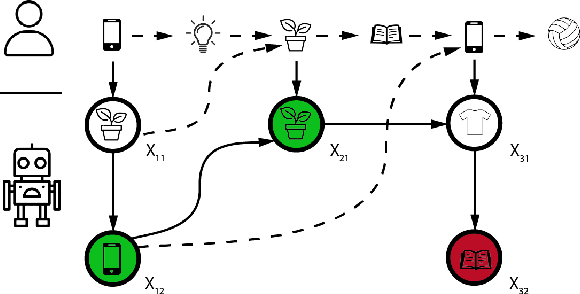

Abstract:We study session-based recommendation scenarios where we want to recommend items to users during sequential interactions to improve their long-term utility. Optimizing a long-term metric is challenging because the learning signal (whether the recommendations achieved their desired goals) is delayed and confounded by other user interactions with the system. Immediately measurable proxies such as clicks can lead to suboptimal recommendations due to misalignment with the long-term metric. Many works have applied episodic reinforcement learning (RL) techniques for session-based recommendation but these methods do not account for policy-induced drift in user intent across sessions. We develop a new batch RL algorithm called Short Horizon Policy Improvement (SHPI) that approximates policy-induced distribution shifts across sessions. By varying the horizon hyper-parameter in SHPI, we recover well-known policy improvement schemes in the RL literature. Empirical results on four recommendation tasks show that SHPI can outperform matrix factorization, offline bandits, and offline RL baselines. We also provide a stable and computationally efficient implementation using weighted regression oracles.
Adaptive Estimator Selection for Off-Policy Evaluation
Feb 18, 2020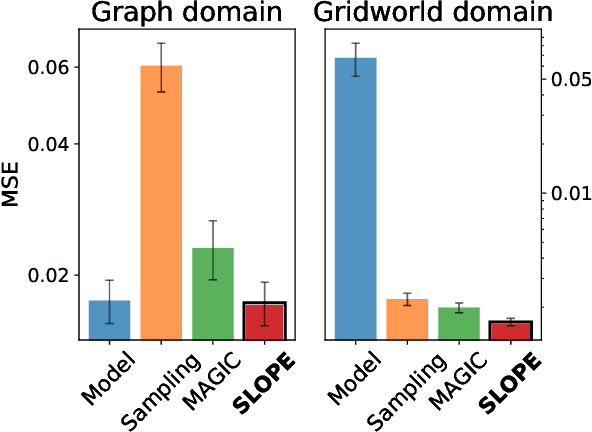
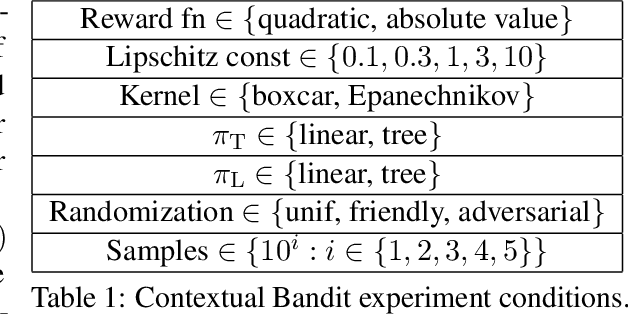
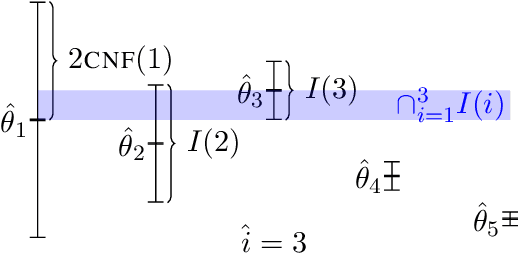

Abstract:We develop a generic data-driven method for estimator selection in off-policy policy evaluation settings. We establish a strong performance guarantee for the method, showing that it is competitive with the oracle estimator, up to a constant factor. Via in-depth case studies in contextual bandits and reinforcement learning, we demonstrate the generality and applicability of the method. We also perform comprehensive experiments, demonstrating the empirical efficacy of our approach and comparing with related approaches. In both case studies, our method compares favorably with existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge