Paul Ullrich
Spatiotemporally adaptive compression for scientific dataset with feature preservation -- a case study on simulation data with extreme climate events analysis
Jan 06, 2024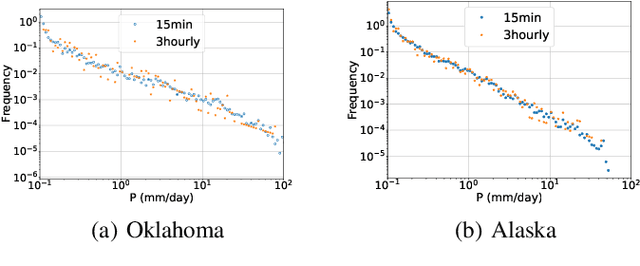
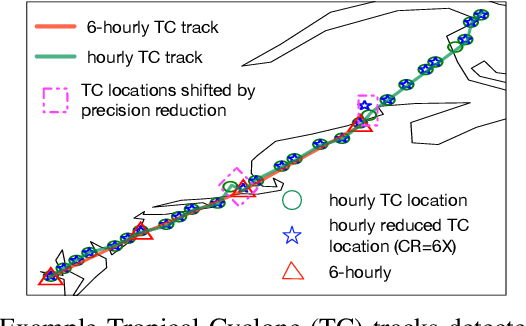
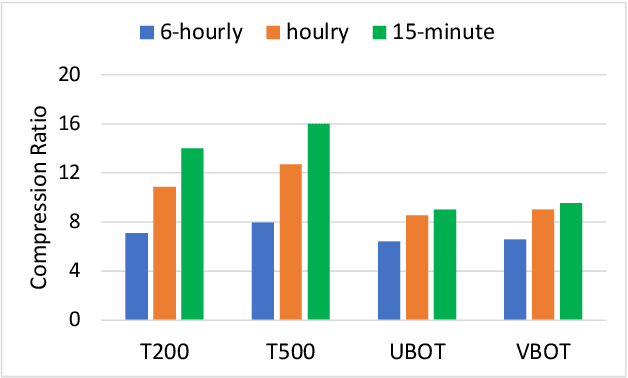
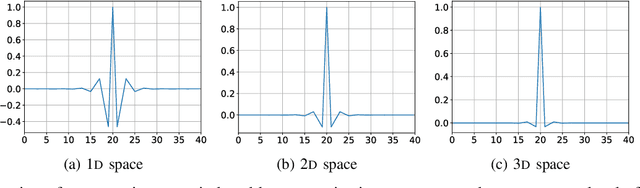
Abstract:Scientific discoveries are increasingly constrained by limited storage space and I/O capacities. For time-series simulations and experiments, their data often need to be decimated over timesteps to accommodate storage and I/O limitations. In this paper, we propose a technique that addresses storage costs while improving post-analysis accuracy through spatiotemporal adaptive, error-controlled lossy compression. We investigate the trade-off between data precision and temporal output rates, revealing that reducing data precision and increasing timestep frequency lead to more accurate analysis outcomes. Additionally, we integrate spatiotemporal feature detection with data compression and demonstrate that performing adaptive error-bounded compression in higher dimensional space enables greater compression ratios, leveraging the error propagation theory of a transformation-based compressor. To evaluate our approach, we conduct experiments using the well-known E3SM climate simulation code and apply our method to compress variables used for cyclone tracking. Our results show a significant reduction in storage size while enhancing the quality of cyclone tracking analysis, both quantitatively and qualitatively, in comparison to the prevalent timestep decimation approach. Compared to three state-of-the-art lossy compressors lacking feature preservation capabilities, our adaptive compression framework improves perfectly matched cases in TC tracking by 26.4-51.3% at medium compression ratios and by 77.3-571.1% at large compression ratios, with a merely 5-11% computational overhead.
* 10 pages, 13 figures, 2023 IEEE International Conference on e-Science and Grid Computing
AutoML-based Almond Yield Prediction and Projection in California
Nov 08, 2022



Abstract:Almonds are one of the most lucrative products of California, but are also among the most sensitive to climate change. In order to better understand the relationship between climatic factors and almond yield, an automated machine learning framework is used to build a collection of machine learning models. The prediction skill is assessed using historical records. Future projections are derived using 17 downscaled climate outputs. The ensemble mean projection displays almond yield changes under two different climate scenarios, along with two technology development scenarios, where the role of technology development is highlighted. The mean projections and distributions provide insightful results to stakeholders and can be utilized by policymakers for climate adaptation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge