Patrick Llull
Compressive Hyperspectral Imaging with Side Information
Feb 22, 2015


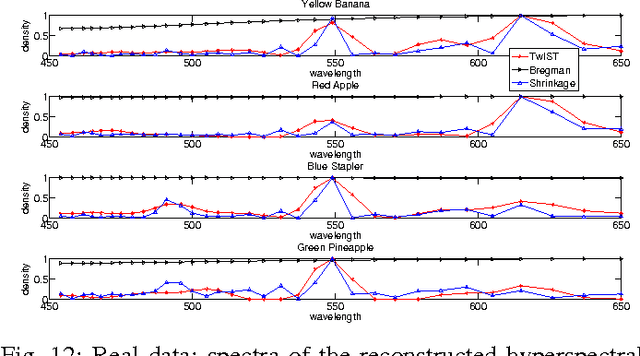
Abstract:A blind compressive sensing algorithm is proposed to reconstruct hyperspectral images from spectrally-compressed measurements.The wavelength-dependent data are coded and then superposed, mapping the three-dimensional hyperspectral datacube to a two-dimensional image. The inversion algorithm learns a dictionary {\em in situ} from the measurements via global-local shrinkage priors. By using RGB images as side information of the compressive sensing system, the proposed approach is extended to learn a coupled dictionary from the joint dataset of the compressed measurements and the corresponding RGB images, to improve reconstruction quality. A prototype camera is built using a liquid-crystal-on-silicon modulator. Experimental reconstructions of hyperspectral datacubes from both simulated and real compressed measurements demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed inversion algorithm, the feasibility of the camera and the benefit of side information.
Tree-Structure Bayesian Compressive Sensing for Video
Oct 12, 2014



Abstract:A Bayesian compressive sensing framework is developed for video reconstruction based on the color coded aperture compressive temporal imaging (CACTI) system. By exploiting the three dimension (3D) tree structure of the wavelet and Discrete Cosine Transformation (DCT) coefficients, a Bayesian compressive sensing inversion algorithm is derived to reconstruct (up to 22) color video frames from a single monochromatic compressive measurement. Both simulated and real datasets are adopted to verify the performance of the proposed algorithm.
Low-Cost Compressive Sensing for Color Video and Depth
Feb 27, 2014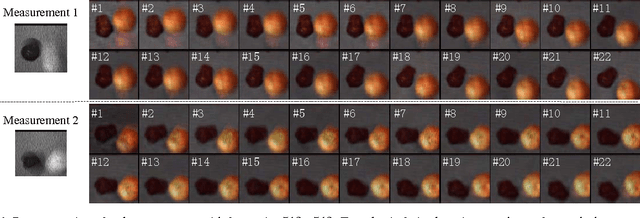



Abstract:A simple and inexpensive (low-power and low-bandwidth) modification is made to a conventional off-the-shelf color video camera, from which we recover {multiple} color frames for each of the original measured frames, and each of the recovered frames can be focused at a different depth. The recovery of multiple frames for each measured frame is made possible via high-speed coding, manifested via translation of a single coded aperture; the inexpensive translation is constituted by mounting the binary code on a piezoelectric device. To simultaneously recover depth information, a {liquid} lens is modulated at high speed, via a variable voltage. Consequently, during the aforementioned coding process, the liquid lens allows the camera to sweep the focus through multiple depths. In addition to designing and implementing the camera, fast recovery is achieved by an anytime algorithm exploiting the group-sparsity of wavelet/DCT coefficients.
Adaptive Temporal Compressive Sensing for Video
Oct 15, 2013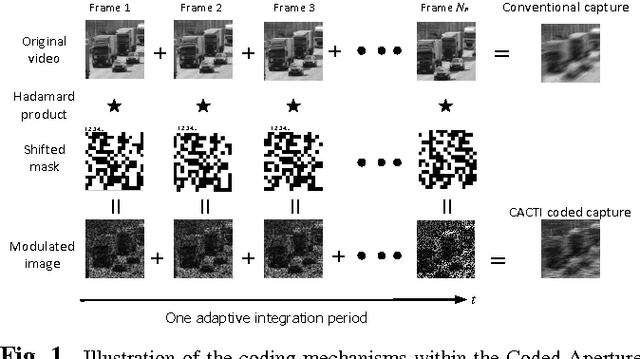


Abstract:This paper introduces the concept of adaptive temporal compressive sensing (CS) for video. We propose a CS algorithm to adapt the compression ratio based on the scene's temporal complexity, computed from the compressed data, without compromising the quality of the reconstructed video. The temporal adaptivity is manifested by manipulating the integration time of the camera, opening the possibility to real-time implementation. The proposed algorithm is a generalized temporal CS approach that can be incorporated with a diverse set of existing hardware systems.
Coded aperture compressive temporal imaging
Feb 04, 2013
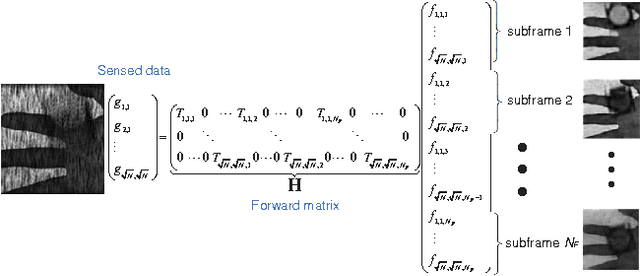

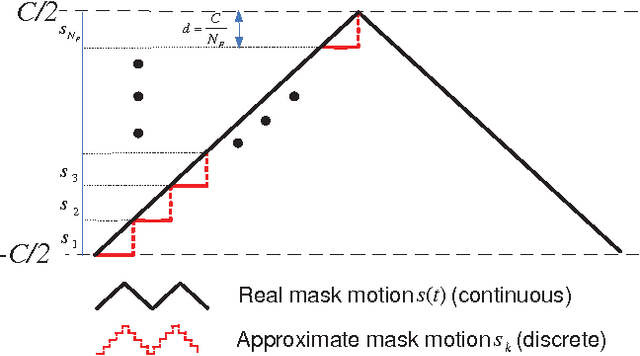
Abstract:We use mechanical translation of a coded aperture for code division multiple access compression of video. We present experimental results for reconstruction at 148 frames per coded snapshot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge