Patrick Ernst
Learning from Relevant Subgoals in Successful Dialogs using Iterative Training for Task-oriented Dialog Systems
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Task-oriented Dialog (ToD) systems have to solve multiple subgoals to accomplish user goals, whereas feedback is often obtained only at the end of the dialog. In this work, we propose SUIT (SUbgoal-aware ITerative Training), an iterative training approach for improving ToD systems. We sample dialogs from the model we aim to improve and determine subgoals that contribute to dialog success using distant supervision to obtain high quality training samples. We show how this data improves supervised fine-tuning or, alternatively, preference learning results. SUIT is able to iteratively generate more data instead of relying on fixed static sets. SUIT reaches new state-of-the-art performance on a popular ToD benchmark.
Calibrating Verbalized Probabilities for Large Language Models
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:Calibrating verbalized probabilities presents a novel approach for reliably assessing and leveraging outputs from black-box Large Language Models (LLMs). Recent methods have demonstrated improved calibration by applying techniques like Platt scaling or temperature scaling to the confidence scores generated by LLMs. In this paper, we explore the calibration of verbalized probability distributions for discriminative tasks. First, we investigate the capability of LLMs to generate probability distributions over categorical labels. We theoretically and empirically identify the issue of re-softmax arising from the scaling of verbalized probabilities, and propose using the invert softmax trick to approximate the "logit" by inverting verbalized probabilities. Through extensive evaluation on three public datasets, we demonstrate: (1) the robust capability of LLMs in generating class distributions, and (2) the effectiveness of the invert softmax trick in estimating logits, which, in turn, facilitates post-calibration adjustments.
Deploying a Retrieval based Response Model for Task Oriented Dialogues
Oct 25, 2022


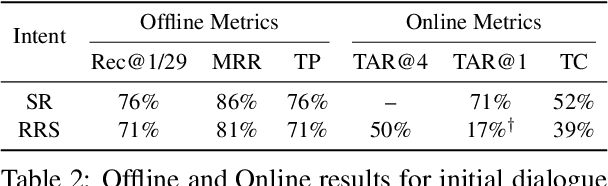
Abstract:Task-oriented dialogue systems in industry settings need to have high conversational capability, be easily adaptable to changing situations and conform to business constraints. This paper describes a 3-step procedure to develop a conversational model that satisfies these criteria and can efficiently scale to rank a large set of response candidates. First, we provide a simple algorithm to semi-automatically create a high-coverage template set from historic conversations without any annotation. Second, we propose a neural architecture that encodes the dialogue context and applicable business constraints as profile features for ranking the next turn. Third, we describe a two-stage learning strategy with self-supervised training, followed by supervised fine-tuning on limited data collected through a human-in-the-loop platform. Finally, we describe offline experiments and present results of deploying our model with human-in-the-loop to converse with live customers online.
Taming Continuous Posteriors for Latent Variational Dialogue Policies
May 16, 2022



Abstract:Utilizing amortized variational inference for latent-action reinforcement learning (RL) has been shown to be an effective approach in Task-oriented Dialogue (ToD) systems for optimizing dialogue success. Until now, categorical posteriors have been argued to be one of the main drivers of performance. In this work we revisit Gaussian variational posteriors for latent-action RL and show that they can yield even better performance than categoricals. We achieve this by simplifying the training procedure and propose ways to regularize the latent dialogue policy to retain good response coherence. Using continuous latent representations our model achieves state of the art dialogue success rate on the MultiWOZ benchmark, and also compares well to categorical latent methods in response coherence.
Learning to Rank in the Position Based Model with Bandit Feedback
Apr 27, 2020



Abstract:Personalization is a crucial aspect of many online experiences. In particular, content ranking is often a key component in delivering sophisticated personalization results. Commonly, supervised learning-to-rank methods are applied, which suffer from bias introduced during data collection by production systems in charge of producing the ranking. To compensate for this problem, we leverage contextual multi-armed bandits. We propose novel extensions of two well-known algorithms viz. LinUCB and Linear Thompson Sampling to the ranking use-case. To account for the biases in a production environment, we employ the position-based click model. Finally, we show the validity of the proposed algorithms by conducting extensive offline experiments on synthetic datasets as well as customer facing online A/B experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge