Paschalis C. Sofotasios
An Effective Spatial Modulation Based Scheme for Indoor VLC Systems
Jan 19, 2022Abstract:We propose an enhanced spatial modulation (SM)-based scheme for indoor visible light communication systems. This scheme enhances the achievable throughput of conventional SM schemes by transmitting higher order complex modulation symbol, which is decomposed into three different parts. These parts carry the amplitude, phase, and quadrant components of the complex symbol, which are then represented by unipolar pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) symbols. Superposition coding is exploited to allocate a fraction of the total power to each part before they are all multiplexed and transmitted simultaneously, exploiting the entire available bandwidth. At the receiver, a two-step decoding process is proposed to decode the active light emitting diode index before the complex symbol is retrieved. It is shown that at higher spectral efficiency values, the proposed modulation scheme outperforms conventional SM schemes with PAM symbols in terms of average symbol error rate (ASER), and hence, enhancing the system throughput. Furthermore, since the performance of the proposed modulation scheme is sensitive to the power allocation factors, we formulated an ASER optimization problem and propose a sub-optimal solution using successive convex programming (SCP). Notably, the proposed algorithm converges after only few iterations, whilst the performance with the optimized power allocation coefficients outperforms both random and fixed power allocation.
Space-Time Block Coded Spatial Modulation for Indoor Visible Light Communications
Nov 06, 2021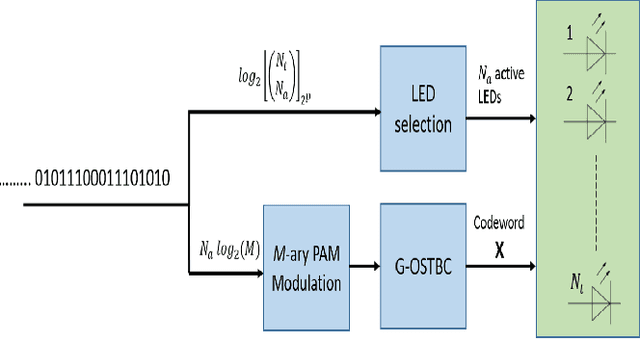
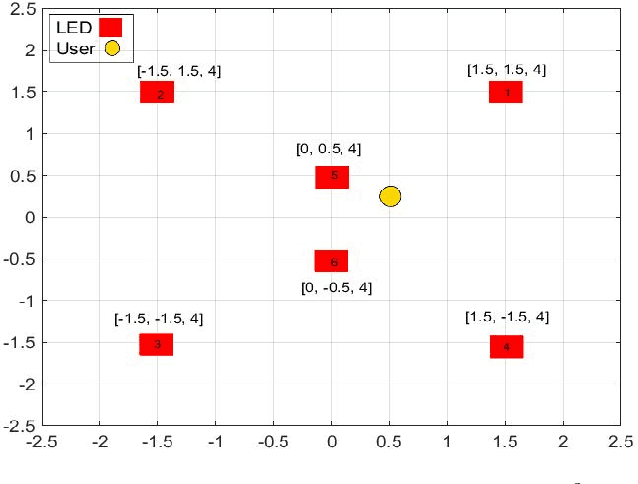
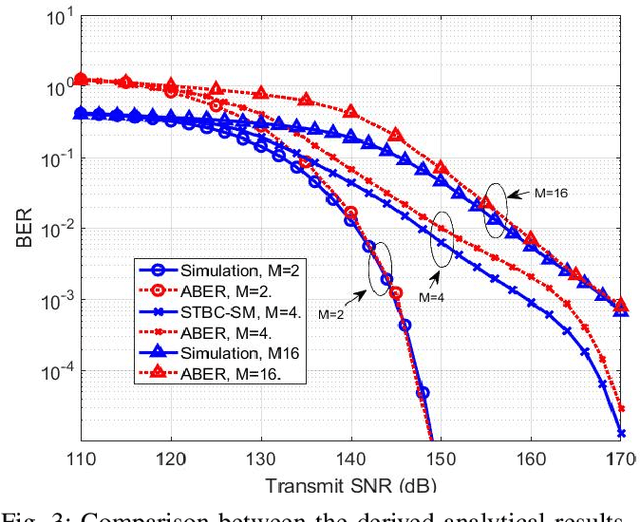
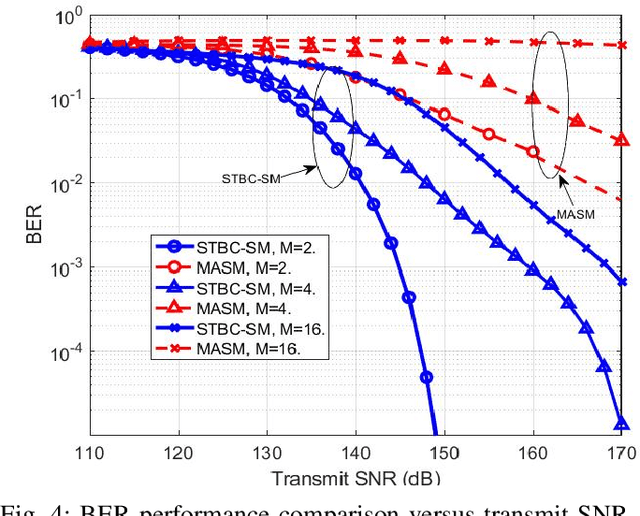
Abstract:Visible light communication (VLC) has been recognized as a promising technology for handling the continuously increasing quality of service and connectivity requirements in modern wireless communications, particularly in indoor scenarios. In this context, the present work considers the integration of two distinct modulation schemes, namely spatial modulation (SM) with space time block codes (STBCs), aiming at improving the overall VLC system reliability. Based on this and in order to further enhance the achievable transmission data rate, we integrate quasi-orthogonal STBC (QOSTBC) with SM, since relaxing the orthogonality condition of OSTBC ultimately provides a higher coding rate. Then, we generalize the developed results to any number of active light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and any M-ary pulse amplitude modulation size. Furthermore, we derive a tight and tractable upper bound for the corresponding bit error rate (BER) by considering a simple two-step decoding procedure to detect the indices of the transmitting LEDs and then decode the signal domain symbols. Notably, the obtained results demonstrate that QOSTBC with SM enhances the achievable BER compared to SM with repetition coding (RC-SM). Finally, we compare STBC-SM with both multiple active SM (MASM) and RC-SM in terms of the achievable BER and overall data rate, which further justifies the usefulness of the proposed scheme.
Towards Federated Learning-Enabled Visible Light Communication in 6G Systems
Oct 07, 2021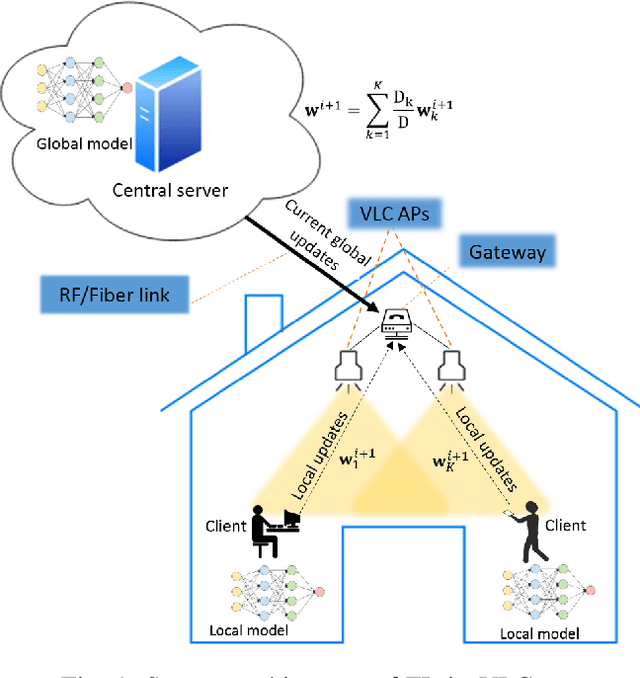
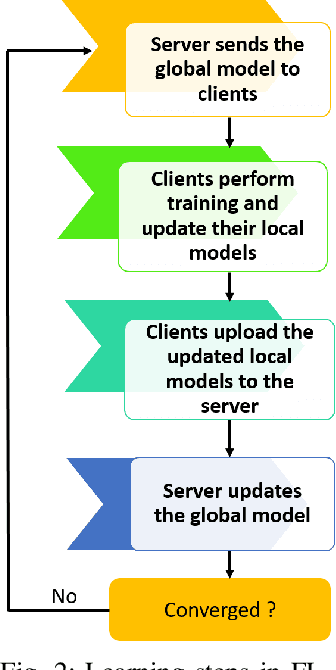
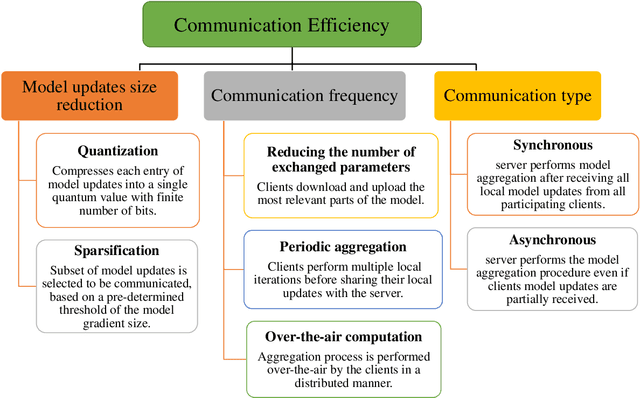
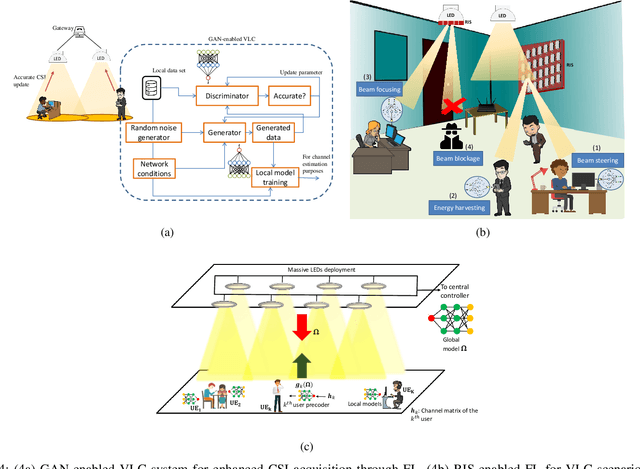
Abstract:Visible light communication (VLC) technology was introduced as a key enabler for the next generation of wireless networks, mainly thanks to its simple and low-cost implementation. However, several challenges prohibit the realization of the full potentials of VLC, namely, limited modulation bandwidth, ambient light interference, optical diffuse reflection effects, devices non-linearity, and random receiver orientation. On the contrary, centralized machine learning (ML) techniques have demonstrated a significant potential in handling different challenges relating to wireless communication systems. Specifically, it was shown that ML algorithms exhibit superior capabilities in handling complicated network tasks, such as channel equalization, estimation and modeling, resources allocation, and opportunistic spectrum access control, to name a few. Nevertheless, concerns pertaining to privacy and communication overhead when sharing raw data of the involved clients with a server constitute major bottlenecks in the implementation of centralized ML techniques. This has motivated the emergence of a new distributed ML paradigm, namely federated learning (FL), which can reduce the cost associated with transferring raw data, and preserve privacy by training ML models locally and collaboratively at the clients' side. Hence, it becomes evident that integrating FL into VLC networks can provide ubiquitous and reliable implementation of VLC systems. With this motivation, this is the first in-depth review in the literature on the application of FL in VLC networks. To that end, besides the different architectures and related characteristics of FL, we provide a thorough overview on the main design aspects of FL based VLC systems. Finally, we also highlight some potential future research directions of FL that are envisioned to substantially enhance the performance and robustness of VLC systems.
Interplay Between NOMA and GSSK: Detection Strategies and Performance Analysis
May 24, 2021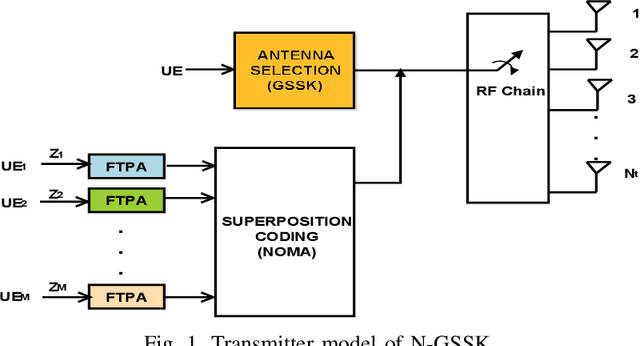
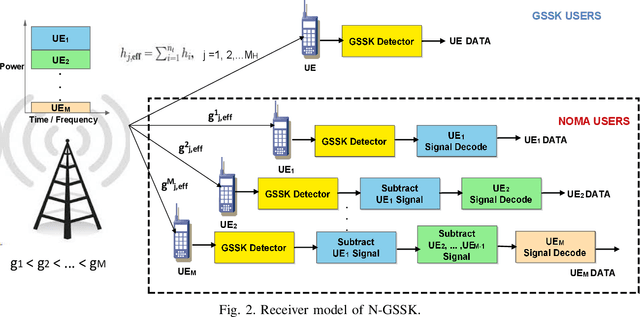
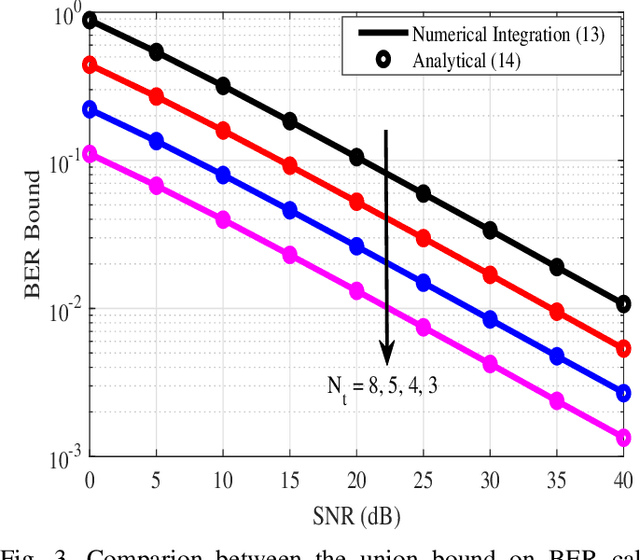
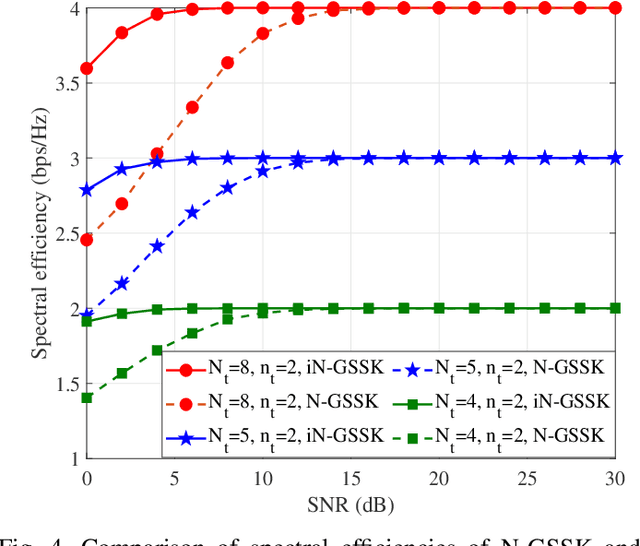
Abstract:Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) is a technology enabler for the fifth generation and beyond networks, which has shown a great flexibility such that it can be readily integrated with other wireless technologies. In this paper, we investigate the interplay between NOMA and generalized space shift keying (GSSK) in a hybrid NOMA-GSSK (N-GSSK) network. Specifically, we provide a comprehensive analytical framework and propose a novel suboptimal energy-based maximum likelihood (ML) detector for the N-GSSK scheme. The proposed ML decoder exploits the energy of the received signals in order to estimate the active antenna indices. Its performance is investigated in terms of pairwise error probability, bit error rate union bound, and achievable rate. Finally, we establish the validity of our analysis through Monte-Carlo simulations and demonstrate that N-GSSK outperforms conventional NOMA and GSSK, particularly in terms of spectral efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge