Omar Ait-Aider
StixelNExT++: Lightweight Monocular Scene Segmentation and Representation for Collective Perception
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:This paper presents StixelNExT++, a novel approach to scene representation for monocular perception systems. Building on the established Stixel representation, our method infers 3D Stixels and enhances object segmentation by clustering smaller 3D Stixel units. The approach achieves high compression of scene information while remaining adaptable to point cloud and bird's-eye-view representations. Our lightweight neural network, trained on automatically generated LiDAR-based ground truth, achieves real-time performance with computation times as low as 10 ms per frame. Experimental results on the Waymo dataset demonstrate competitive performance within a 30-meter range, highlighting the potential of StixelNExT++ for collective perception in autonomous systems.
StixelNExT: Toward Monocular Low-Weight Perception for Object Segmentation and Free Space Detection
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we present a novel approach for general object segmentation from a monocular image, eliminating the need for manually labeled training data and enabling rapid, straightforward training and adaptation with minimal data. Our model initially learns from LiDAR during the training process, which is subsequently removed from the system, allowing it to function solely on monocular imagery. This study leverages the concept of the Stixel-World to recognize a medium level representation of its surroundings. Our network directly predicts a 2D multi-layer Stixel-World and is capable of recognizing and locating multiple, superimposed objects within an image. Due to the scarcity of comparable works, we have divided the capabilities into modules and present a free space detection in our experiments section. Furthermore, we introduce an improved method for generating Stixels from LiDAR data, which we use as ground truth for our network.
The OPNV Data Collection: A Dataset for Infrastructure-Supported Perception Research with Focus on Public Transportation
Jul 11, 2024Abstract:This paper we present our vision and ongoing work for a novel dataset designed to advance research into the interoperability of intelligent vehicles and infrastructure, specifically aimed at enhancing cooperative perception and interaction in the realm of public transportation. Unlike conventional datasets centered on ego-vehicle data, this approach encompasses both a stationary sensor tower and a moving vehicle, each equipped with cameras, LiDARs, and GNSS, while the vehicle additionally includes an inertial navigation system. Our setup features comprehensive calibration and time synchronization, ensuring seamless and accurate sensor data fusion crucial for studying complex, dynamic scenes. Emphasizing public transportation, the dataset targets to include scenes like bus station maneuvers and driving on dedicated bus lanes, reflecting the specifics of small public buses. We introduce the open-source ".4mse" file format for the new dataset, accompanied by a research kit. This kit provides tools such as ego-motion compensation or LiDAR-to-camera projection enabling advanced research on intelligent vehicle-infrastructure integration. Our approach does not include annotations; however, we plan to implement automatically generated labels sourced from state-of-the-art public repositories. Several aspects are still up for discussion, and timely feedback from the community would be greatly appreciated. A sneak preview on one data frame will be available at a Google Colab Notebook. Moreover, we will use the related GitHub Repository to collect remarks and suggestions.
Blur aware metric depth estimation with multi-focus plenoptic cameras
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:While a traditional camera only captures one point of view of a scene, a plenoptic or light-field camera, is able to capture spatial and angular information in a single snapshot, enabling depth estimation from a single acquisition. In this paper, we present a new metric depth estimation algorithm using only raw images from a multi-focus plenoptic camera. The proposed approach is especially suited for the multi-focus configuration where several micro-lenses with different focal lengths are used. The main goal of our blur aware depth estimation (BLADE) approach is to improve disparity estimation for defocus stereo images by integrating both correspondence and defocus cues. We thus leverage blur information where it was previously considered a drawback. We explicitly derive an inverse projection model including the defocus blur providing depth estimates up to a scale factor. A method to calibrate the inverse model is then proposed. We thus take into account depth scaling to achieve precise and accurate metric depth estimates. Our results show that introducing defocus cues improves the depth estimation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework and depth scaling calibration on relative depth estimation setups and on real-world 3D complex scenes with ground truth acquired with a 3D lidar scanner.
Leveraging blur information for plenoptic camera calibration
Nov 09, 2021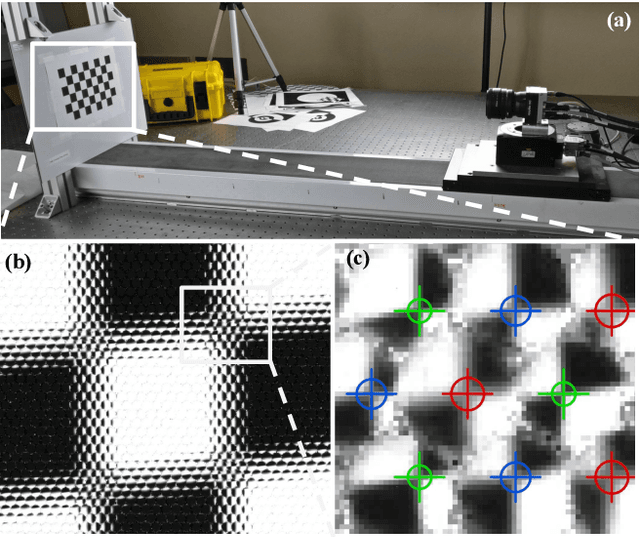
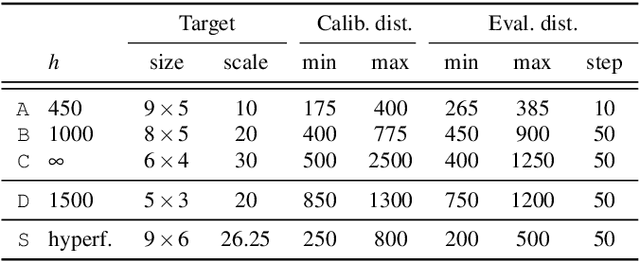
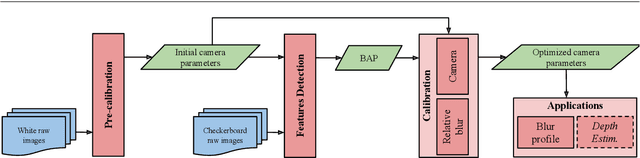
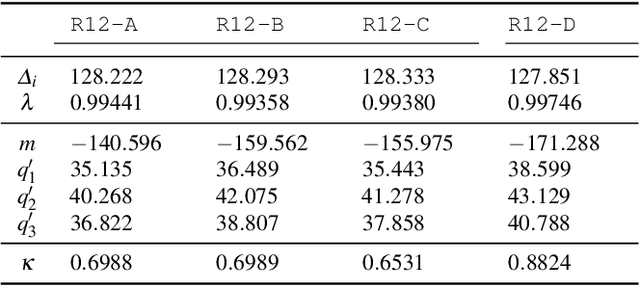
Abstract:This paper presents a novel calibration algorithm for plenoptic cameras, especially the multi-focus configuration, where several types of micro-lenses are used, using raw images only. Current calibration methods rely on simplified projection models, use features from reconstructed images, or require separated calibrations for each type of micro-lens. In the multi-focus configuration, the same part of a scene will demonstrate different amounts of blur according to the micro-lens focal length. Usually, only micro-images with the smallest amount of blur are used. In order to exploit all available data, we propose to explicitly model the defocus blur in a new camera model with the help of our newly introduced Blur Aware Plenoptic (BAP) feature. First, it is used in a pre-calibration step that retrieves initial camera parameters, and second, to express a new cost function to be minimized in our single optimization process. Third, it is exploited to calibrate the relative blur between micro-images. It links the geometric blur, i.e., the blur circle, to the physical blur, i.e., the point spread function. Finally, we use the resulting blur profile to characterize the camera's depth of field. Quantitative evaluations in controlled environment on real-world data demonstrate the effectiveness of our calibrations.
Blur Aware Calibration of Multi-Focus Plenoptic Camera
Apr 16, 2020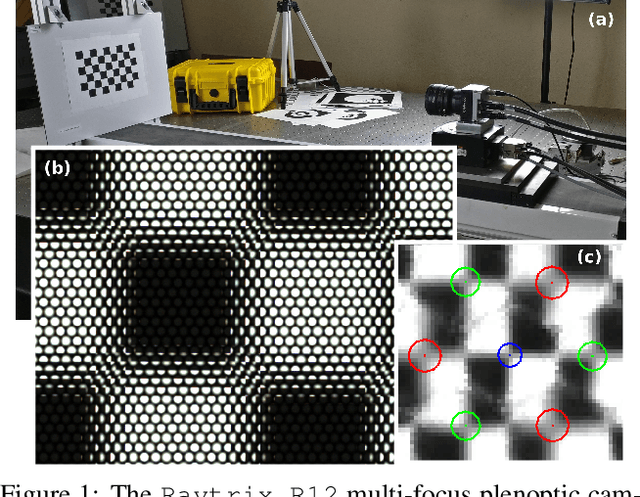
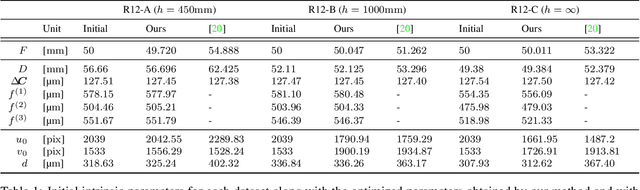
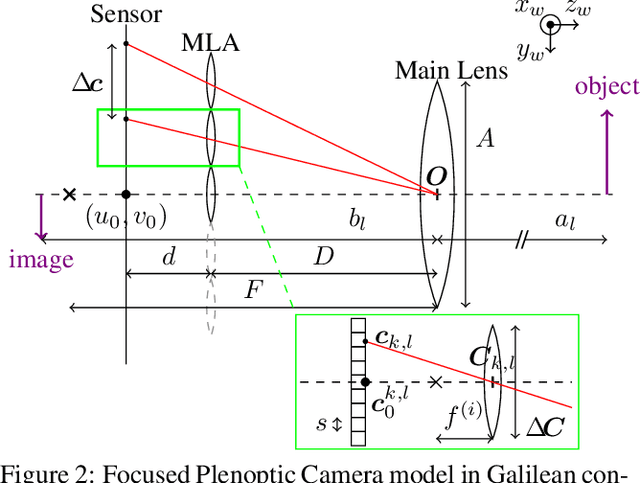
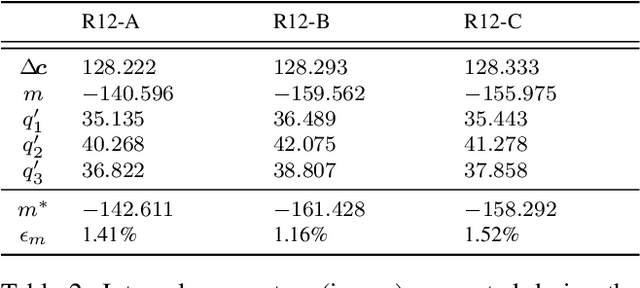
Abstract:This paper presents a novel calibration algorithm for Multi-Focus Plenoptic Cameras (MFPCs) using raw images only. The design of such cameras is usually complex and relies on precise placement of optic elements. Several calibration procedures have been proposed to retrieve the camera parameters but relying on simplified models, reconstructed images to extract features, or multiple calibrations when several types of micro-lens are used. Considering blur information, we propose a new Blur Aware Plenoptic (BAP) feature. It is first exploited in a pre-calibration step that retrieves initial camera parameters, and secondly to express a new cost function for our single optimization process. The effectiveness of our calibration method is validated by quantitative and qualitative experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge