Oksana Yakhnenko
Constructing High Precision Knowledge Bases with Subjective and Factual Attributes
Jun 13, 2019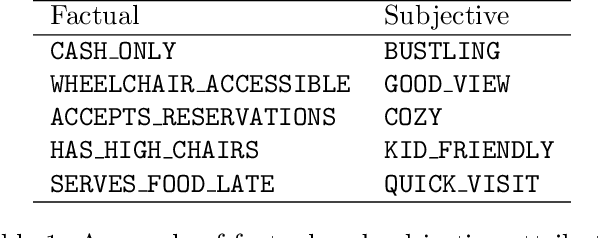
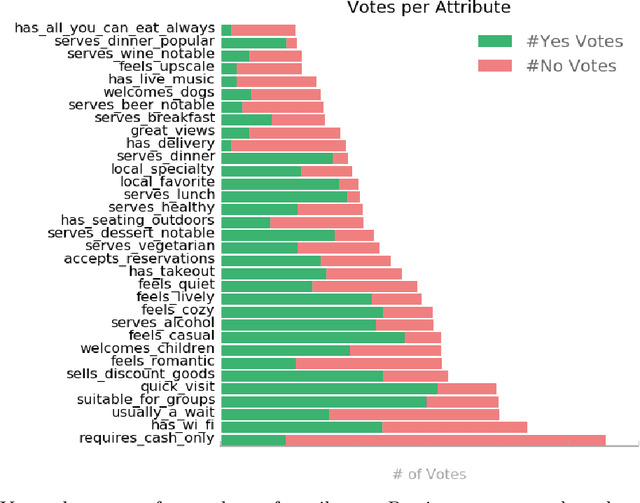
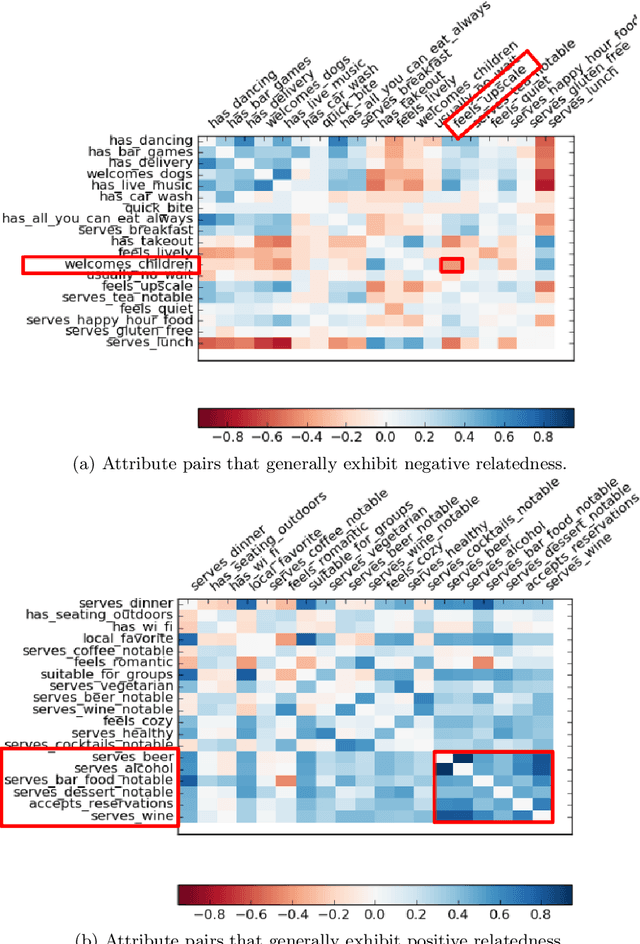
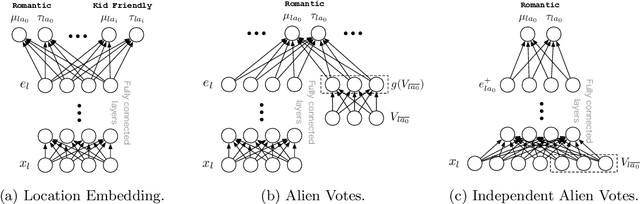
Abstract:Knowledge bases (KBs) are the backbone of many ubiquitous applications and are thus required to exhibit high precision. However, for KBs that store subjective attributes of entities, e.g., whether a movie is "kid friendly", simply estimating precision is complicated by the inherent ambiguity in measuring subjective phenomena. In this work, we develop a method for constructing KBs with tunable precision--i.e., KBs that can be made to operate at a specific false positive rate, despite storing both difficult-to-evaluate subjective attributes and more traditional factual attributes. The key to our approach is probabilistically modeling user consensus with respect to each entity-attribute pair, rather than modeling each pair as either True or False. Uncertainty in the model is explicitly represented and used to control the KB's precision. We propose three neural networks for fitting the consensus model and evaluate each one on data from Google Maps--a large KB of locations and their subjective and factual attributes. The results demonstrate that our learned models are well-calibrated and thus can successfully be used to control the KB's precision. Moreover, when constrained to maintain 95% precision, the best consensus model matches the F-score of a baseline that models each entity-attribute pair as a binary variable and does not support tunable precision. When unconstrained, our model dominates the same baseline by 12% F-score. Finally, we perform an empirical analysis of attribute-attribute correlations and show that leveraging them effectively contributes to reduced uncertainty and better performance in attribute prediction.
Connecting Language and Knowledge Bases with Embedding Models for Relation Extraction
Jul 30, 2013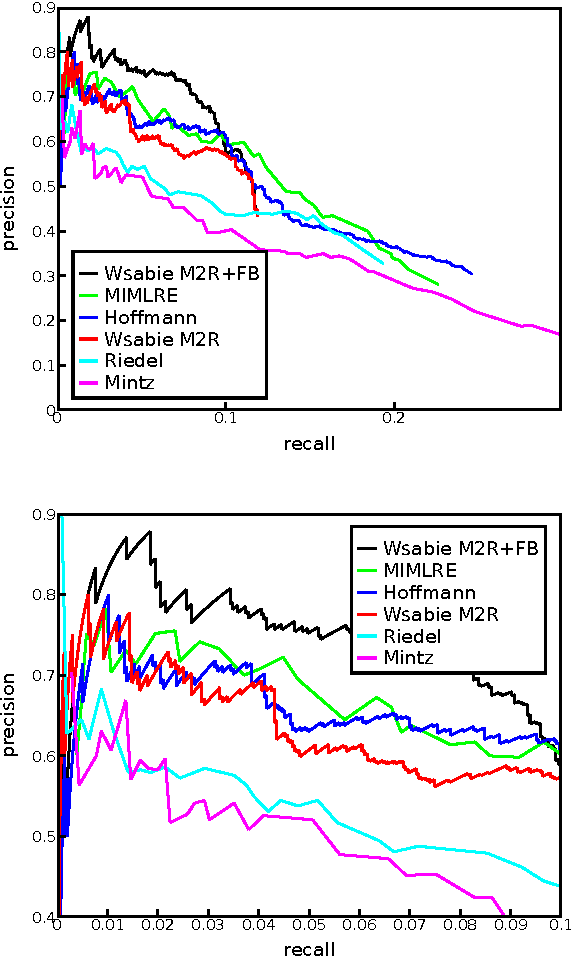
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel approach for relation extraction from free text which is trained to jointly use information from the text and from existing knowledge. Our model is based on two scoring functions that operate by learning low-dimensional embeddings of words and of entities and relationships from a knowledge base. We empirically show on New York Times articles aligned with Freebase relations that our approach is able to efficiently use the extra information provided by a large subset of Freebase data (4M entities, 23k relationships) to improve over existing methods that rely on text features alone.
Irreflexive and Hierarchical Relations as Translations
Apr 26, 2013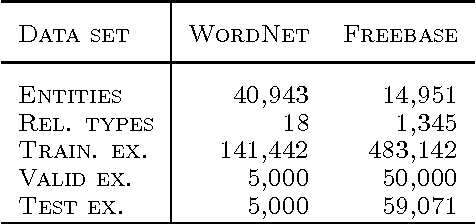
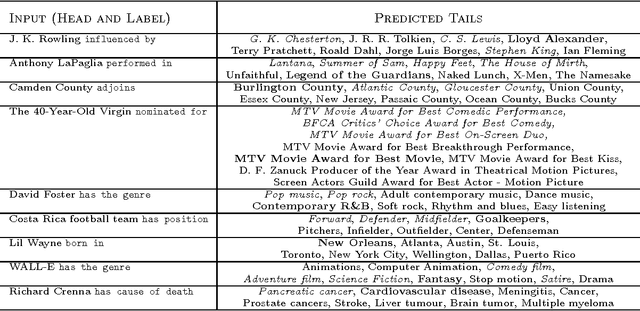
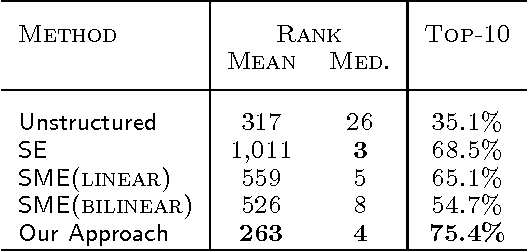
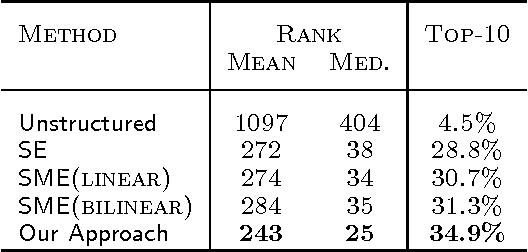
Abstract:We consider the problem of embedding entities and relations of knowledge bases in low-dimensional vector spaces. Unlike most existing approaches, which are primarily efficient for modeling equivalence relations, our approach is designed to explicitly model irreflexive relations, such as hierarchies, by interpreting them as translations operating on the low-dimensional embeddings of the entities. Preliminary experiments show that, despite its simplicity and a smaller number of parameters than previous approaches, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance according to standard evaluation protocols on data from WordNet and Freebase.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge