Nuttapong Chairatanakul
Leaping Through Time with Gradient-based Adaptation for Recommendation
Dec 28, 2021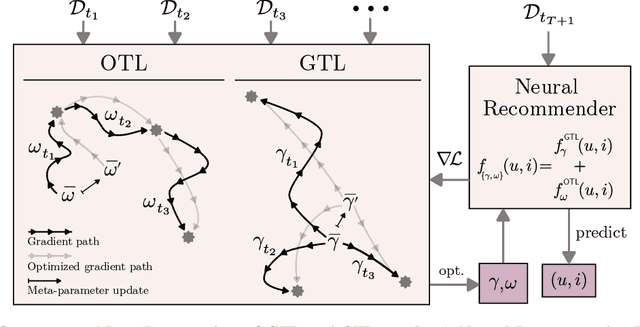
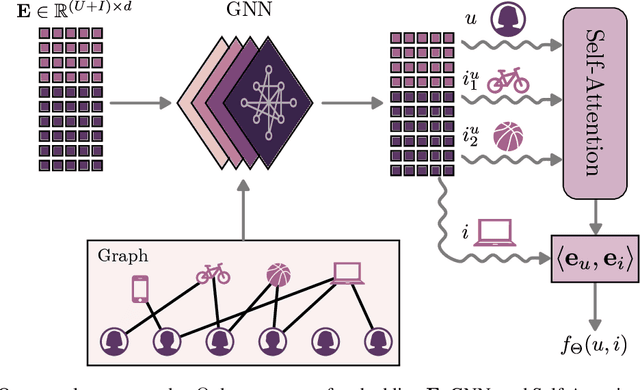
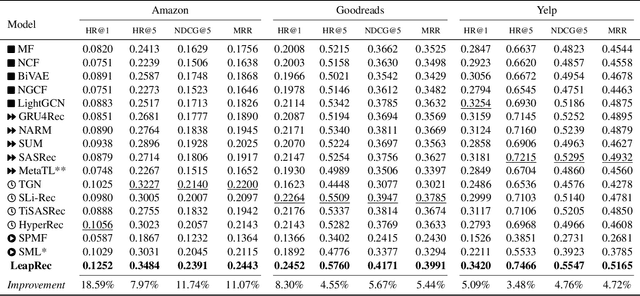
Abstract:Modern recommender systems are required to adapt to the change in user preferences and item popularity. Such a problem is known as the temporal dynamics problem, and it is one of the main challenges in recommender system modeling. Different from the popular recurrent modeling approach, we propose a new solution named LeapRec to the temporal dynamic problem by using trajectory-based meta-learning to model time dependencies. LeapRec characterizes temporal dynamics by two complement components named global time leap (GTL) and ordered time leap (OTL). By design, GTL learns long-term patterns by finding the shortest learning path across unordered temporal data. Cooperatively, OTL learns short-term patterns by considering the sequential nature of the temporal data. Our experimental results show that LeapRec consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on several datasets and recommendation metrics. Furthermore, we provide an empirical study of the interaction between GTL and OTL, showing the effects of long- and short-term modeling.
Cross-lingual Transfer for Text Classification with Dictionary-based Heterogeneous Graph
Sep 10, 2021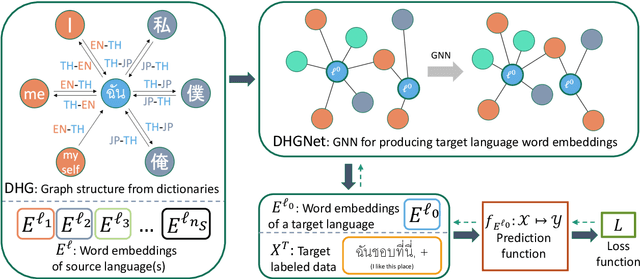
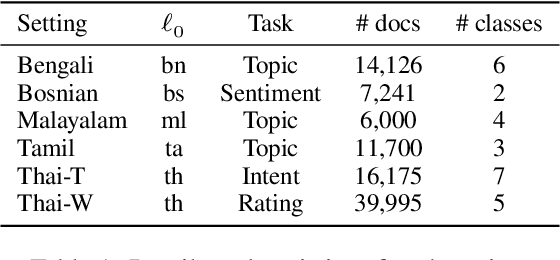
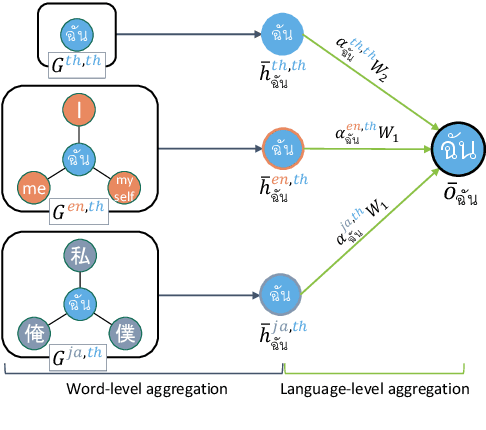
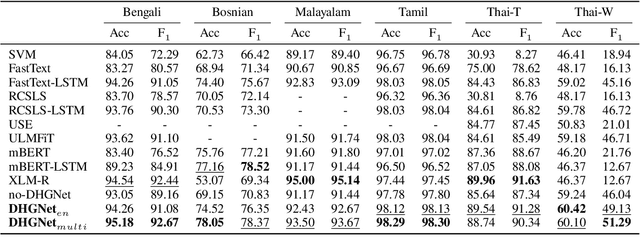
Abstract:In cross-lingual text classification, it is required that task-specific training data in high-resource source languages are available, where the task is identical to that of a low-resource target language. However, collecting such training data can be infeasible because of the labeling cost, task characteristics, and privacy concerns. This paper proposes an alternative solution that uses only task-independent word embeddings of high-resource languages and bilingual dictionaries. First, we construct a dictionary-based heterogeneous graph (DHG) from bilingual dictionaries. This opens the possibility to use graph neural networks for cross-lingual transfer. The remaining challenge is the heterogeneity of DHG because multiple languages are considered. To address this challenge, we propose dictionary-based heterogeneous graph neural network (DHGNet) that effectively handles the heterogeneity of DHG by two-step aggregations, which are word-level and language-level aggregations. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms pretrained models even though it does not access to large corpora. Furthermore, it can perform well even though dictionaries contain many incorrect translations. Its robustness allows the usage of a wider range of dictionaries such as an automatically constructed dictionary and crowdsourced dictionary, which are convenient for real-world applications.
On Focal Loss for Class-Posterior Probability Estimation: A Theoretical Perspective
Dec 14, 2020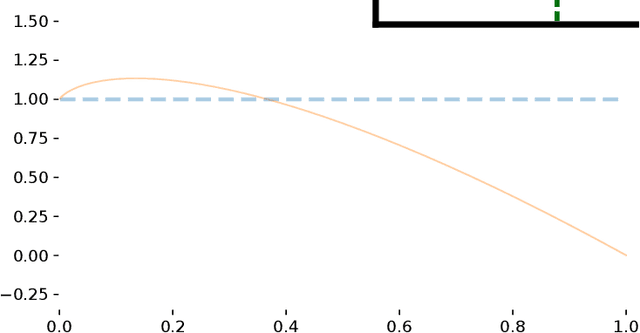
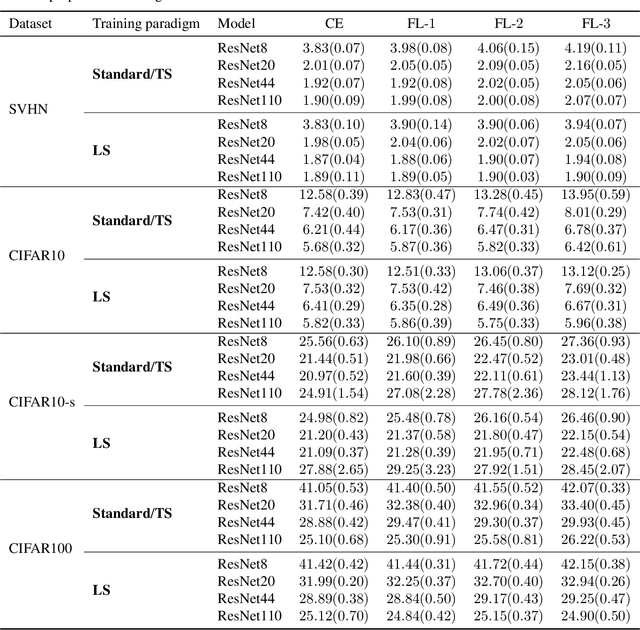
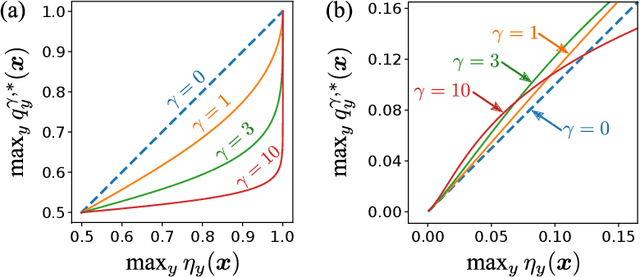
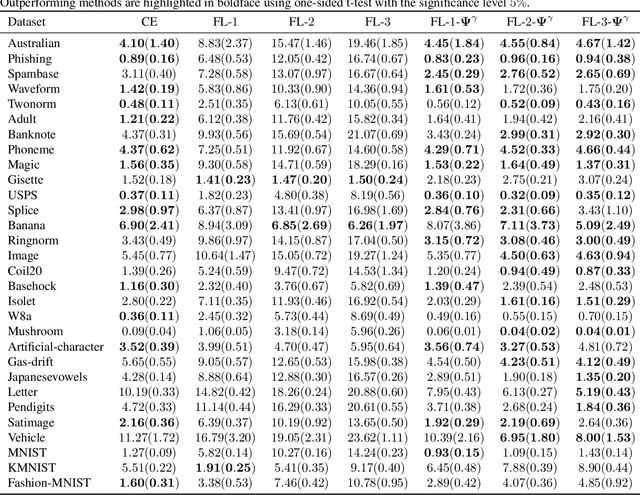
Abstract:The focal loss has demonstrated its effectiveness in many real-world applications such as object detection and image classification, but its theoretical understanding has been limited so far. In this paper, we first prove that the focal loss is classification-calibrated, i.e., its minimizer surely yields the Bayes-optimal classifier and thus the use of the focal loss in classification can be theoretically justified. However, we also prove a negative fact that the focal loss is not strictly proper, i.e., the confidence score of the classifier obtained by focal loss minimization does not match the true class-posterior probability and thus it is not reliable as a class-posterior probability estimator. To mitigate this problem, we next prove that a particular closed-form transformation of the confidence score allows us to recover the true class-posterior probability. Through experiments on benchmark datasets, we demonstrate that our proposed transformation significantly improves the accuracy of class-posterior probability estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge