Nirmal Punjabi
MHQA: A Diverse, Knowledge Intensive Mental Health Question Answering Challenge for Language Models
Feb 21, 2025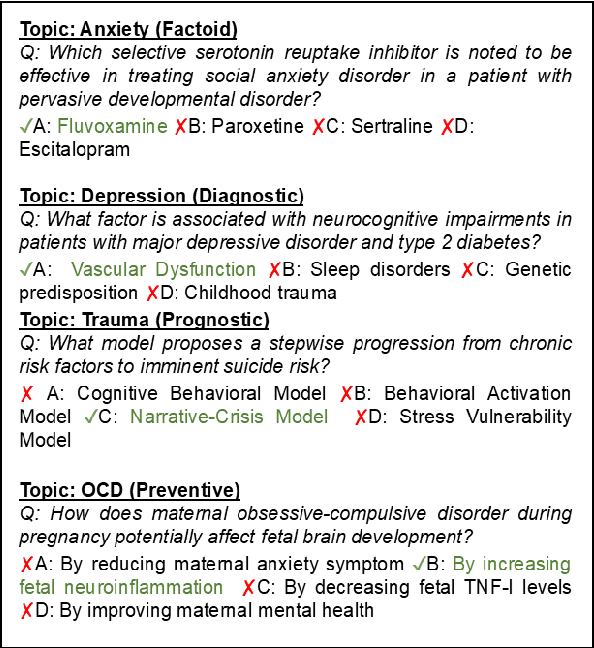
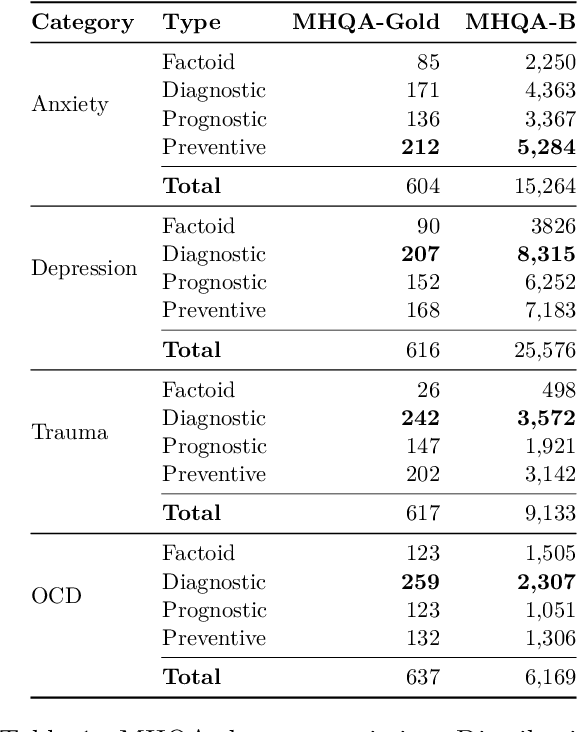
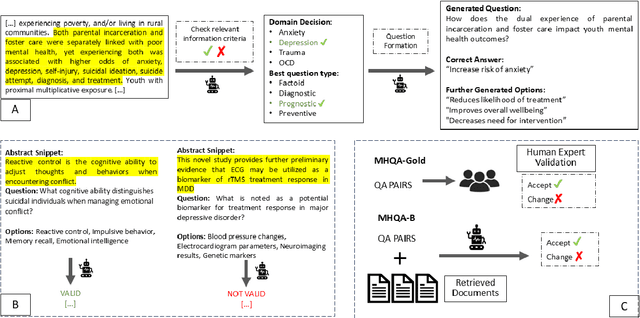
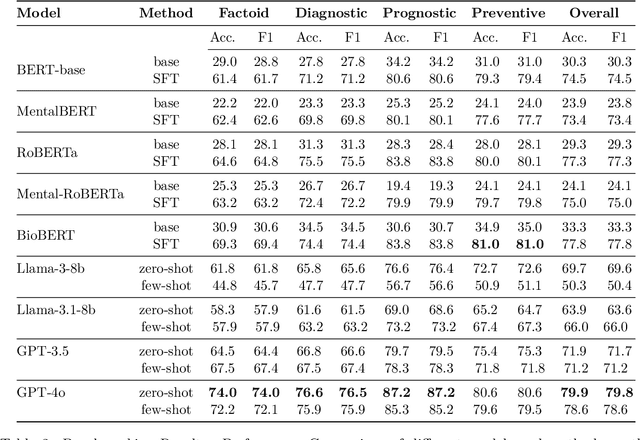
Abstract:Mental health remains a challenging problem all over the world, with issues like depression, anxiety becoming increasingly common. Large Language Models (LLMs) have seen a vast application in healthcare, specifically in answering medical questions. However, there is a lack of standard benchmarking datasets for question answering (QA) in mental health. Our work presents a novel multiple choice dataset, MHQA (Mental Health Question Answering), for benchmarking Language models (LMs). Previous mental health datasets have focused primarily on text classification into specific labels or disorders. MHQA, on the other hand, presents question-answering for mental health focused on four key domains: anxiety, depression, trauma, and obsessive/compulsive issues, with diverse question types, namely, factoid, diagnostic, prognostic, and preventive. We use PubMed abstracts as the primary source for QA. We develop a rigorous pipeline for LLM-based identification of information from abstracts based on various selection criteria and converting it into QA pairs. Further, valid QA pairs are extracted based on post-hoc validation criteria. Overall, our MHQA dataset consists of 2,475 expert-verified gold standard instances called MHQA-gold and ~56.1k pairs pseudo labeled using external medical references. We report F1 scores on different LLMs along with few-shot and supervised fine-tuning experiments, further discussing the insights for the scores.
Classifier Enhanced Deep Learning Model for Erythroblast Differentiation with Limited Data
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Hematological disorders, which involve a variety of malignant conditions and genetic diseases affecting blood formation, present significant diagnostic challenges. One such major challenge in clinical settings is differentiating Erythroblast from WBCs. Our approach evaluates the efficacy of various machine learning (ML) classifiers$\unicode{x2014}$SVM, XG-Boost, KNN, and Random Forest$\unicode{x2014}$using the ResNet-50 deep learning model as a backbone in detecting and differentiating erythroblast blood smear images across training splits of different sizes. Our findings indicate that the ResNet50-SVM classifier consistently surpasses other models' overall test accuracy and erythroblast detection accuracy, maintaining high performance even with minimal training data. Even when trained on just 1% (168 images per class for eight classes) of the complete dataset, ML classifiers such as SVM achieved a test accuracy of 86.75% and an erythroblast precision of 98.9%, compared to 82.03% and 98.6% of pre-trained ResNet-50 models without any classifiers. When limited data is available, the proposed approach outperforms traditional deep learning models, thereby offering a solution for achieving higher classification accuracy for small and unique datasets, especially in resource-scarce settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge