Nikolaos Bousias
eCP: Informative uncertainty quantification via Equivariantized Conformal Prediction with pre-trained models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:We study the effect of group symmetrization of pre-trained models on conformal prediction (CP), a post-hoc, distribution-free, finite-sample method of uncertainty quantification that offers formal coverage guarantees under the assumption of data exchangeability. Unfortunately, CP uncertainty regions can grow significantly in long horizon missions, rendering the statistical guarantees uninformative. To that end, we propose infusing CP with geometric information via group-averaging of the pretrained predictor to distribute the non-conformity mass across the orbits. Each sample now is treated as a representative of an orbit, thus uncertainty can be mitigated by other samples entangled to it via the orbit inducing elements of the symmetry group. Our approach provably yields contracted non-conformity scores in increasing convex order, implying improved exponential-tail bounds and sharper conformal prediction sets in expectation, especially at high confidence levels. We then propose an experimental design to test these theoretical claims in pedestrian trajectory prediction.
Towards X-embodiment safety: A control theory perspective on transferring safety certificates across dynamical systems
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Control barrier functions (CBFs) provide a powerful tool for enforcing safety constraints in control systems, but their direct application to complex, high-dimensional dynamics is often challenging. In many settings, safety certificates are more naturally designed for simplified or alternative system models that do not exactly match the dynamics of interest. This paper addresses the problem of transferring safety guarantees between dynamical systems with mismatched dynamics. We propose a transferred control barrier function (tCBF) framework that enables safety constraints defined on one system to be systematically enforced on another system using a simulation function and an explicit margin term. The resulting transferred barrier accounts for model mismatch and induces a safety condition that can be enforced on the target system via a quadratic-program-based safety filter. The proposed approach is general and does not require the two systems to share the same state dimension or dynamics. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the framework on a quadrotor navigation task with the transferred barrier ensuring collision avoidance for the target system, while remaining minimally invasive to a nominal controller. These results highlight the potential of transferred control barrier functions as a general mechanism for enforcing safety across heterogeneous dynamical systems.
Deep Equivariant Multi-Agent Control Barrier Functions
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:With multi-agent systems increasingly deployed autonomously at scale in complex environments, ensuring safety of the data-driven policies is critical. Control Barrier Functions have emerged as an effective tool for enforcing safety constraints, yet existing learning-based methods often lack in scalability, generalization and sampling efficiency as they overlook inherent geometric structures of the system. To address this gap, we introduce symmetries-infused distributed Control Barrier Functions, enforcing the satisfaction of intrinsic symmetries on learnable graph-based safety certificates. We theoretically motivate the need for equivariant parametrization of CBFs and policies, and propose a simple, yet efficient and adaptable methodology for constructing such equivariant group-modular networks via the compatible group actions. This approach encodes safety constraints in a distributed data-efficient manner, enabling zero-shot generalization to larger and denser swarms. Through extensive simulations on multi-robot navigation tasks, we demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in terms of safety, scalability, and task success rates, highlighting the importance of embedding symmetries in safe distributed neural policies.
Symmetries-enhanced Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning has emerged as a powerful framework for enabling agents to learn complex, coordinated behaviors but faces persistent challenges regarding its generalization, scalability and sample efficiency. Recent advancements have sought to alleviate those issues by embedding intrinsic symmetries of the systems in the policy. Yet, most dynamical systems exhibit little to no symmetries to exploit. This paper presents a novel framework for embedding extrinsic symmetries in multi-agent system dynamics that enables the use of symmetry-enhanced methods to address systems with insufficient intrinsic symmetries, expanding the scope of equivariant learning to a wide variety of MARL problems. Central to our framework is the Group Equivariant Graphormer, a group-modular architecture specifically designed for distributed swarming tasks. Extensive experiments on a swarm of symmetry-breaking quadrotors validate the effectiveness of our approach, showcasing its potential for improved generalization and zero-shot scalability. Our method achieves significant reductions in collision rates and enhances task success rates across a diverse range of scenarios and varying swarm sizes.
Graph Neural Networks for Multi-Robot Active Information Acquisition
Sep 24, 2022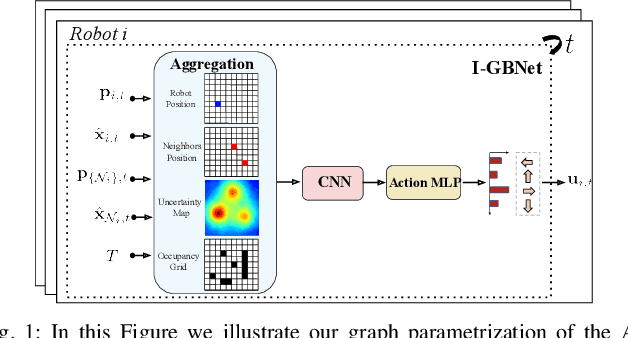
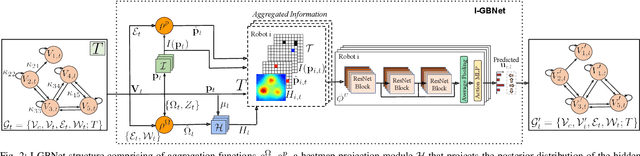
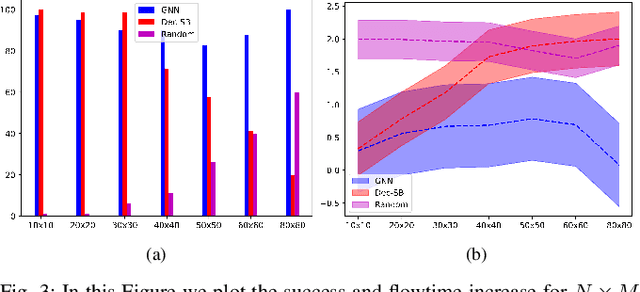
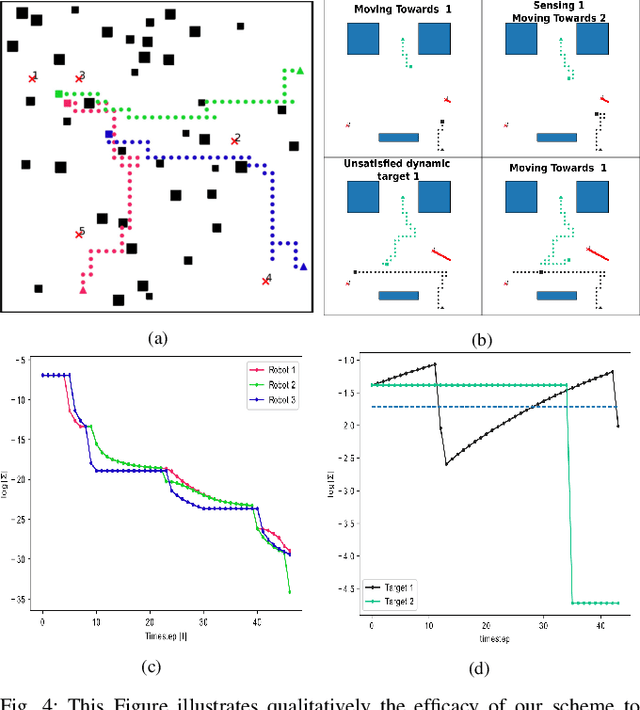
Abstract:This paper addresses the Multi-Robot Active Information Acquisition (AIA) problem, where a team of mobile robots, communicating through an underlying graph, estimates a hidden state expressing a phenomenon of interest. Applications like target tracking, coverage and SLAM can be expressed in this framework. Existing approaches, though, are either not scalable, unable to handle dynamic phenomena or not robust to changes in the communication graph. To counter these shortcomings, we propose an Information-aware Graph Block Network (I-GBNet), an AIA adaptation of Graph Neural Networks, that aggregates information over the graph representation and provides sequential-decision making in a distributed manner. The I-GBNet, trained via imitation learning with a centralized sampling-based expert solver, exhibits permutation equivariance and time invariance, while harnessing the superior scalability, robustness and generalizability to previously unseen environments and robot configurations. Experiments on significantly larger graphs and dimensionality of the hidden state and more complex environments than those seen in training validate the properties of the proposed architecture and its efficacy in the application of localization and tracking of dynamic targets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge