Nian Ran
Position: Intelligent Science Laboratory Requires the Integration of Cognitive and Embodied AI
Jun 24, 2025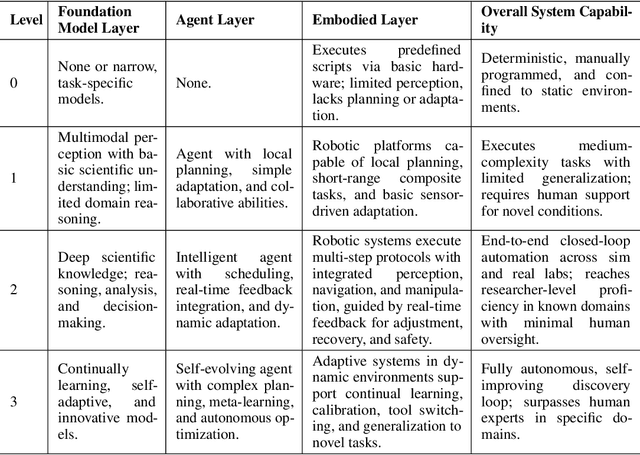
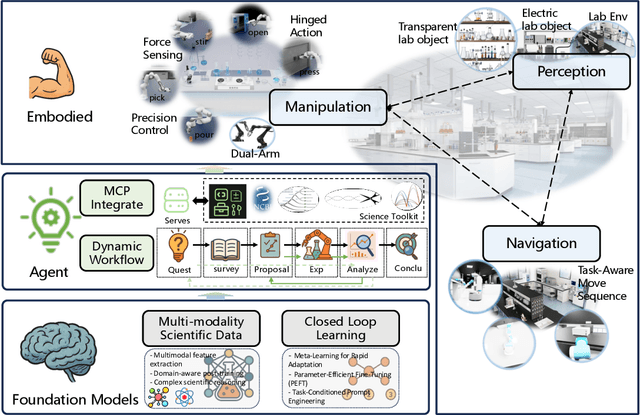
Abstract:Scientific discovery has long been constrained by human limitations in expertise, physical capability, and sleep cycles. The recent rise of AI scientists and automated laboratories has accelerated both the cognitive and operational aspects of research. However, key limitations persist: AI systems are often confined to virtual environments, while automated laboratories lack the flexibility and autonomy to adaptively test new hypotheses in the physical world. Recent advances in embodied AI, such as generalist robot foundation models, diffusion-based action policies, fine-grained manipulation learning, and sim-to-real transfer, highlight the promise of integrating cognitive and embodied intelligence. This convergence opens the door to closed-loop systems that support iterative, autonomous experimentation and the possibility of serendipitous discovery. In this position paper, we propose the paradigm of Intelligent Science Laboratories (ISLs): a multi-layered, closed-loop framework that deeply integrates cognitive and embodied intelligence. ISLs unify foundation models for scientific reasoning, agent-based workflow orchestration, and embodied agents for robust physical experimentation. We argue that such systems are essential for overcoming the current limitations of scientific discovery and for realizing the full transformative potential of AI-driven science.
Automated Flow Pattern Classification in Multi-phase Systems Using AI and Capacitance Sensing Techniques
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:In multiphase flow systems, classifying flow patterns is crucial to optimize fluid dynamics and enhance system efficiency. Current industrial methods and scientific laboratories mainly depend on techniques such as flow visualization using regular cameras or the naked eye, as well as high-speed imaging at elevated flow rates. These methods are limited by their reliance on subjective interpretations and are particularly applicable in transparent pipes. Consequently, conventional techniques usually achieve context-dependent accuracy rates and often lack generalizability. This study introduces a novel platform that integrates a capacitance sensor and AI-driven classification methods, benchmarked against traditional techniques. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach, utilizing a 1D SENet deep learning model, achieves over 85\% accuracy on experiment-based datasets and 71\% accuracy on pattern-based datasets. These results highlight significant improvements in robustness and reliability compared to existing methodologies. This work offers a transformative pathway for real-time flow monitoring and predictive modeling, addressing key challenges in industrial applications.
MOLLM: Multi-Objective Large Language Model for Molecular Design -- Optimizing with Experts
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Molecular design plays a critical role in advancing fields such as drug discovery, materials science, and chemical engineering. This work introduces the Multi-Objective Large Language Model for Molecular Design (MOLLM), a novel framework that combines domain-specific knowledge with the adaptability of Large Language Models to optimize molecular properties across multiple objectives. Leveraging in-context learning and multi-objective optimization, MOLLM achieves superior efficiency, innovation, and performance, significantly surpassing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. Recognizing the substantial impact of initial populations on evolutionary algorithms, we categorize them into three types: best initial, worst initial, and random initial, to ensure the initial molecules are the same for each method across experiments. Our results demonstrate that MOLLM consistently outperforms SOTA models in all of our experiments. We also provide extensive ablation studies to evaluate the superiority of our components.
HR-Extreme: A High-Resolution Dataset for Extreme Weather Forecasting
Sep 27, 2024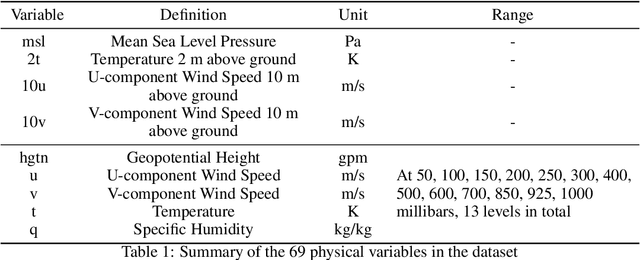


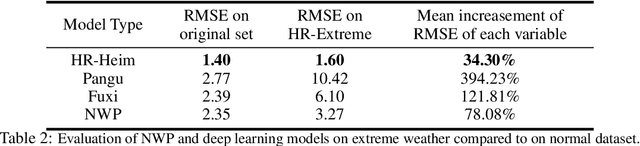
Abstract:The application of large deep learning models in weather forecasting has led to significant advancements in the field, including higher-resolution forecasting and extended prediction periods exemplified by models such as Pangu and Fuxi. Despite these successes, previous research has largely been characterized by the neglect of extreme weather events, and the availability of datasets specifically curated for such events remains limited. Given the critical importance of accurately forecasting extreme weather, this study introduces a comprehensive dataset that incorporates high-resolution extreme weather cases derived from the High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) data, a 3-km real-time dataset provided by NOAA. We also evaluate the current state-of-the-art deep learning models and Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) systems on HR-Extreme, and provide a improved baseline deep learning model called HR-Heim which has superior performance on both general loss and HR-Extreme compared to others. Our results reveal that the errors of extreme weather cases are significantly larger than overall forecast error, highlighting them as an crucial source of loss in weather prediction. These findings underscore the necessity for future research to focus on improving the accuracy of extreme weather forecasts to enhance their practical utility.
Multi-objective evolutionary GAN for tabular data synthesis
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:Synthetic data has a key role to play in data sharing by statistical agencies and other generators of statistical data products. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), typically applied to image synthesis, are also a promising method for tabular data synthesis. However, there are unique challenges in tabular data compared to images, eg tabular data may contain both continuous and discrete variables and conditional sampling, and, critically, the data should possess high utility and low disclosure risk (the risk of re-identifying a population unit or learning something new about them), providing an opportunity for multi-objective (MO) optimization. Inspired by MO GANs for images, this paper proposes a smart MO evolutionary conditional tabular GAN (SMOE-CTGAN). This approach models conditional synthetic data by applying conditional vectors in training, and uses concepts from MO optimisation to balance disclosure risk against utility. Our results indicate that SMOE-CTGAN is able to discover synthetic datasets with different risk and utility levels for multiple national census datasets. We also find a sweet spot in the early stage of training where a competitive utility and extremely low risk are achieved, by using an Improvement Score. The full code can be downloaded from https://github.com/HuskyNian/SMO\_EGAN\_pytorch.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge