Nhat Nguyen
United We Stand: Decentralized Multi-Agent Planning With Attrition
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:Decentralized planning is a key element of cooperative multi-agent systems for information gathering tasks. However, despite the high frequency of agent failures in realistic large deployment scenarios, current approaches perform poorly in the presence of failures, by not converging at all, and/or by making very inefficient use of resources (e.g. energy). In this work, we propose Attritable MCTS (A-MCTS), a decentralized MCTS algorithm capable of timely and efficient adaptation to changes in the set of active agents. It is based on the use of a global reward function for the estimation of each agent's local contribution, and regret matching for coordination. We evaluate its effectiveness in realistic data-harvesting problems under different scenarios. We show both theoretically and experimentally that A-MCTS enables efficient adaptation even under high failure rates. Results suggest that, in the presence of frequent failures, our solution improves substantially over the best existing approaches in terms of global utility and scalability.
SMARTS: Scalable Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Training School for Autonomous Driving
Nov 01, 2020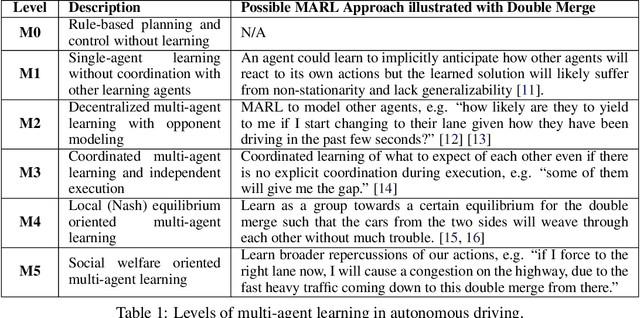
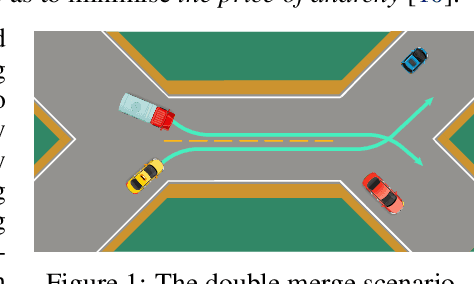
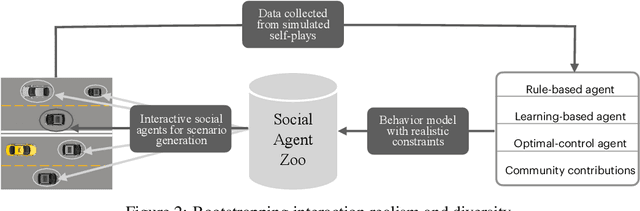
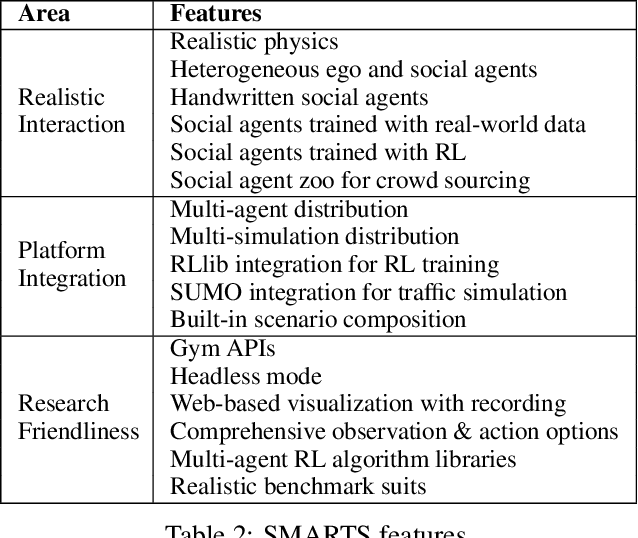
Abstract:Multi-agent interaction is a fundamental aspect of autonomous driving in the real world. Despite more than a decade of research and development, the problem of how to competently interact with diverse road users in diverse scenarios remains largely unsolved. Learning methods have much to offer towards solving this problem. But they require a realistic multi-agent simulator that generates diverse and competent driving interactions. To meet this need, we develop a dedicated simulation platform called SMARTS (Scalable Multi-Agent RL Training School). SMARTS supports the training, accumulation, and use of diverse behavior models of road users. These are in turn used to create increasingly more realistic and diverse interactions that enable deeper and broader research on multi-agent interaction. In this paper, we describe the design goals of SMARTS, explain its basic architecture and its key features, and illustrate its use through concrete multi-agent experiments on interactive scenarios. We open-source the SMARTS platform and the associated benchmark tasks and evaluation metrics to encourage and empower research on multi-agent learning for autonomous driving. Our code is available at https://github.com/huawei-noah/SMARTS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge