Neeta Nain
Longitudinal Analysis of Mask and No-Mask on Child Face Recognition
Nov 19, 2021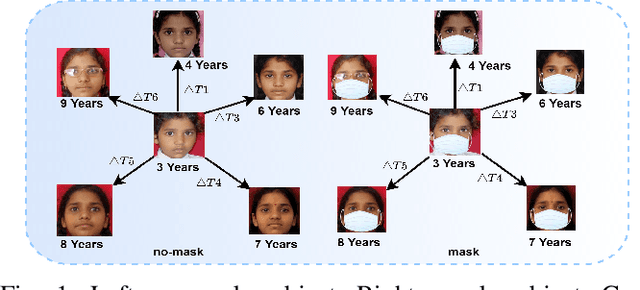
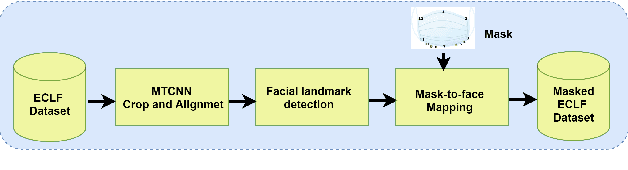
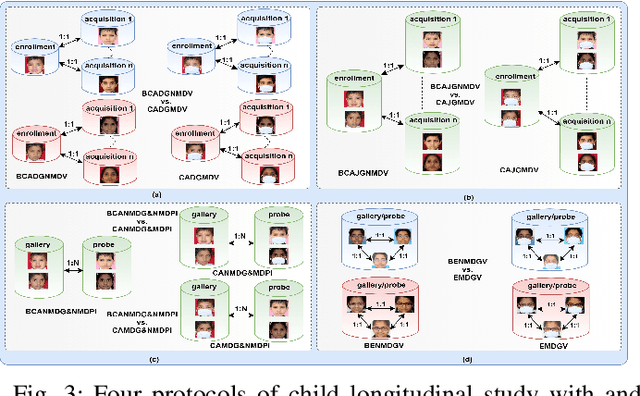
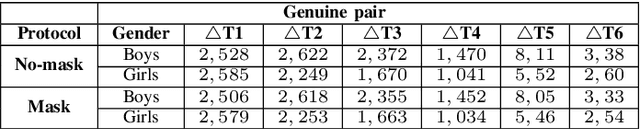
Abstract:Face is one of the most widely employed traits for person recognition, even in many large-scale applications. Despite technological advancements in face recognition systems, they still face obstacles caused by pose, expression, occlusion, and aging variations. Owing to the COVID-19 pandemic, contactless identity verification has become exceedingly vital. To constrain the pandemic, people have started using face mask. Recently, few studies have been conducted on the effect of face mask on adult face recognition systems. However, the impact of aging with face mask on child subject recognition has not been adequately explored. Thus, the main objective of this study is analyzing the child longitudinal impact together with face mask and other covariates on face recognition systems. Specifically, we performed a comparative investigation of three top performing publicly available face matchers and a post-COVID-19 commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) system under child cross-age verification and identification settings using our generated synthetic mask and no-mask samples. Furthermore, we investigated the longitudinal consequence of eyeglasses with mask and no-mask. The study exploited no-mask longitudinal child face dataset (i.e., extended Indian Child Longitudinal Face Dataset) that contains $26,258$ face images of $7,473$ subjects in the age group of $[2, 18]$ over an average time span of $3.35$ years. Due to the combined effects of face mask and face aging, the FaceNet, PFE, ArcFace, and COTS face verification system accuracies decrease approximately $25\%$, $22\%$, $18\%$, $12\%$, respectively.
Matching Fingerphotos to Slap Fingerprint Images
Apr 22, 2018



Abstract:We address the problem of comparing fingerphotos, fingerprint images from a commodity smartphone camera, with the corresponding legacy slap contact-based fingerprint images. Development of robust versions of these technologies would enable the use of the billions of standard Android phones as biometric readers through a simple software download, dramatically lowering the cost and complexity of deployment relative to using a separate fingerprint reader. Two fingerphoto apps running on Android phones and an optical slap reader were utilized for fingerprint collection of 309 subjects who primarily work as construction workers, farmers, and domestic helpers. Experimental results show that a True Accept Rate (TAR) of 95.79 at a False Accept Rate (FAR) of 0.1% can be achieved in matching fingerphotos to slaps (two thumbs and two index fingers) using a COTS fingerprint matcher. By comparison, a baseline TAR of 98.55% at 0.1% FAR is achieved when matching fingerprint images from two different contact-based optical readers. We also report the usability of the two smartphone apps, in terms of failure to acquire rate and fingerprint acquisition time. Our results show that fingerphotos are promising to authenticate individuals (against a national ID database) for banking, welfare distribution, and healthcare applications in developing countries.
Longitudinal Study of Child Face Recognition
Nov 10, 2017



Abstract:We present a longitudinal study of face recognition performance on Children Longitudinal Face (CLF) dataset containing 3,682 face images of 919 subjects, in the age group [2, 18] years. Each subject has at least four face images acquired over a time span of up to six years. Face comparison scores are obtained from (i) a state-of-the-art COTS matcher (COTS-A), (ii) an open-source matcher (FaceNet), and (iii) a simple sum fusion of scores obtained from COTS-A and FaceNet matchers. To improve the performance of the open-source FaceNet matcher for child face recognition, we were able to fine-tune it on an independent training set of 3,294 face images of 1,119 children in the age group [3, 18] years. Multilevel statistical models are fit to genuine comparison scores from the CLF dataset to determine the decrease in face recognition accuracy over time. Additionally, we analyze both the verification and open-set identification accuracies in order to evaluate state-of-the-art face recognition technology for tracing and identifying children lost at a young age as victims of child trafficking or abduction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge