Nancy Pollard
Design and Control Co-Optimization for Automated Design Iteration of Dexterous Anthropomorphic Soft Robotic Hands
Mar 15, 2024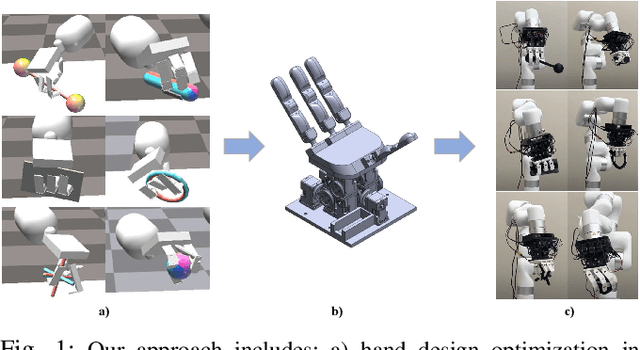


Abstract:We automate soft robotic hand design iteration by co-optimizing design and control policy for dexterous manipulation skills in simulation. Our design iteration pipeline combines genetic algorithms and policy transfer to learn control policies for nearly 400 hand designs, testing grasp quality under external force disturbances. We validate the optimized designs in the real world through teleoperation of pickup and reorient manipulation tasks. Our real world evaluation, from over 900 teleoperated tasks, shows that the trend in design performance in simulation resembles that of the real world. Furthermore, we show that optimized hand designs from our approach outperform existing soft robot hands from prior work in the real world. The results highlight the usefulness of simulation in guiding parameter choices for anthropomorphic soft robotic hand systems, and the effectiveness of our automated design iteration approach, despite the sim-to-real gap.
A Framework for Designing Anthropomorphic Soft Hands through Interaction
Jun 07, 2023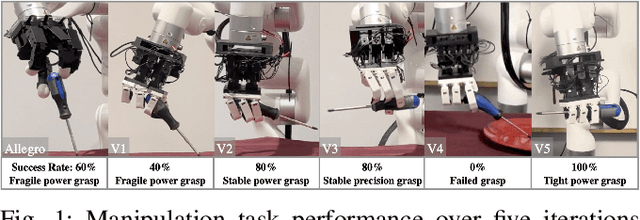
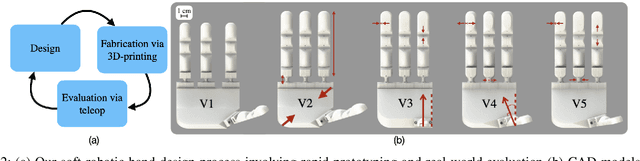
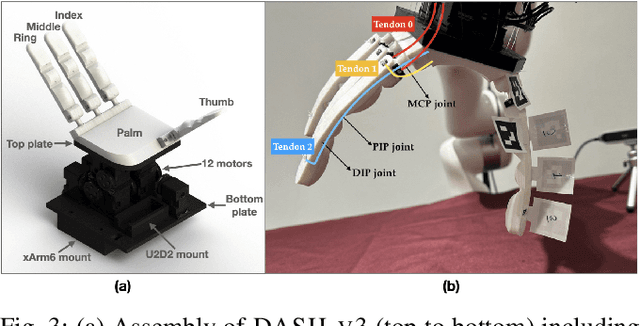
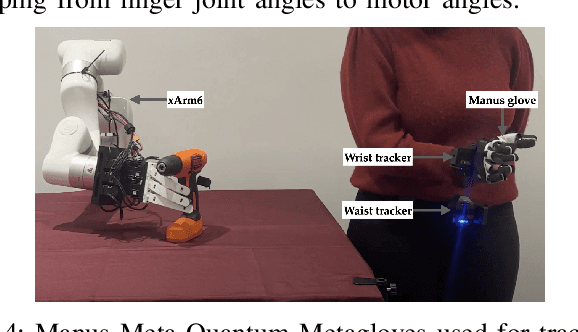
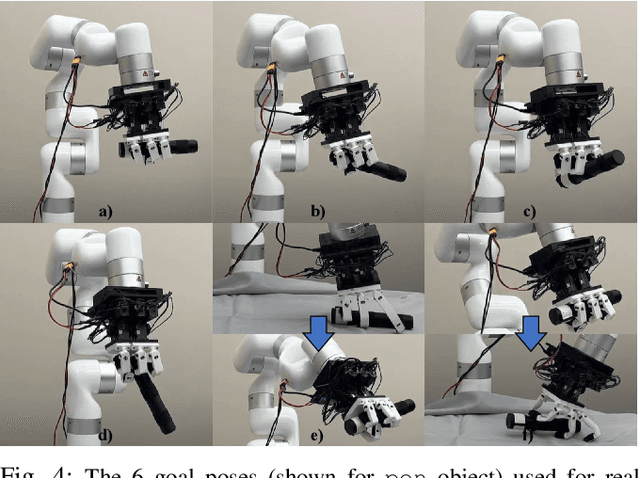
Abstract:Modeling and simulating soft robot hands can aid in design iteration for complex and high degree-of-freedom (DoF) morphologies. This can be further supplemented by iterating on the design based on its performance in real world manipulation tasks. However, this requires a framework that allows us to iterate quickly at low costs. In this paper, we present a framework that leverages rapid prototyping of the hand using 3D-printing, and utilizes teleoperation to evaluate the hand in real world manipulation tasks. Using this framework, we design a 3D-printed 16-DoF dexterous anthropomorphic soft hand (DASH) and iteratively improve its design over three iterations. Rapid prototyping techniques such as 3D-printing allow us to directly evaluate the fabricated hand without modeling it in simulation. We show that the design is improved at each iteration through the hand's performance in 30 real-world teleoperated manipulation tasks. Testing over 600 demonstrations shows that our final version of DASH can solve 16 of the 30 tasks compared to Allegro, a popular rigid hand in the market, which can only solve 7 tasks. We open-source our CAD models as well as the teleoperated dataset for further study and are available on our website (https://dash-through-interaction.github.io.)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge