Naijing Zhang
Discovering Hypernymy in Text-Rich Heterogeneous Information Network by Exploiting Context Granularity
Sep 04, 2019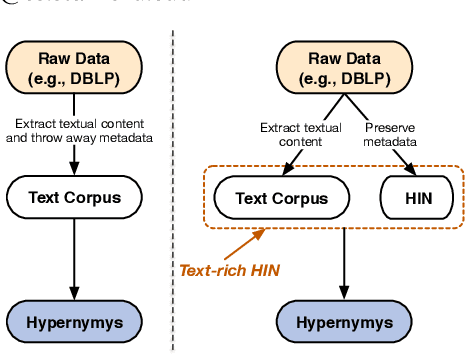
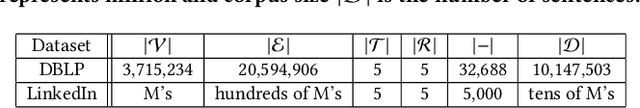
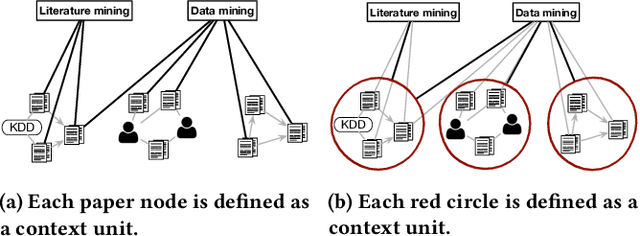
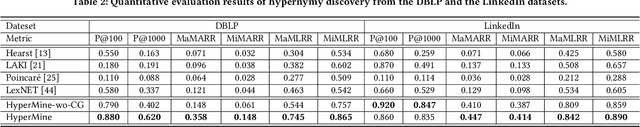
Abstract:Text-rich heterogeneous information networks (text-rich HINs) are ubiquitous in real-world applications. Hypernymy, also known as is-a relation or subclass-of relation, lays in the core of many knowledge graphs and benefits many downstream applications. Existing methods of hypernymy discovery either leverage textual patterns to extract explicitly mentioned hypernym-hyponym pairs, or learn a distributional representation for each term of interest based its context. These approaches rely on statistical signals from the textual corpus, and their effectiveness would therefore be hindered when the signals from the corpus are not sufficient for all terms of interest. In this work, we propose to discover hypernymy in text-rich HINs, which can introduce additional high-quality signals. We develop a new framework, named HyperMine, that exploits multi-granular contexts and combines signals from both text and network without human labeled data. HyperMine extends the definition of context to the scenario of text-rich HIN. For example, we can define typed nodes and communities as contexts. These contexts encode signals of different granularities and we feed them into a hypernymy inference model. HyperMine learns this model using weak supervision acquired based on high-precision textual patterns. Extensive experiments on two large real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of HyperMine and the utility of modeling context granularity. We further show a case study that a high-quality taxonomy can be generated solely based on the hypernymy discovered by HyperMine.
Higher-Order Clustering in Heterogeneous Information Networks
Nov 28, 2018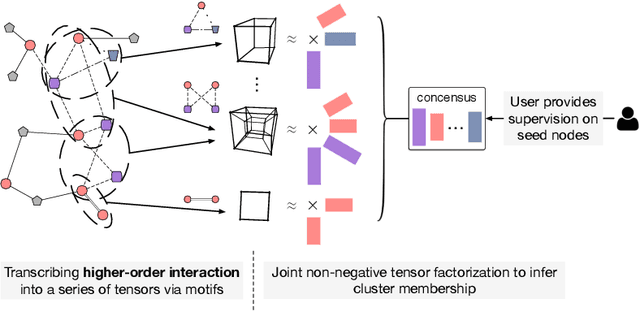
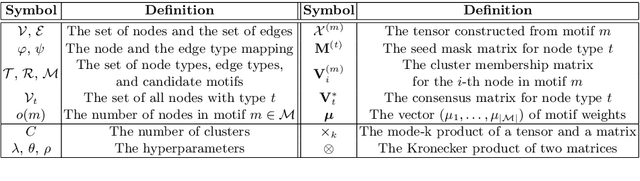
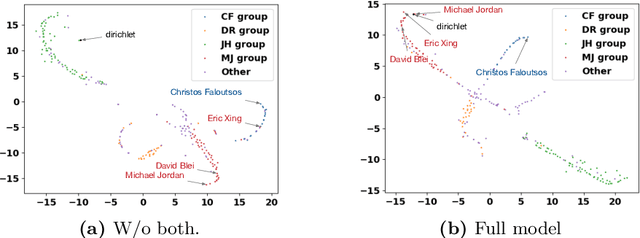
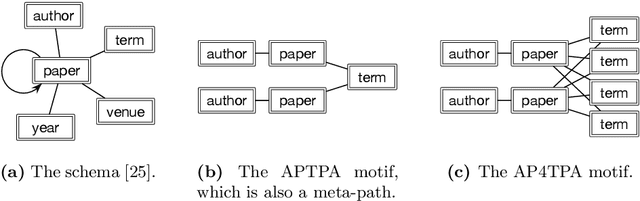
Abstract:As one type of complex networks widely-seen in real-world application, heterogeneous information networks (HINs) often encapsulate higher-order interactions that crucially reflect the complex nature among nodes and edges in real-world data. Modeling higher-order interactions in HIN facilitates the user-guided clustering problem by providing an informative collection of signals. At the same time, network motifs have been used extensively to reveal higher-order interactions and network semantics in homogeneous networks. Thus, it is natural to extend the use of motifs to HIN, and we tackle the problem of user-guided clustering in HIN by using motifs. We highlight the benefits of comprehensively modeling higher-order interactions instead of decomposing the complex relationships to pairwise interaction. We propose the MoCHIN model which is applicable to arbitrary forms of HIN motifs, which is often necessary for the application scenario in HINs due to their rich and diverse semantics encapsulated in the heterogeneity. To overcome the curse of dimensionality since the tensor size grows exponentially as the number of nodes increases in our model, we propose an efficient inference algorithm for MoCHIN. In our experiment, MoCHIN surpasses all baselines in three evaluation tasks under different metrics. The advantage of our model when the supervision is weak is also discussed in additional experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge