Muhammad Shoaib
Comparison of Maximum Likelihood Classification Before and After Applying Weierstrass Transform
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:The aim of this paper is to use Maximum Likelihood (ML) Classification on multispectral data by means of qualitative and quantitative approaches. Maximum Likelihood is a supervised classification algorithm which is based on the Classical Bayes theorem. It makes use of a discriminant function to assign pixel to the class with the highest likelihood. Class means vector and covariance matrix are the key inputs to the function and can be estimated from training pixels of a particular class. As Maximum Likelihood need some assumptions before it has to be applied on the data. In this paper we will compare the results of Maximum Likelihood Classification (ML) before apply the Weierstrass Transform and apply Weierstrass Transform and will see the difference between the accuracy on training pixels of high resolution Quickbird satellite image. Principle Component analysis (PCA) is also used for dimension reduction and also used to check the variation in bands. The results shows that the separation between mean of the classes in the decision space is to be the main factor that leads to the high classification accuracy of Maximum Likelihood (ML) after using Weierstrass Transform than without using it.
Unification of Balti and trans-border sister dialects in the essence of LLMs and AI Technology
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:The language called Balti belongs to the Sino-Tibetan, specifically the Tibeto-Burman language family. It is understood with variations, across populations in India, China, Pakistan, Nepal, Tibet, Burma, and Bhutan, influenced by local cultures and producing various dialects. Considering the diverse cultural, socio-political, religious, and geographical impacts, it is important to step forward unifying the dialects, the basis of common root, lexica, and phonological perspectives, is vital. In the era of globalization and the increasingly frequent developments in AI technology, understanding the diversity and the efforts of dialect unification is important to understanding commonalities and shortening the gaps impacted by unavoidable circumstances. This article analyzes and examines how artificial intelligence AI in the essence of Large Language Models LLMs, can assist in analyzing, documenting, and standardizing the endangered Balti Language, based on the efforts made in different dialects so far.
Sequence-Based Nanobody-Antigen Binding Prediction
Jul 15, 2023



Abstract:Nanobodies (Nb) are monomeric heavy-chain fragments derived from heavy-chain only antibodies naturally found in Camelids and Sharks. Their considerably small size (~3-4 nm; 13 kDa) and favorable biophysical properties make them attractive targets for recombinant production. Furthermore, their unique ability to bind selectively to specific antigens, such as toxins, chemicals, bacteria, and viruses, makes them powerful tools in cell biology, structural biology, medical diagnostics, and future therapeutic agents in treating cancer and other serious illnesses. However, a critical challenge in nanobodies production is the unavailability of nanobodies for a majority of antigens. Although some computational methods have been proposed to screen potential nanobodies for given target antigens, their practical application is highly restricted due to their reliance on 3D structures. Moreover, predicting nanobodyantigen interactions (binding) is a time-consuming and labor-intensive task. This study aims to develop a machine-learning method to predict Nanobody-Antigen binding solely based on the sequence data. We curated a comprehensive dataset of Nanobody-Antigen binding and nonbinding data and devised an embedding method based on gapped k-mers to predict binding based only on sequences of nanobody and antigen. Our approach achieves up to 90% accuracy in binding prediction and is significantly more efficient compared to the widely-used computational docking technique.
Cable Driven Rehabilitation Robots: Comparison of Applications and Control Strategies
Aug 05, 2021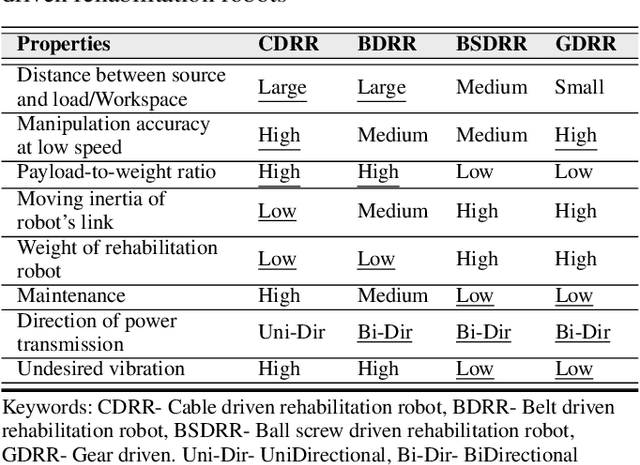

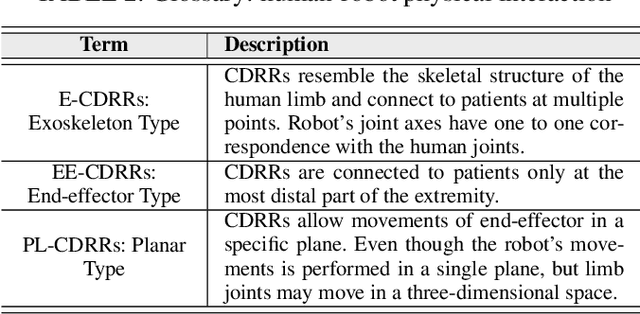
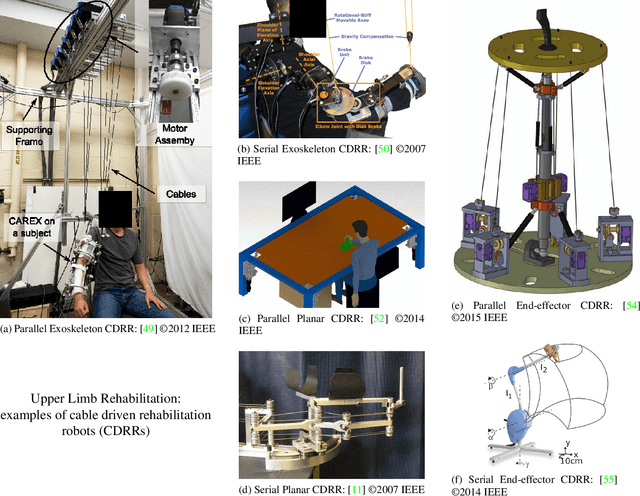
Abstract:Significant attention has been paid to robotic rehabilitation using various types of actuator and power transmission. Amongst those, cable-driven rehabilitation robots (CDRRs) are relatively newer and their control strategies have been evolving in recent years. CDRRs offer several promising features, such as low inertia, lightweight, high payload-to-weight ratio, large work-space and configurability. In this paper, we categorize and review the cable-driven rehabilitation robots in three main groups concerning their applications for upper limb, lower limb, and waist rehabilitation. For each group, target movements are identified, and promising designs of CDRRs are analyzed in terms of types of actuators, controllers and their interactions with humans. Particular attention has been given to robots with verified clinical performance in actual rehabilitation settings. A large part of this paper is dedicated to comparing the control strategies and techniques of CDRRs under five main categories of: Impedance-based, PID-based, Admittance-based, Assist-as-needed (AAN) and Adaptive controllers. We have carefully contrasted the advantages and disadvantages of those methods with the aim of assisting the design of future CDRRs
An Efficient Indexing and Searching Technique for Information Retrieval for Urdu Language
Feb 28, 2021


Abstract:Indexing techniques are used to improve retrieval of data in response to certain search condition. Inverted files are mostly used for creating indexes. This paper proposes indexing technique for Urdu language. Language processing step in Index creation is different for a particular language. We discuss index creation steps specifically for Urdu language. We explore morphological rules for Urdu language and implement these rules to create Urdu stemmer. We implement our proposed technique with different implementations and compare results. We suggest that indexes should be created without stop words and also index file should be an order index file.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge